Back to: ASP.NET Core Identity Tutorials
Claims Management in ASP.NET Core Identity
In this article, I will discuss Claims Management in ASP.NET Core Identity. Please read our previous article discussing Role-Based Authorization in ASP.NET Core Identity. In modern applications, security is more than just verifying who a user is; it’s about defining what they are allowed to do. Claims in ASP.NET Core Identity provide a flexible and powerful way to represent user attributes, rights, and permissions beyond traditional roles.
What is a Claim?
A Claim in ASP.NET Core Identity (and in security in general) is a piece of information (a statement) about a user. It is essentially a key–value pair (e.g., ClaimType = “Email”, ClaimValue = “abc@example.com”) that describes something about the user’s identity, role, or permissions. Claims are stored as part of a user’s security identity and are used by the application to make authorization decisions.
- A claim might state: The user’s email is abc@example.com, or the user has permission to edit roles, or the user belongs to the Finance department.
- Claims are flexible and can carry any information that an application needs for authentication or authorization.
In modern authentication systems (ASP.NET Core Identity, JWT, OAuth, etc.), claims are central to how user identity and permissions are described.
What are the different types of Claims?
Claims can represent different categories of information. Some common types are:
- Identity Claims
- Provide information about the user’s identity.
- Examples: Name, Email, Date of Birth, Gender.
- Role Claims
- Indicate the user’s role(s) in the system.
- Examples: “Admin”, “Manager”, “Customer”.
- Permission or Authorization Claims
- Specify what actions a user is allowed to perform.
- Examples: “AddUser”, “DeleteRole”, “ViewReports”.
- Custom/Business Claims
- Application-specific claims that represent domain rules.
- Examples: “Department=HR”, “SubscriptionLevel=Premium”, “Region=Asia”.
- Security/Access Claims
- Used for fine-grained security control.
- Examples: “TwoFactorEnabled=true”, “IsActive=true”, “EmailConfirmed=false”.
How to Implement Claims Management Application in ASP.NET Core Identity
Claims Management is a key feature in modern Identity-based applications that allows administrators to define, assign, and control user permissions beyond simple roles. Now, we will implement a complete claims management module inside our ASP.NET Core MVC + Identity setup.
Pages to be developed for Claim Management:
We will develop the following Pages for Claim Management.
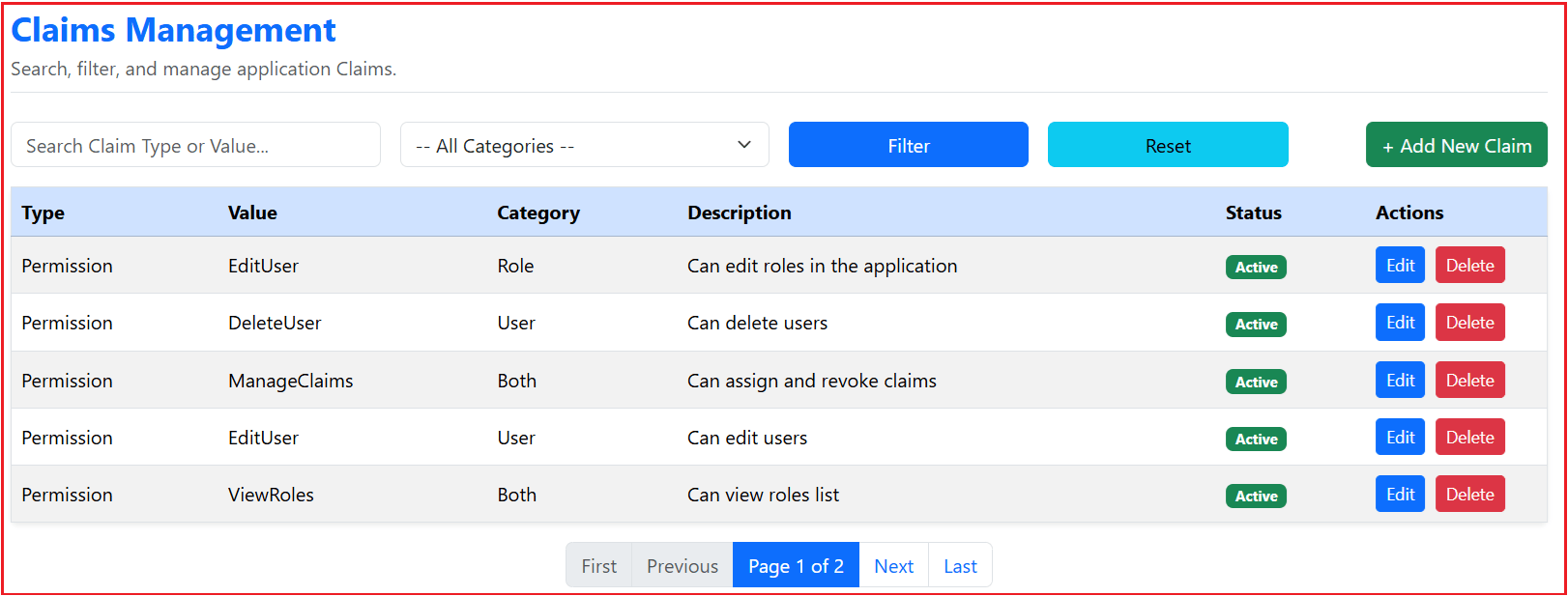
Index Page:
The Index Page acts as the central listing interface where all claims are displayed. Its use case is to allow administrators to view, search, filter, and navigate through claims efficiently. It serves as the entry point for managing claims and provides quick access to actions like creating, editing, or deleting claims.
