Back to: ADO.NET Core Tutorial For Beginners and Professionals
Dynamic SQL in ADO.NET Core with Examples
In this article, I will discuss Dynamic SQL in ADO.NET Core with Examples. Please read our previous article discussing SQL Injection and Prevention using ADO.NET Core with Examples. Dynamic SQL is a method of constructing SQL queries or statements dynamically at runtime. It is useful when the SQL queries vary depending on certain conditions.
What is Dynamic SQL?
Dynamic SQL refers to SQL statements that are constructed and executed at runtime rather than being hard-coded in the application’s source code. Unlike static SQL, which is predefined and does not change, dynamic SQL allows flexibility to change the SQL query as needed based on user input, application logic, or other conditions encountered during runtime. This flexibility is ideal for scenarios like dynamic search filters, report generation, or conditional query logic.
Why Do We Need Dynamic SQL?
Dynamic SQL is essential when we cannot determine the exact SQL queries at compile time. It provides flexibility, allowing SQL queries to adapt based on varying inputs and conditions. Suppose you create a search feature enabling users to filter employees by department, salary range, or hire date. Since the combination of filters isn’t known in advance, dynamic SQL can help build the exact query based on the user’s specifications. Dynamic SQL is valuable when:
Note: Dynamic SQL comes with its own set of challenges, such as SQL Injection risks if not parameterized properly and difficulty in debugging.
SQL Server Database Setup
Please execute the following SQL Script in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to set up a sample EmployeeDB database with tables and dummy data for testing purposes:
-- Create EmployeeDB database
CREATE DATABASE EmployeeDB;
GO
-- Switch to EmployeeDB database
USE EmployeeDB;
GO
-- Create Departments table
CREATE TABLE Departments (
DepartmentId INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1),
Name NVARCHAR(100) NOT NULL
);
-- Create Employees table
CREATE TABLE Employees (
EmployeeId INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1),
FirstName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
LastName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
DepartmentId INT NOT NULL FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES Departments(DepartmentId),
Salary DECIMAL(10,2) NOT NULL,
HireDate DATE NOT NULL
);
-- Insert dummy data into Departments table
INSERT INTO Departments (Name) VALUES
('Sales'),
('IT'),
('HR'),
('Finance');
-- Insert dummy data into Employees table
INSERT INTO Employees (FirstName, LastName, DepartmentId, Salary, HireDate) VALUES
('Alice', 'Johnson', 1, 55000, '2020-03-15'),
('Bob', 'Smith', 2, 72000, '2019-07-01'),
('Carol', 'Lee', 2, 68000, '2021-01-10'),
('David', 'Wang', 3, 62000, '2018-11-23'),
('Sara', 'Taylor', 1, 68000, '2021-01-10'),
('James', 'Smith', 2, 65000, '2018-11-23'),
('Eve', 'Davis', 4, 80000, '2022-05-30');
Script Explanations:
- Create Database: Creates a new database EmployeeDB.
- Departments Table: Creates a table to store department information.
- Employees Table: Creates a table to store employee data, including references to departments.
- Dummy Data Insertion: Inserts some data into both the Departments and Employees tables to be used in the dynamic SQL queries.
Dynamic Query in .NET Core Application
In the example below, a dynamic SQL query is constructed to filter employees based on optional parameters, such as department and minimum salary. The SQL query is built dynamically and parameterized to avoid SQL injection.
