Back to: Cloud Computing Tutorials for Beginners and Professionals
Differences Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Cloud Computing
In this article, I will discuss the Differences Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Cloud Computing and give you a detailed explanation of the three main service models in cloud computing: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each model offers different levels of control, management, and flexibility, depending on the various business needs.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in Cloud Computing
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. It’s the most flexible cloud computing model that offers virtual servers, storage, and networks. It allows businesses to purchase resources on-demand and as-needed instead of investing in costly physical hardware.
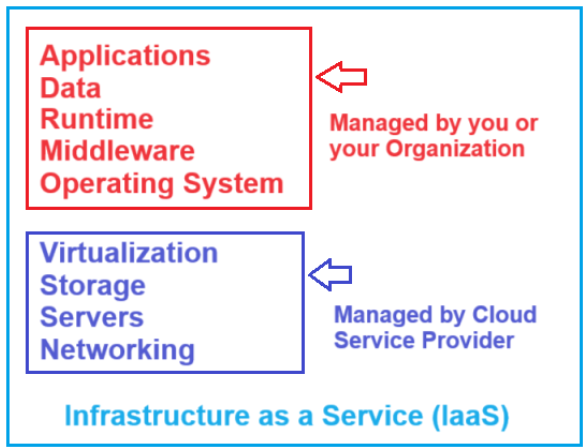
What it provides:
- Virtualization
- Storage
- Servers
- Networking
When to use:
- When you need full control over the infrastructure
- For developing and testing environments
- For high-scale web applications
- For hosting websites with fluctuating demand
Benefits:
- Flexibility and scalability
- Cost savings compared to on-premises infrastructure
- Full control over the infrastructure
- Easy to manage and automate
Limitations:
- Requires technical expertise to manage and configure
- Security and compliance responsibility lies heavily on the user
IaaS Service Providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – EC2
- Microsoft Azure – Virtual Machines
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) – Compute Engine
Platform as a Service (PaaS) in Cloud Computing
PaaS provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without dealing with the underlying infrastructure. The enterprise or a third-party provider can manage all servers, storage, and networking, while the developers can maintain application management.
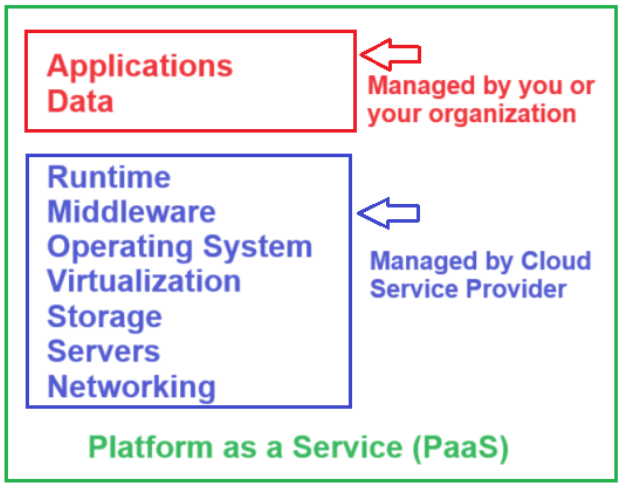
What it provides:
- Runtime
- Middleware
- Operating System
- Virtualization
- Storage
- Servers
- Networking
When to use:
- When you want to develop or deploy an application quickly without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- This is for developers who want to focus on the development and management of applications.
- To streamline workflows when multiple developers are working on the same development project.
Benefits:
- Reduces the complexity of building, managing, and deploying applications
- Provides all necessary tools to develop, test, and host applications in the same platform
- More cost-effective for developers as it minimizes the need to invest in hardware and software
Limitations:
- Less control over the underlying infrastructure
- Potential for vendor lock-in
- Limited to the features and services provided by the PaaS provider
PaaS Service Providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Elastic Beanstalk
- Microsoft Azure – App Service
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) – App Engine
Software as a Service (SaaS) in Cloud Computing
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. It allows users to connect to and use cloud-based apps over the Internet. The most common examples are email, calendaring, and office tools (such as Microsoft Office 365).

What it provides:
- Applications
- Data
- Runtime
- Middleware
- Operating System
- Virtualization
- Storage
- Servers
- Networking
When to use:
- For applications that require web or mobile access
- For standardized business processes
- For collaboration and communication tools
- For CRM, ERP, and other business management tools
Benefits:
- No need for software installation and maintenance
- Accessibility from any location with an Internet connection
- Scalable usage
- Cost-effective as it operates on a subscription model
Limitations:
- Limited customization options
- Data security concerns
- Dependency on the service provider for uptime and performance
SaaS Service Providers:
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)
- Microsoft Office 365
- Salesforce
- Dropbox
Summary
- IaaS provides virtualized infrastructure and is ideal for those needing complete control over their environment. It offers high flexibility and scalability but requires technical management.
- PaaS offers a development platform that simplifies application development and deployment with less management overhead but with potential vendor lock-in and limited control.
- SaaS delivers software over the Internet, perfect for accessing applications on demand with minimal management. However, it offers less customization and potential data security concerns.
In the next article, I will discuss Containers as a Service (CaaS) in Cloud Computing. In this article, I explain the Differences Between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS in Cloud Computing. I hope you enjoy this article.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