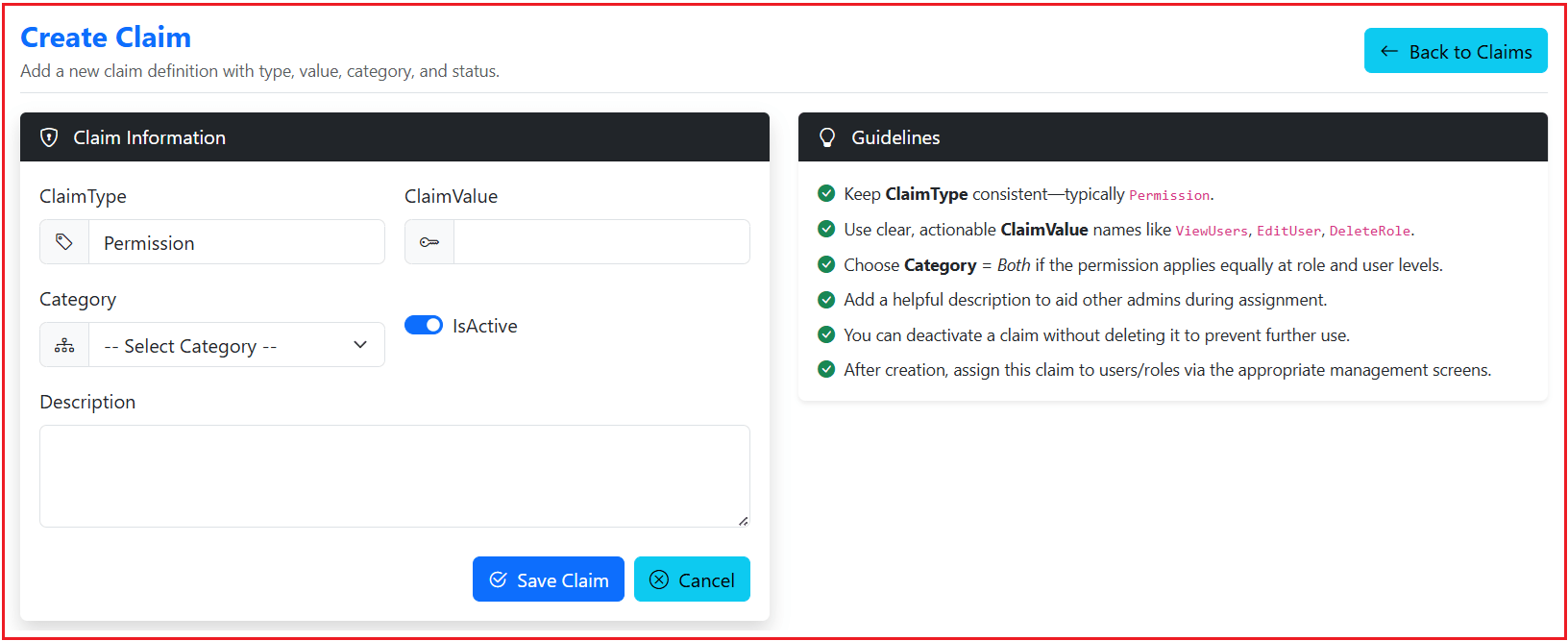
Create Page:
The Create Page is used to add new claims to the system. Its primary use case is to capture details such as claim type, value, category, description, and status. This page ensures that administrators can define new claims in a structured and validated manner.
Edit Page:
The Edit Page is designed for updating existing claims. Its use case revolves around modifying details of a claim that may have changed over time, such as updating descriptions, adjusting categories, or correcting values. It provides a controlled way to keep claims accurate and up to date.

Delete Page:
The Delete Page is meant for removing claims from the system. Its use case is to provide a confirmation step before deletion, ensuring administrators understand the consequences of permanently removing a claim. This prevents accidental deletions and enforces careful decision-making.

Create Claims Master Entity
We will create a dedicated table to store claim definitions. So, create a class file named ClaimMaster.cs within the Models folder, then copy and paste the following code into it. The ClaimMaster class is the entity that represents claims in the database. It contains fields like ClaimType, ClaimValue, Category, Description, and IsActive, and acts as the main data model for storing and retrieving claim records.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Models
{
// Unique composite index on (ClaimType, ClaimValue, Category)
[Index(nameof(ClaimType), nameof(ClaimValue), nameof(Category),
IsUnique = true, Name = "UX_ClaimMasters_TypeValueCategory")]
public class ClaimMaster
{
[Key]
public Guid Id { get; set; }
[Required, StringLength(200)]
public string ClaimType { get; set; } = null!; // e.g., "Permission"
[Required, StringLength(200)]
public string ClaimValue { get; set; } = null!;
// Where the claim is allowed to be assigned
// Allowed: "Role", "User", "Both"
[Required, StringLength(64)]
public string Category { get; set; } = "Both"; //User, Role, Both
[StringLength(500)]
public string? Description { get; set; }
public bool IsActive { get; set; } = true;
public DateTime CreatedOn { get; set; } = DateTime.UtcNow;
public DateTime? ModifiedOn { get; set; }
}
}
Code Explanations:
- ClaimType: Logical grouping (e.g., “Permission”).
- ClaimValue: Specific permission or identifier.
- Category: Indicates assignability scope:
- “User” → assign to users only.
- “Role” → assign to roles only.
- “Both” → assign to both users and roles.
Modifying DbContext
Next, please modify the DbContext class as follows. Now, we are adding the ClaimMaster DbSet property so that EF Core will generate a database table.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Data
{
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser, ApplicationRole, Guid>
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(builder);
// Rename tables
builder.Entity<ApplicationUser>().ToTable("Users");
builder.Entity<ApplicationRole>().ToTable("Roles");
builder.Entity<IdentityUserRole<Guid>>().ToTable("UserRoles");
builder.Entity<IdentityUserClaim<Guid>>().ToTable("UserClaims");
builder.Entity<IdentityUserLogin<Guid>>().ToTable("UserLogins");
builder.Entity<IdentityRoleClaim<Guid>>().ToTable("RoleClaims");
builder.Entity<IdentityUserToken<Guid>>().ToTable("UserTokens");
builder.Entity<ClaimMaster>().ToTable("ClaimMasters");
// Seed initial roles using HasData
var adminRoleId = Guid.Parse("c8d89a25-4b96-4f20-9d79-7f8a54c5213d");
var userRoleId = Guid.Parse("b92f0a3e-573b-4b12-8db1-2ccf6d58a34a");
var managerRoleId = Guid.Parse("d7f4a42e-1c1b-4c9f-8a50-55f6b234e8e2");
var guestRoleId = Guid.Parse("f2e6b8a1-9d43-4a7c-9f32-71d7c5dbe9f0");
builder.Entity<ApplicationRole>().HasData(
new ApplicationRole { Id = adminRoleId, Name = "Admin", NormalizedName = "ADMIN", Description = "Administrator role with full permissions.", IsActive = true, CreatedOn = new DateTime(2025, 8, 4), ModifiedOn = new DateTime(2025, 8, 4) },
new ApplicationRole { Id = userRoleId, Name = "User", NormalizedName = "USER", Description = "Standard user role.", IsActive = true, CreatedOn = new DateTime(2025, 8, 4), ModifiedOn = new DateTime(2025, 8, 4) },
new ApplicationRole { Id = managerRoleId, Name = "Manager", NormalizedName = "MANAGER", Description = "Manager role with moderate permissions.", IsActive = true, CreatedOn = new DateTime(2025, 8, 4), ModifiedOn = new DateTime(2025, 8, 4) },
new ApplicationRole { Id = guestRoleId, Name = "Guest", NormalizedName = "GUEST", Description = "Guest role with limited access.", IsActive = true, CreatedOn = new DateTime(2025, 8, 4), ModifiedOn = new DateTime(2025, 8, 4) }
);
}
public DbSet<Address> Addresses { get; set; }
public DbSet<ClaimMaster> ClaimMasters { get; set; }
}
}
Seed Initial Claims with Category = User / Role / Both
Please create a class file named ClaimSeeder.cs within the Data folder, then copy and paste the following code. The ClaimSeeder class is responsible for seeding initial claim data into the database. It ensures that some predefined claims exist when the application starts, which is useful for testing and for setting up default permissions.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Models;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Data
{
public static class ClaimSeeder
{
public static async Task SeedClaimsMaster(IServiceProvider services)
{
try
{
using var scope = services.CreateScope();
var context = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<ApplicationDbContext>();
if (context.ClaimMasters.Any())
{
Console.WriteLine("ClaimMasters table already seeded. Skipping...");
return;
}
var claims = new List<ClaimMaster>
{
// User-level only
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "AddUser", Category = "User", Description = "Can create new users" },
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "EditUser", Category = "User", Description = "Can edit users" },
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "DeleteUser", Category = "User", Description = "Can delete users" },
// Role-level only
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "AddRole", Category = "Role", Description = "Can create new roles" },
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "EditRole", Category = "Role", Description = "Can edit roles" },
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "DeleteRole", Category = "Role", Description = "Can delete roles" },
