Back to: Cloud Computing Tutorials for Beginners and Professionals
Software as a Service (SaaS) in Cloud Computing
In this article, I will discuss Software as a Service, also called SaaS, in Cloud Computing. Please read our previous article discussing Platform as a Service (PaaS) in Cloud Computing. At the end of this article, you will understand Software as a Service (SaaS) in Cloud Computing. Who uses this service, and what are the advantages it provides?
What is Software as a Service (SaaS) in Cloud Computing?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a cloud computing model that delivers software applications over the Internet. Users access them through a web browser without needing to install or maintain the software on their local devices. SaaS providers manage the infrastructure, security, and maintenance, enabling users to focus solely on using the software to meet their business or personal needs. For a better understanding, please have a look at the following image.
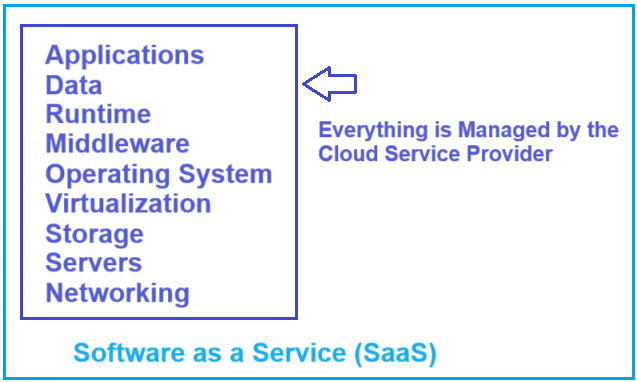
As you can see in the above diagram, with Software as a Service (SaaS), the cloud service provider manages everything for us. We do not have to worry about any of the following.
- Purchasing and setting up physical hardware.
- Installing operating system.
- Virtualization.
- Setting up the network.
- Installing and maintaining middleware, runtime, and applications.
All these are taken care of by the Cloud Service Provider. So, the bottom line is that with the SaaS model, all the hardware and software are maintained by the cloud service provider for us. We access the software, i.e., the application we want to use for our business, over the Internet. The software runs at the cloud service provider data center on their physical servers. The data the application captures is stored at the cloud service provider data center. So, the point that I am trying to make it clear is that everything is managed for us by the cloud service provider. We access the cloud services provided by cloud service providers over the Internet, and as it supports the pay-as-you-go model, we pay a monthly fee based on our usage.
Who uses Software as a Service?
Everyone, individuals and organizations of all sizes – small, medium, and even large enterprises. Most of us, as an Individual, use at least 2 to 3 Software as a Service application. Examples of Software as a Service are GMAIL, Netflix, Amazon Prime, Dropbox, Google Drive, and Office 365. How many of these SaaS applications do you use? If you ask me, I will use all of them. If we take GMAIL, for example, it is hosted by Google on their physical servers at their data centers. We don’t host or install anything on our computer or laptop. We fire up our favorite browser, point it to GMAIL.com, and access the GMAIL software as a service over the internet.
Examples of SaaS Providers:
- Google Workspace: It offers a suite of productivity and collaboration tools including Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, and Google Meet.
- Microsoft 365: A collection of productivity applications such as Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Teams, along with cloud storage and collaboration features.
- Salesforce: A customer relationship management (CRM) platform that offers sales, service, marketing, and analytics solutions.
- Zoom: It is a video conferencing and communication platform that enables virtual meetings, webinars, and collaboration.
- Adobe Creative Cloud: Offers a collection of software for graphic design, video editing, web development, photography, and cloud services.
- Slack: A messaging and collaboration platform that facilitates communication within teams and integrates with other business tools.
Benefits of Software as a Service in Cloud Computing:
The following are some Benefits of using Software as a Service in Cloud Computing.
Very Easy to Get Started
It is very easy to get started with a SaaS application. Think about a traditional business application running on-premise. You need to purchase hardware, i.e., a physical server and all the related hardware. Install the operating system, runtime, middleware, and any other dependencies. On top of this, you install the software application, configure it, and then make it available for business. You also need to recruit a workforce to maintain the servers and the application, i.e., install patches and updates.
Compare this to a SaaS application. You fire up your favorite browser and access the SaaS application over the internet. There might be some customization and configuration required, but it is very easy to get started with a SaaS application than running that same application on-premise.
Accessibility
You access SaaS applications over the Internet. This means that as long as you have an internet connection, you can access a SaaS application from anywhere and on any internet-enabled device.
Automatic Updates
With a SaaS application, you don’t have to worry about installing updates or patches. These are automatically provided by the cloud service provider, that too, in most cases, with ZERO downtime. This reduces the burden on the in-house development and IT staff.
Flexible Usage-Based Pricing
Flexible usage-based pricing. No upfront huge capital expenditure. You only pay for what you use. For example, if you have 10 users using the application, you only pay for that 10 users. You also have the flexibility to scale the number of users up and down depending on your business needs.
Reduced Financial Risk
With SaaS applications, there is less financial risk. For example, if you want to see if a SaaS application adds value to your business, you can start with 1 or 2 users and see if it’s adding value. If it is, then you have the option to scale up the number of users. If it does not add value, you stop using the app and the payments. These days, most cloud service providers also offer free trials. You can try a SaaS app for free and see if it is adding any value. If it is not, there is no cost to your business anyway. Compare this to buying expensive hardware and a packaged app upfront. With SaaS applications, businesses have reduced financial risks.
Affordability
Another great benefit is affordability. Applications and solutions such as CRM (Customer Relationship Management) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), for example, are very expensive to buy outright. This is a huge burden, especially for individuals and small and medium organizations. However, the SaaS application’s flexible pay-as-you-go model allows even small and medium organizations to experiment with whether these expensive apps add value to their business. Basically, it levels the playing field for everyone, including small businesses and individuals.
In the next article, I will discuss the Differences Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Cloud Computing. In this article, I will explain Software as a Service (SaaS) in Cloud Computing. I hope you enjoy this Software as a Service (SaaS) in Cloud Computing article.