using System.Data;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
namespace DynamicSqlDemo
{
public class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
// Connection string to EmployeeDB
string connectionString = "Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=EmployeeDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;";
Console.WriteLine("Enter department name (or leave blank):");
var dept = Console.ReadLine(); // optional filter
Console.WriteLine("Enter minimum salary (or leave blank):");
var minSalaryInput = Console.ReadLine();
decimal? minSalary = null;
//Validate the Salary
if (decimal.TryParse(minSalaryInput, out var salary))
{
minSalary = salary;
}
try
{
using (var conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
conn.Open(); // open DB connection
using (var cmd = new SqlCommand())
{
// Assign connecction object to the Connection property of the command object
cmd.Connection = conn;
// Base Query without dynamic filters
var sql = @"
SELECT e.EmployeeId, e.FirstName, e.LastName,
d.Name AS Department, e.Salary, e.HireDate
FROM Employees e
INNER JOIN Departments d ON e.DepartmentId = d.DepartmentId
WHERE 1=1";
// Dynamically append filters
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(dept))
{
//You can specify AND - OR Conditions based on your requirements
//Here, I am using AND Conditions
sql += " AND d.Name = @Dept";
var DeptParameter = new SqlParameter("@Dept", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 100)
{
Value = dept
};
cmd.Parameters.Add(DeptParameter);
}
if (minSalary.HasValue)
{
sql += " AND e.Salary >= @MinSalary";
var MinSalaryParameter = new SqlParameter("@MinSalary", SqlDbType.Decimal)
{
Value = minSalary.Value
};
cmd.Parameters.Add(MinSalaryParameter);
}
// Assign constructed query to the CommandText property of the command object
cmd.CommandText = sql;
// Execute the command and read results
using (var reader = await cmd.ExecuteReaderAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine("\nId\tName\tDepartment\tSalary\t\tHireDate");
//Console.WriteLine("EmployeeId | Name | Department | Salary | HireDate");
if (reader.HasRows)
{
while (await reader.ReadAsync())
{
// Print Each Row
Console.WriteLine(
$"{reader["EmployeeId"]}\t" +
$"{reader["FirstName"]}\t" +
$"{reader["Department"]}\t\t" +
$"{reader.GetDecimal(reader.GetOrdinal("Salary"))}\t" +
$"{reader.GetDateTime(reader.GetOrdinal("HireDate")):yyyy-MM-dd}");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("With the above Filter, No data available");
}
}
}
}
}
catch (SqlException ex)
{
// Handle SQL errors
Console.WriteLine($"SQL Error: {ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle general errors
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}
Code Explanation:
- User Input: The program prompts the user to enter a department name and a minimum salary. Both of these inputs are optional.
- Dynamic Query Construction: The base query starts with WHERE 1=1, which simplifies the logic for appending conditions later. Based on user inputs, conditions like AND d.Name = @Dept and AND e.Salary >= @MinSalary is dynamically added.
- Parameterized Queries: SQL parameters insert user inputs into the query safely, preventing SQL injection.
- Query Execution: The query is executed asynchronously using ExecuteReaderAsync(), and the results are displayed in a tabular format.
For a better understanding, please refer to the following images. Here, I am showing different scenarios with and without optional parameters:
Output1: Department IT and Minimum Salary 66000
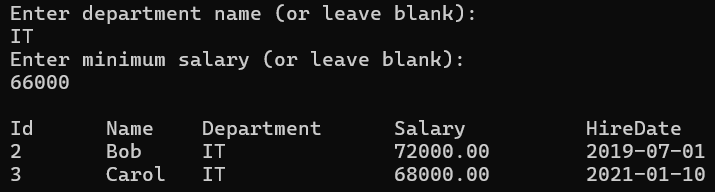
Output2: Department IT and Minimum Salary null
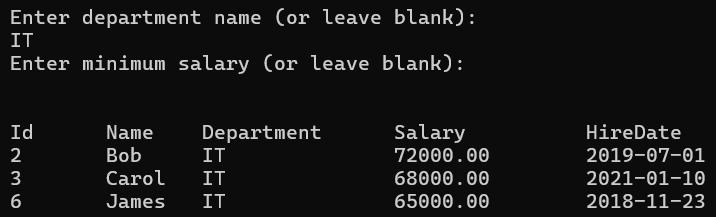
Output3: Department null and Minimum Salary null

Stored Procedure with Dynamic SQL
Please execute the following SQL Script to create the Stored Procedure. The stored procedure sp_GetEmployeesDynamic is designed to handle dynamic SQL. This procedure builds an SQL string based on the parameters it receives and executes the query via sp_executesql, which ensures that parameters are safely passed into the query.