// Shared claims (Both)
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "ViewUsers", Category = "Both", Description = "Can view users list" },
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "ViewRoles", Category = "Both", Description = "Can view roles list" },
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "ExportReports", Category="Both", Description = "Can export reports to CSV/PDF" },
new() { Id = Guid.NewGuid(), ClaimType = "Permission", ClaimValue = "ManageClaims", Category="Both", Description = "Can assign and revoke claims" }
};
// Prevent accidental duplicates
var distinctClaims = claims
.GroupBy(c => c.ClaimValue)
.Select(g => g.First())
.ToList();
await context.ClaimMasters.AddRangeAsync(distinctClaims);
await context.SaveChangesAsync();
Console.WriteLine("ClaimMasters seeded successfully.");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error occurred while seeding ClaimMasters: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}
Creating View Models:
First, create a folder named Claims within the ViewModels folder, where we will create all our Claims-related view models.
ClaimListItemViewModel
Create a class file named ClaimListItemViewModel.cs within the ViewModels/Claims folder, then copy and paste the following code. The ClaimListItemViewModel is used to show claims in the Index page. It only carries the necessary details like type, value, category, and active status, so the list view loads quickly and looks clean.
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims
{
public class ClaimListItemViewModel
{
public Guid Id { get; init; }
public string ClaimType { get; init; } = string.Empty;
public string ClaimValue { get; init; } = string.Empty;
public string Category { get; init; } = string.Empty; // User, Role, Both
public string? Description { get; init; }
public bool IsActive { get; init; }
}
}
ClaimCreateViewModel
Create a class file named ClaimCreateViewModel.cs within the ViewModels/Claims folder, then copy and paste the following code. The ClaimCreateViewModel class is used when creating a new claim. It contains the properties that must be filled in by the user along with validation attributes, ensuring that valid claim data is collected during creation.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims
{
public class ClaimCreateViewModel
{
[Display(Name = "Claim Type")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Claim Type is required.")]
[StringLength(200, ErrorMessage = "Claim Type cannot exceed {1} characters.")]
public string ClaimType { get; set; } = "Permission";
[Display(Name = "Claim Value")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Claim Value is required.")]
[StringLength(200, ErrorMessage = "Claim Value cannot exceed {1} characters.")]
public string ClaimValue { get; set; } = null!;
[Display(Name = "Assign To")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Please choose where to assign this claim (User, Role, or Both).")]
[StringLength(64, ErrorMessage = "Assign To cannot exceed {1} characters.")]
[RegularExpression("^(User|Role|Both)$", ErrorMessage = "Assign To must be one of: User, Role, Both.")]
public string Category { get; set; } = null!; // User, Role, Both
[Display(Name = "Description")]
[StringLength(500, ErrorMessage = "Description cannot exceed {1} characters.")]
public string? Description { get; set; }
}
}
ClaimEditViewModel
Create a class file named ClaimEditViewModel.cs within the ViewModels/Claims folder, then copy and paste the following code. The ClaimEditViewModel class is used when editing or deleting an existing claim. It includes all the fields of a claim, along with the ID, so that updates or deletions can be applied correctly in the database.
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims
{
public class ClaimEditViewModel
{
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Id is required.")]
public Guid Id { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Claim Type")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Claim Type is required.")]
[StringLength(200, ErrorMessage = "Claim Type cannot exceed {1} characters.")]
public string ClaimType { get; set; } = "Permission";
[Display(Name = "Claim Value")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Claim Value is required.")]
[StringLength(200, ErrorMessage = "Claim Value cannot exceed {1} characters.")]
public string ClaimValue { get; set; } = null!;
[Display(Name = "Assign To")]
[Required(ErrorMessage = "Please choose where to assign this claim (User, Role, or Both).")]
[StringLength(64, ErrorMessage = "Assign To cannot exceed {1} characters.")]
[RegularExpression("^(User|Role|Both)$", ErrorMessage = "Assign To must be one of: User, Role, Both.")]
public string Category { get; set; } = null!;
[Display(Name = "Description")]
[StringLength(500, ErrorMessage = "Description cannot exceed {1} characters.")]
public string? Description { get; set; }
[Display(Name = "Active")]
public bool IsActive { get; set; }
}
}
IClaimsService
Create an interface named IClaimsService.cs within the Services folder, then copy and paste the following code. The IClaimsService interface defines the contract for all claim operations. It declares methods for listing, creating, updating, and deleting claims, which the service implementation must provide.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Services
{
public interface IClaimsService
{
Task<PagedResult<ClaimListItemViewModel>> GetPagedClaimsAsync(string? search, string? category, int pageNumber, int pageSize);
Task<ClaimEditViewModel?> GetClaimByIdAsync(Guid id);
Task<bool> DeleteClaimAsync(Guid id);
Task<(bool Success, string Message)> CreateClaimAsync(ClaimEditViewModel model);
Task<(bool Success, string Message)> UpdateClaimAsync(ClaimEditViewModel model);
}
}
ClaimsService
Create a class file named ClaimsService.cs within the Services folder, then copy and paste the following code. The ClaimsService class implements IClaimsService and contains the actual business logic for managing claims. It interacts with the ApplicationDbContext, applies validation, and performs database operations for claims.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Data;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Models;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Services
{
// Application service for Claims catalog (ClaimMasters).
// Encapsulates query logic (search, filter, paging) and CRUD with basic guards.
// Controllers should call this service instead of touching DbContext directly.
public class ClaimsService : IClaimsService
{
private readonly ApplicationDbContext _context;
private readonly ILogger<ClaimsService> _logger;
// Hard guard for paging; avoid accidental "SELECT *" with huge pageSize.
private const int MaxPageSize = 100;
public ClaimsService(ApplicationDbContext context, ILogger<ClaimsService> logger)
{
_context = context;
_logger = logger;
}
// Returns a paged, filtered list of claims for the Index grid.
// - search: matches ClaimType, ClaimValue, or Description (contains).
// - category: exact match on Category ("User", "Role", "Both").
// Read path is AsNoTracking for best performance.
public async Task<PagedResult<ClaimListItemViewModel>> GetPagedClaimsAsync(
string? search, string? category, int pageNumber, int pageSize)
{
try
{
// Defensive paging (never page 0 or negative; clamp size).
pageNumber = Math.Max(1, pageNumber);
pageSize = Math.Clamp(pageSize <= 0 ? 10 : pageSize, 1, MaxPageSize);
// Read-only query → AsNoTracking avoids change-tracker overhead.
var query = _context.ClaimMasters.AsNoTracking().AsQueryable();
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(search))
{
search = search.Trim();
// NOTE:
// Contains translates to SQL LIKE '%search%'.
// This is user-friendly for admins and fine for moderate datasets.
// For very large tables, consider full-text search.
query = query.Where(c =>
c.ClaimType.Contains(search) ||
c.ClaimValue.Contains(search) ||
(c.Description != null && c.Description.Contains(search)));
}
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(category))
{
category = category.Trim();
query = query.Where(c => c.Category == category);
}
// Count first (before Skip/Take); EF will translate efficiently.
var totalCount = await query.CountAsync();
// Stable ordering ensures consistent paging between requests.
var claims = await query
.OrderBy(c => c.ClaimType)
.ThenBy(c => c.ClaimValue)
.Skip((pageNumber - 1) * pageSize)
.Take(pageSize)
.Select(c => new ClaimListItemViewModel
{
Id = c.Id,
ClaimType = c.ClaimType,
ClaimValue = c.ClaimValue,
Category = c.Category,
Description = c.Description,
IsActive = c.IsActive
})
.ToListAsync();
return new PagedResult<ClaimListItemViewModel>
{
Items = claims,
TotalCount = totalCount,
PageNumber = pageNumber,
PageSize = pageSize
};
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error fetching paged claims (search: {Search}, category: {Category}, page: {Page}, size: {Size})",
search, category, pageNumber, pageSize);
// Fail soft: return empty page but preserve requested paging info.
return new PagedResult<ClaimListItemViewModel>
{
Items = Array.Empty<ClaimListItemViewModel>(),
TotalCount = 0,
PageNumber = pageNumber,
PageSize = pageSize
};
}
}
// Returns a single claim mapped to the edit view model.
// Read path uses AsNoTracking since the entity is reloaded in Update anyway.
public async Task<ClaimEditViewModel?> GetClaimByIdAsync(Guid id)
{
try
{
return await _context.ClaimMasters
.AsNoTracking()
.Where(c => c.Id == id)
.Select(c => new ClaimEditViewModel
{
Id = c.Id,
ClaimType = c.ClaimType,
ClaimValue = c.ClaimValue,
Category = c.Category,
Description = c.Description,
IsActive = c.IsActive
})
.FirstOrDefaultAsync();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error fetching claim by Id {Id}", id);
return null;
}
}
// Creates a new claim in the catalog after performing duplicate checks.
// Returns (Success, Message) suitable for TempData or model-level errors.
public async Task<(bool Success, string Message)> CreateClaimAsync(ClaimEditViewModel model)
{
try
{
// Basic field validation.
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(model.ClaimType) || string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(model.ClaimValue))
return (false, "Claim Type and Claim Value are required.");
// Normalize input to reduce duplicate risk from accidental whitespace.
var type = model.ClaimType.Trim();
var value = model.ClaimValue.Trim();
var category = model.Category?.Trim();
// Duplicate check: same Type + Value + Category not allowed.
bool exists = await _context.ClaimMasters
.AnyAsync(c => c.ClaimType == type &&
c.ClaimValue == value &&
c.Category == category);
if (exists)
return (false, "A claim with the same type, value, and category already exists.");
var claim = new ClaimMaster
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid(),
ClaimType = type,
ClaimValue = value,
Category = category!,
Description = model.Description?.Trim(),
IsActive = model.IsActive,
CreatedOn = DateTime.UtcNow,
ModifiedOn = DateTime.UtcNow
};
_context.ClaimMasters.Add(claim);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return (true, "Claim created successfully.");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error creating claim (Type: {Type}, Value: {Value}, Category: {Category})",
model.ClaimType, model.ClaimValue, model.Category);
return (false, "An error occurred while creating the claim.");
}
}
// Updates an existing claim after duplicate checks.
// Uses FindAsync to load the tracked entity, then mutates properties and saves.
public async Task<(bool Success, string Message)> UpdateClaimAsync(ClaimEditViewModel model)
{
try
{
if (model.Id == Guid.Empty)
return (false, "Invalid claim identifier.");
var claim = await _context.ClaimMasters.FindAsync(model.Id);
if (claim == null)
return (false, "Claim not found.");
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(model.ClaimType) || string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(model.ClaimValue))
return (false, "Claim Type and Claim Value are required.");
var type = model.ClaimType.Trim();
var value = model.ClaimValue.Trim();
var category = model.Category?.Trim();
// Duplicate check excluding self.
bool duplicateExists = await _context.ClaimMasters
.AnyAsync(c => c.Id != model.Id &&
c.ClaimType == type &&
c.ClaimValue == value &&
c.Category == category);
if (duplicateExists)
return (false, "Another claim with the same type, value, and category already exists.");
// Apply updates to the tracked entity.
claim.ClaimType = type;
claim.ClaimValue = value;
claim.Category = category!;
claim.Description = model.Description?.Trim();
claim.IsActive = model.IsActive;
claim.ModifiedOn = DateTime.UtcNow;
// No need to call _context.Update(claim) here since it's tracked; SaveChanges will detect changes.
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return (true, "Claim updated successfully.");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error updating claim Id {Id}", model.Id);
return (false, "An error occurred while updating the claim.");
}
}
// Soft delete: marks IsActive = false.
// Keeps history and prevents broken references.
// Returns true if the record existed and was deactivated.
public async Task<bool> DeleteClaimAsync(Guid id)
{
try
{
var claim = await _context.ClaimMasters.FindAsync(id);
if (claim == null) return false;
if (!claim.IsActive)
{
// Already inactive; treat as success to keep the endpoint idempotent.
return true;
}
claim.IsActive = false;
claim.ModifiedOn = DateTime.UtcNow;
// Tracked entity → SaveChanges is enough.
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
return true;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error deleting (deactivating) claim Id {Id}", id);
return false;
}
}
}
}
ClaimsController
Create an empty MVC controller named ClaimsController within the Controllers folder, then copy and paste the following code. The ClaimsController class is the MVC controller that handles HTTP requests related to claims. It uses the ClaimsService to perform operations and returns the correct Razor views for Index, Create, Edit, and Delete actions.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Services;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels;
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Controllers
{
[Authorize(Roles = "Admin")]
public class ClaimsController : Controller
{
private readonly IClaimsService _claimsService;
private readonly ILogger<ClaimsController> _logger;
public ClaimsController(IClaimsService claimsService, ILogger<ClaimsController> logger)
{
_claimsService = claimsService;
_logger = logger;
}
public async Task<IActionResult> Index(string? search, string? category, int pageNumber = 1, int pageSize = 5)
{
try
{
var result = await _claimsService.GetPagedClaimsAsync(search, category, pageNumber, pageSize);
ViewBag.Search = search;
ViewBag.Category = category;
return View(result);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error loading claims list");
TempData["Error"] = "Something went wrong while fetching claims.";
return View(new PagedResult<ClaimListItemViewModel>());
}
}
public IActionResult Create()
{
return View(new ClaimEditViewModel { IsActive = true });
}
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> Create(ClaimEditViewModel model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
try
{
var result = await _claimsService.CreateClaimAsync(model);
if (result.Success)
{
TempData["Success"] = result.Message;
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, result.Message);
return View(model);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Unexpected error while creating claim");
TempData["Error"] = "An unexpected error occurred.";
return View(model);
}
}
public async Task<IActionResult> Edit(Guid id)
{
try
{
var claim = await _claimsService.GetClaimByIdAsync(id);
if (claim == null)
{
TempData["Error"] = "Claim not found.";
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
return View(claim);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error loading claim for edit");
TempData["Error"] = "An error occurred while loading the claim.";
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
}
[HttpPost]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> Edit(ClaimEditViewModel model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
return View(model);
try
{
var result = await _claimsService.UpdateClaimAsync(model);
if (result.Success)
{
TempData["Success"] = result.Message;
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, result.Message);
return View(model);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Unexpected error while updating claim");
TempData["Error"] = "An unexpected error occurred.";
return View(model);
}
}
// GET: Delete
public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(Guid id)
{
try
{
var claim = await _claimsService.GetClaimByIdAsync(id);
if (claim == null)
{
TempData["Error"] = "Claim not found.";
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
return View(claim);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error loading claim for deletion");
TempData["Error"] = "Something went wrong while preparing deletion.";
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
}
// POST: Delete
[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")]
[ValidateAntiForgeryToken]
public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteConfirmed(Guid id)
{
try
{
var success = await _claimsService.DeleteClaimAsync(id);
if (success)
{
TempData["Success"] = "Claim deleted successfully.";
}
else
{
TempData["Error"] = "Failed to delete claim.";
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
_logger.LogError(ex, "Error deleting claim");
TempData["Error"] = "Something went wrong while deleting claim.";
}
return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));
}
}
}
Creating Index View:
Create a view named Index.cshtml within the Views/Claims folder, then copy and paste the following code. The Index View is used to display the list of all claims in a structured table format. It uses the ClaimListItemViewModel and shows details like ClaimType, ClaimValue, Category, and Status. It also provides action links (Edit, Delete) so that the user can manage claims easily.
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels
@model PagedResult<ClaimListItemViewModel>
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Claims Management";
}
<div class="container mt-1">
<div class="d-flex flex-wrap align-items-center justify-content-between gap-2 mb-4 pb-2 border-bottom">
<div>
<h1 class="h3 mb-1 fw-bold text-primary">Claims Management</h1>
<p class="text-muted mb-0">Search, filter, and manage application Claims.</p>
</div>
</div>
@if (TempData["Success"] is string sMsg)
{
<div class="alert alert-success alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<i class="bi bi-check-circle me-2"></i>@sMsg
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
@if (TempData["Error"] is string eMsg)
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<i class="bi bi-exclamation-triangle me-2"></i>@eMsg
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<!-- Search & Filter -->
<form method="get" class="row g-3 mb-3">
<div class="col-md-3">
<input type="text" name="search" value="@Context.Request.Query["search"]"
class="form-control" placeholder="Search Claim Type or Value..." />
</div>
<div class="col-md-3">
<select name="category" class="form-select">
<option value="">-- All Categories --</option>
<option value="User" selected="@("User" == Context.Request.Query["category"])">User</option>
<option value="Role" selected="@("Role" == Context.Request.Query["category"])">Role</option>
<option value="Both" selected="@("Both" == Context.Request.Query["category"])">Both</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="col-md-2">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary w-100">Filter</button>
</div>
<div class="col-md-2">
<button type="reset" class="btn btn-info w-100">Reset</button>
</div>
<div class="col-md-2 text-end">
<a asp-action="Create" class="btn btn-success">+ Add New Claim</a>
</div>
</form>
<!-- Claims Table -->
@if (!Model.Items.Any())
{
<div class="alert alert-info">No claims found.</div>
}
else
{
<table class="table table-striped table-hover align-middle shadow-sm border rounded">
<thead class="table-primary">
<tr>
<th>Type</th>
<th>Value</th>
<th>Category</th>
<th>Description</th>
<th>Status</th>
<th style="width: 150px;">Actions</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var claim in Model.Items)
{
<tr>
<td>@claim.ClaimType</td>
<td>@claim.ClaimValue</td>
<td>@claim.Category</td>
<td>@claim.Description</td>
<td>
@if (claim.IsActive)
{
<span class="badge bg-success">Active</span>
}
else
{
<span class="badge bg-danger">Inactive</span>
}
</td>
<td>
<a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@claim.Id" class="btn btn-sm btn-primary me-1">Edit</a>
<a asp-action="Delete" asp-route-id="@claim.Id" class="btn btn-sm btn-danger me-1">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
<!-- Pager -->
<partial name="~/Views/Shared/_Pager.cshtml"
model="new PagedResult<object> { Items = Array.Empty<object>(), TotalCount = Model.TotalCount, PageNumber = Model.PageNumber, PageSize = Model.PageSize }" />
}
</div>
Creating Create View:
Create a view named Create.cshtml within the Views/Claims folder, then copy and paste the following code. The Create View is used to add a new claim to the system. It provides a form with fields such as ClaimType, ClaimValue, Category, Description, and IsActive. When submitted, the form passes the data to the controller so a new claim can be stored in the database.
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims
@model ClaimEditViewModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Create Claim";
}
<div class="container mt-1">
<!-- Page header -->
<div class="d-flex flex-wrap align-items-center justify-content-between gap-2 mb-3 pb-2 border-bottom">
<div>
<h1 class="h4 fw-bold mb-1 text-primary">Create Claim</h1>
<p class="text-muted small mb-0">Add a new claim definition with type, value, category, and status.</p>
</div>
<div class="d-flex gap-2">
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-info">
<i class="bi bi-arrow-left me-1"></i> Back to Claims
</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row g-4">
<!-- Form Section -->
<div class="col-lg-7 col-xl-6">
<div class="card shadow border-0 rounded">
<div class="card-header bg-dark text-white">
<i class="bi bi-shield-lock me-2"></i> Claim Information
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<form asp-action="Create" method="post" novalidate>
<!-- Validation -->
@if (!ViewData.ModelState.IsValid && ViewData.ModelState.Values.Any(v => v.Errors.Count > 0))
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<div class="fw-semibold mb-1">We couldn’t create the claim.</div>
<div class="small text-muted mb-2">Please review the messages below and try again.</div>
<div asp-validation-summary="All"></div>
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<div class="row g-3">
<!-- Claim Type -->
<div class="col-md-6">
<label asp-for="ClaimType" class="form-label"></label>
<div class="input-group">
<span class="input-group-text"><i class="bi bi-tag"></i></span>
<input asp-for="ClaimType" class="form-control" />
</div>
<span asp-validation-for="ClaimType" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Claim Value -->
<div class="col-md-6">
<label asp-for="ClaimValue" class="form-label"></label>
<div class="input-group">
<span class="input-group-text"><i class="bi bi-key"></i></span>
<input asp-for="ClaimValue" class="form-control" />
</div>
<span asp-validation-for="ClaimValue" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Category -->
<div class="col-md-6">
<label asp-for="Category" class="form-label"></label>
<div class="input-group">
<span class="input-group-text"><i class="bi bi-diagram-3"></i></span>
<select asp-for="Category" class="form-select">
<option value="">-- Select Category --</option>
<option value="User">User</option>
<option value="Role">Role</option>
<option value="Both">Both</option>
</select>
</div>
<span asp-validation-for="Category" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Is Active -->
<div class="col-md-6 d-flex align-items-center">
<div class="form-check form-switch">
<input asp-for="IsActive" class="form-check-input" />
<label asp-for="IsActive" class="form-check-label"></label>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Description full width -->
<div class="col-12">
<label asp-for="Description" class="form-label"></label>
<textarea asp-for="Description" class="form-control" rows="3"></textarea>
<span asp-validation-for="Description" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Actions -->
<div class="d-flex justify-content-end gap-2 mt-4">
<button class="btn btn-primary">
<i class="bi bi-check2-circle me-1"></i> Save Claim
</button>
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-info">
<i class="bi bi-x-circle me-1"></i> Cancel
</a>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Guidelines Section -->
<div class="col-lg-5 col-xl-6">
<div class="card border-0 shadow-sm">
<div class="card-header bg-dark text-white">
<i class="bi bi-lightbulb me-2"></i> Guidelines
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<ul class="list-unstyled small mb-0">
<li class="mb-2"><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> Keep <strong>ClaimType</strong> consistent—typically <code>Permission</code>.</li>
<li class="mb-2"><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> Use clear, actionable <strong>ClaimValue</strong> names like <code>ViewUsers</code>, <code>EditUser</code>, <code>DeleteRole</code>.</li>
<li class="mb-2"><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> Choose <strong>Category</strong> = <em>Both</em> if the permission applies equally at role and user levels.</li>
<li class="mb-2"><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> Add a helpful description to aid other admins during assignment.</li>
<li class="mb-2"><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> You can deactivate a claim without deleting it to prevent further use.</li>
<li><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> After creation, assign this claim to users/roles via the appropriate management screens.</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
}
Creating Edit View:
Create a view named Edit.cshtml within the Views/Claims folder, then copy and paste the following code. The Edit View is used to modify an existing claim. It pre-populates the form fields with the claim’s current data so the user can make changes. Once submitted, the updated details are saved to the database through the controller and service.
@using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims
@model ClaimEditViewModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Edit Claim";
}
<div class="container mt-1">
<!-- Page header -->
<div class="d-flex flex-wrap align-items-center justify-content-between gap-2 mb-3 pb-2 border-bottom">
<div>
<h1 class="h4 fw-bold mb-1 text-primary">Edit Claim</h1>
<p class="text-muted small mb-0">Update claim details such as type, value, category, and status.</p>
</div>
<div class="d-flex gap-2">
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-info">
<i class="bi bi-arrow-left me-1"></i> Back to Claims
</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row g-4">
<!-- Form Section -->
<div class="col-lg-7 col-xl-6">
<div class="card shadow border-0 rounded">
<div class="card-header bg-dark text-white">
<i class="bi bi-pencil-square me-2"></i> Edit Claim Information
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<form asp-action="Edit" method="post" novalidate>
<input type="hidden" asp-for="Id" />
<!-- Validation -->
@if (!ViewData.ModelState.IsValid && ViewData.ModelState.Values.Any(v => v.Errors.Count > 0))
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<div class="fw-semibold mb-1">We couldn’t update the claim.</div>
<div class="small text-muted mb-2">Please review the messages below and try again.</div>
<div asp-validation-summary="All"></div>
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<div class="row g-3">
<!-- Claim Type -->
<div class="col-md-6">
<label asp-for="ClaimType" class="form-label"></label>
<div class="input-group">
<span class="input-group-text"><i class="bi bi-tag"></i></span>
<input asp-for="ClaimType" class="form-control" />
</div>
<span asp-validation-for="ClaimType" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Claim Value -->
<div class="col-md-6">
<label asp-for="ClaimValue" class="form-label"></label>
<div class="input-group">
<span class="input-group-text"><i class="bi bi-key"></i></span>
<input asp-for="ClaimValue" class="form-control" />
</div>
<span asp-validation-for="ClaimValue" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Category -->
<div class="col-md-6">
<label asp-for="Category" class="form-label"></label>
<div class="input-group">
<span class="input-group-text"><i class="bi bi-diagram-3"></i></span>
<select asp-for="Category" class="form-select">
<option value="">-- Select Category --</option>
<option value="User">User</option>
<option value="Role">Role</option>
<option value="Both">Both</option>
</select>
</div>
<span asp-validation-for="Category" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<!-- Is Active -->
<div class="col-md-6 d-flex align-items-center">
<div class="form-check form-switch">
<input asp-for="IsActive" class="form-check-input" />
<label asp-for="IsActive" class="form-check-label"></label>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Description full width -->
<div class="col-12">
<label asp-for="Description" class="form-label"></label>
<textarea asp-for="Description" class="form-control" rows="3"></textarea>
<span asp-validation-for="Description" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Actions -->
<div class="d-flex justify-content-end gap-2 mt-4">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">
<i class="bi bi-check2-circle me-1"></i> Update Claim
</button>
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-info">
<i class="bi bi-x-circle me-1"></i> Cancel
</a>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Guidelines Section -->
<div class="col-lg-5 col-xl-6">
<div class="card border-0 shadow-sm">
<div class="card-header bg-dark text-white">
<i class="bi bi-lightbulb me-2"></i> Editing Guidelines
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<ul class="list-unstyled small mb-0">
<li class="mb-2"><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> Update <strong>ClaimType</strong> only if absolutely necessary to keep consistency across the system.</li>
<li class="mb-2"><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> Adjust <strong>ClaimValue</strong> to reflect precise permissions (e.g., <code>EditUser</code>, <code>DeleteRole</code>).</li>
<li class="mb-2"><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> Changing the <strong>Category</strong> may affect both role and user-level assignments—review before saving.</li>
<li class="mb-2"><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> Keep the <strong>Description</strong> clear and concise to assist other admins.</li>
<li><i class="bi bi-check-circle-fill text-success me-1"></i> If the claim is no longer needed, mark it inactive rather than deleting for audit safety.</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
<partial name="_ValidationScriptsPartial" />
}
Delete View:
Create a view named Delete.cshtml within the Views/Claims folder, then copy and paste the following code. The Delete View is used to confirm and process the deletion of a claim. It shows the details of the claim in a read-only format so the user can review them before final deletion. A confirmation button is provided to remove the claim from the database permanently.
@model ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.ViewModels.Claims.ClaimEditViewModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Delete Claim";
}
<div class="container mt-0">
<div class="row g-4 justify-content-center">
<div class="col-lg-8 col-xl-7">
<div class="card shadow border-0 rounded">
<div class="card-header bg-danger text-white">
<i class="bi bi-exclamation-octagon me-2"></i> Confirm Claim Deletion
</div>
@if (TempData["Error"] is string err)
{
<div class="alert alert-danger alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<i class="bi bi-exclamation-triangle me-2"></i>@err
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
@if (TempData["Success"] is string ok)
{
<div class="alert alert-success alert-dismissible fade show" role="alert">
<i class="bi bi-check-circle me-2"></i>@ok
<button type="button" class="btn-close" data-bs-dismiss="alert" aria-label="Close"></button>
</div>
}
<div class="card-body">
<!-- Strong warning -->
<div class="alert alert-danger" role="alert">
<div class="fw-semibold mb-1">Are you sure you want to delete this claim?</div>
<div class="small mb-0">
This action <strong>cannot be undone</strong>. If this claim is assigned to users or roles, those assignments will also be removed.
</div>
</div>
<!-- Claim summary -->
<div class="mb-3">
<div class="small text-uppercase text-muted mb-2">Claim Summary</div>
<ul class="list-group list-group-flush">
<li class="list-group-item d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center px-0">
<span class="text-muted"><i class="bi bi-tag me-2"></i>Claim Type</span>
<span class="fw-semibold">@Model.ClaimType</span>
</li>
<li class="list-group-item d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center px-0">
<span class="text-muted"><i class="bi bi-key me-2"></i>Claim Value</span>
<span class="fw-semibold">@Model.ClaimValue</span>
</li>
<li class="list-group-item d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center px-0">
<span class="text-muted"><i class="bi bi-diagram-3 me-2"></i>Category</span>
<span>
<span class="badge rounded-pill bg-primary">@Model.Category</span>
</span>
</li>
<li class="list-group-item d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center px-0">
<span class="text-muted"><i class="bi bi-info-circle me-2"></i>Description</span>
<span class="fw-semibold">@(!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(Model.Description) ? Model.Description : "-")</span>
</li>
<li class="list-group-item d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center px-0">
<span class="text-muted"><i class="bi bi-activity me-2"></i>Status</span>
<span>
<span class="badge rounded-pill @(Model.IsActive ? "bg-success" : "bg-secondary")">
@(Model.IsActive ? "Active" : "Inactive")
</span>
</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
<!-- Confirm form -->
<form asp-action="Delete" method="post" class="mt-3">
<input type="hidden" asp-for="Id" />
<div class="form-check mb-3">
<input class="form-check-input" type="checkbox" value="true" id="confirmChk">
<label class="form-check-label" for="confirmChk">
I understand this action is permanent and cannot be undone.
</label>
</div>
<div class="d-flex justify-content-end gap-2">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-danger" id="deleteBtn" disabled>
<i class="bi bi-trash3 me-1"></i> Yes, Delete
</button>
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-info">
<i class="bi bi-x-circle me-1"></i> Cancel
</a>
<a asp-action="Index" class="btn btn-primary">
<i class="bi bi-arrow-left me-1"></i> Back to Claims
</a>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div class="card-footer bg-light small text-muted">
Deleted claims cannot be recovered. If you might need this claim later, consider deactivating it instead.
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
@section Scripts {
<script>
// Enable Delete button only when confirmation is checked
const chk = document.getElementById('confirmChk');
const btn = document.getElementById('deleteBtn');
if (chk && btn) {
chk.addEventListener('change', () => btn.disabled = !chk.checked);
}
</script>
}
Modify the Layout File:
Please modify the Layout File to include a link for Claims Management.
@{
ViewData["Title"] = ViewData["Title"] ?? "Dot Net Tutorials";
bool isAuthenticated = User?.Identity?.IsAuthenticated ?? false;
bool isAdmin = User?.IsInRole("Admin") ?? false;
bool isManager = User?.IsInRole("Manager") ?? false;
bool isStaff = isAdmin || isManager; // Admin OR Manager
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>@ViewData["Title"] - Dot Net Tutorials</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap-icons@1.11.3/font/bootstrap-icons.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body class="d-flex flex-column min-vh-100">
<!-- Dark Navbar -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-dark bg-dark">
<div class="container">
<a class="navbar-brand fw-bold" href="@Url.Action("Index", "Home")">Dot Net Tutorials</a>
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button" data-bs-toggle="collapse" data-bs-target="#navbarContent"
aria-controls="navbarContent" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="navbarContent">
<!-- Left: Primary navigation -->
<ul class="navbar-nav me-auto mb-2 mb-lg-0">
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="@Url.Action("Index", "Home")">Home</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" href="@Url.Action("About", "Home")">About</a>
</li>
<!-- Any authenticated user -->
@if (isAuthenticated)
{
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="SecureMethod">
Secure
</a>
</li>
}
<!-- Public -->
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" asp-controller="Home" asp-action="NonSecureMethod">
Non Secure
</a>
</li>
<!-- Admin-only -->
@if (isAdmin)
{
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" asp-controller="Roles" asp-action="Index">
Roles
</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" asp-controller="Claims" asp-action="Index">
Claims
</a>
</li>
}
<!-- Admin OR Manager -->
@if (isStaff)
{
<li class="nav-item">
<a class="nav-link" asp-controller="Users" asp-action="Index">
Users
</a>
</li>
}
</ul>
<!-- Right: Auth links / user menu -->
<ul class="navbar-nav mb-2 mb-lg-0">
@if (isAuthenticated)
{
<li class="nav-item dropdown">
<a class="nav-link dropdown-toggle" href="#" id="userDropdown" role="button"
data-bs-toggle="dropdown" aria-expanded="false">
<i class="bi bi-person-circle me-1"></i>
Hello, @User!.Identity!.Name
</a>
<ul class="dropdown-menu dropdown-menu-end" aria-labelledby="userDropdown">
<li>
<a class="dropdown-item" href="@Url.Action("Profile", "Account")">
<i class="bi bi-person-lines-fill me-2"></i> Profile
</a>
</li>
<li><hr class="dropdown-divider" /></li>
<li>
<form method="post" asp-controller="Account" asp-action="Logout" class="px-3 py-1">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-link text-decoration-none w-100 text-start">
<i class="bi bi-box-arrow-right me-2"></i> Logout
</button>
</form>
</li>
</ul>
</li>
}
else
{
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="@Url.Action("Login", "Account")">Login</a></li>
<li class="nav-item"><a class="nav-link" href="@Url.Action("Register", "Account")">Register</a></li>
}
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
<!-- Main Content -->
<main class="container flex-grow-1 py-3">
@RenderBody()
</main>
<!-- Footer -->
<footer class="bg-dark text-light py-4 mt-auto">
<div class="container d-flex flex-column flex-md-row justify-content-between align-items-center">
<div>
© @DateTime.Now.Year Dot Net Tutorials. All rights reserved.
</div>
<div>
<a href="@Url.Action("Contact", "Home")" class="text-light me-3 text-decoration-none">Contact</a>
<a href="@Url.Action("Privacy", "Home")" class="text-light me-3 text-decoration-none">Privacy Policy</a>
<a href="@Url.Action("Terms", "Home")" class="text-light text-decoration-none">Terms of Service</a>
</div>
</div>
</footer>
<!-- Scripts -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
<script src="~/js/site.js" asp-append-version="true"></script>
<script src="~/lib/jquery/dist/jquery.min.js"></script>
@await RenderSectionAsync("Scripts", required: false)
</body>
</html>
Add Claims Service:
Please add the following statement in the Program class:
builder.Services.AddScoped<IClaimsService, ClaimsService>();
Modifying the DataSeedingController
Please modify the DataSeedingController as follows. The DataSeedingController class is a utility controller used to trigger claim seeding manually. It provides an endpoint that can be invoked to insert predefined claims into the database, useful during development or setup.
using ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Data;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ASPNETCoreIdentityDemo.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class DataSeedingController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly IServiceProvider _services;
public DataSeedingController(IServiceProvider services)
{
_services = services;
}
[HttpPost("seed-dummy-users")]
public async Task<IActionResult> SeedDummyUsers()
{
await IdentityUserSeeder.SeedUsersAsync(_services);
return Ok("Dummy users have been seeded successfully.");
}
[HttpPost("seed-dummy-claims")]
public async Task<IActionResult> SeedDummyClaims()
{
await ClaimSeeder.SeedClaimsMaster(_services);
return Ok("Dummy claims have been seeded successfully.");
}
}
}
Database Migration:
Now, we need to generate the Migration file and update the database to include the Claim Master table. So, open the Visual Studio Package Manager Console and execute the following Add-Migration and Update-Database commands.

Now, if you verify the database, you should see the newly added ClaimMasters table in the IdentityCoreDB database, as shown in the image below.

Seeding Dummy Claims:
Invoke the following endpoint to seed the data from Postman using a POST Request. Please update the Port number on which your application is running.
https://localhost:7049/api/DataSeeding/seed-dummy-claims
By invoking this endpoint (e.g., https://localhost:7091/api/DataSeeding/seed-dummy-claims) we trigger the seeding process only when we want it. This avoids re-running seeding every time the app starts and keeps production safer.
Now, run the application and test its functionalities; it should work as expected. The claims will be stored in the ClaimMasters able.

Why do we need Claims?
We need claims because they provide a flexible and powerful way to handle authorization in modern applications:
Flexible Authorization
- Roles are often too broad (e.g., “Admin”).
- Claims allow more specific control (e.g., “Admin with EditUser permission”).
- This allows role-based + claim-based hybrid security.
Centralized User Information
- Claims carry user information in a structured way.
- For example, instead of hitting the database every time to know a user’s department, you can store it in claims.
Extensibility
- Applications can define any custom claim to support business rules.
- No need to create new roles for every possible permission.
Fine-Grained Security
- Claims let you enforce rules like:
- Only users from HR department can view employee salaries.
- Only users with SubscriptionType = Premium can access advanced features.
Cross-Application and Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Claims travel inside tokens (like JWT), so when the same user accesses multiple systems, their identity and permissions are already embedded.
- This enables SSO and federation scenarios.
The Claim Management application provides a complete lifecycle solution for defining, assigning, and enforcing claims in an ASP.NET Core Identity system. It bridges the gap between rigid role-based access and the need for fine-grained, flexible, and scalable authorization. Next, we are going to discuss how to assign Claims to users and roles in our application.
In the next article, I will discuss how to Manage User Claims in ASP.NET Core Identity. In this article, I explain Claims Management in ASP.NET Core Identity. I hope you enjoy this article, ASP.NET Core Identity Role-Based Authorization.

🎥 Watch the Complete Video Tutorial
We’ve also created a step-by-step video on Claims Management in ASP.NET Core Identity. In this video, you’ll learn how to create, assign, and manage claims with real implementation examples.
👉 Watch here: Claims Management in ASP.NET Core Identity | Complete Guide
If you prefer learning visually, this video will walk you through the entire process in a clear and practical way. Don’t forget to subscribe to our channel for more in-depth .NET tutorials!