CREATE OR ALTER PROCEDURE sp_GetEmployeesDynamic
@Dept NVARCHAR(100) = NULL,
@MinSalary DECIMAL(10,2) = NULL
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
DECLARE @sql NVARCHAR(MAX);
-- Base Query
SET @sql = N'
SELECT e.EmployeeId, e.FirstName, e.LastName,
d.Name AS Department, e.Salary, e.HireDate
FROM Employees e
INNER JOIN Departments d ON e.DepartmentId = d.DepartmentId
WHERE 1=1';
-- Append Dynamic Conditions
IF @Dept IS NOT NULL
SET @sql += ' AND d.Name = @DeptParam';
IF @MinSalary IS NOT NULL
SET @sql += ' AND e.Salary >= @MinSalParam';
-- Execute with parameterized sp_executesql stored procedure
EXEC sp_executesql
@sql,
N'@DeptParam NVARCHAR(100) = NULL, @MinSalParam DECIMAL(10,2) = NULL',
@DeptParam = @Dept,
@MinSalParam = @MinSalary;
END;
Script Explanations:
- Dynamic Query in Stored Procedure: Based on optional input parameters (@Dept and @MinSalary), the stored procedure dynamically constructs a query and executes it using sp_executesql.
- Parameterized Execution: sp_executesql safely executes the dynamic query, with parameters passed separately to prevent SQL injection.
Noe: The N prefix before a string in SQL Server (like N ‘Some SQL Text’) is used to indicate that the string is Unicode. Always use N’…’ when writing literal strings that will be treated as nvarchar.
What is sp_executesql?
It is a system stored procedure that executes a dynamically constructed SQL string. sp_executesql allows parameters to be passed in separately, ensuring the query is executed securely and efficiently.
Consume the Stored Procedure in .NET Core.
Now, we will modify our application to consume the stored procedure sp_GetEmployeesDynamic. The procedure is called with optional parameters that determine which employees to retrieve.
using System.Data;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
namespace DynamicSqlDemo
{
public class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
// Connection string to EmployeeDB
string connectionString = "Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=EmployeeDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;";
Console.WriteLine("Enter department name (or leave blank):");
var dept = Console.ReadLine(); // optional filter
Console.WriteLine("Enter minimum salary (or leave blank):");
var minSalaryInput = Console.ReadLine();
decimal? minSalary = null;
//Validate the Salary
if (decimal.TryParse(minSalaryInput, out var salary))
{
minSalary = salary;
}
try
{
using (var conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
using (var cmd = new SqlCommand("sp_GetEmployeesDynamic", conn))
{
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
// Pass parameters only if values are present
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Dept", string.IsNullOrEmpty(dept) ? DBNull.Value : dept);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@MinSalary", minSalary > 0 ? minSalary : DBNull.Value);
await conn.OpenAsync(); // open DB connection asynchrounsly
// Execute the command and read results
using (var reader = await cmd.ExecuteReaderAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine("\nId\tName\tDepartment\tSalary\t\tHireDate");
if (reader.HasRows)
{
while (await reader.ReadAsync())
{
// Print Each Row
Console.WriteLine(
$"{reader["EmployeeId"]}\t" +
$"{reader["FirstName"]}\t" +
$"{reader["Department"]}\t\t" +
$"{reader.GetDecimal(reader.GetOrdinal("Salary"))}\t" +
$"{reader.GetDateTime(reader.GetOrdinal("HireDate")):yyyy-MM-dd}");
}
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("With the above Filter, No data available");
}
}
}
}
}
catch (SqlException ex)
{
// Handle SQL errors
Console.WriteLine($"SQL Error: {ex.Message}");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle general errors
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}
Output:

Dynamic SQL is a powerful feature that enables flexible and secure query construction at runtime. By constructing SQL queries dynamically, applications can easily handle complex user-driven scenarios like reporting, searching, or filtering. Parameterized queries and stored procedures help ensure dynamic SQL remains secure and efficient, preventing issues like SQL injection and performance bottlenecks.
In the next article, I will discuss Performance Improvements in ADO.NET Core with Examples. In this article, I explain Dynamic SQL in ADO.NET Core with examples. I hope you enjoy this article.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
