Back to: ADO.NET Core Tutorial For Beginners and Professionals
CRUD Operations using ADO.NET Core with Stored Procedures
In this article, I will discuss how to perform CRUD Operations using ADO.NET Core with Stored Procedures and examples. Please read our previous article discussing ADO.NET Core Using Stored Procedure.
What are Database CRUD Operations?
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete, which are the fundamental operations we perform on data stored in any database. These operations let you:
- Create: Insert new data (e.g., new customer records) using an INSERT statement.
- Read: Retrieve or view existing data using a SELECT statement.
- Update: Modify existing data using an UPDATE statement.
- Delete: Remove data using a DELETE statement.
These operations are essential for managing the data lifecycle in a real-world application. For example, you may want to add new users, display customer information, update account details, or delete outdated records. When you encapsulate the SQL logic (such as INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, and DELETE) in Stored Procedures, you benefit from:
- Performance: SQL Server caches execution plans for stored procedures.
- Security: They help protect against SQL injection attacks.
- Maintainability: Centralizes data access logic on the server, simplifying updates and debugging.
SQL Server Database Setup
Before using CRUD operations, you need to set up your SQL Server database. For example, consider creating a database named CustomersDB with a Customers table. Please execute the following SQL scripts in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or any SQL client. The following SQL script creates a database named CustomersDB, table Customers, and inserts Dummy Data into Customers table.
-- Create a new database called CustomersDB
CREATE DATABASE CustomersDB;
GO
-- Switch to the CustomersDB database
USE CustomersDB;
GO
-- Create Customers table
CREATE TABLE Customers (
CustomerID INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1),
FirstName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
LastName NVARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
Email NVARCHAR(100)
);
GO
-- Insert dummy data into Customers table
INSERT INTO Customers (FirstName, LastName, Email, Phone)
VALUES
('John', 'Doe', 'john.doe@example.com'),
('Jane', 'Smith', 'jane.smith@example.com');
GO
Stored Procedures with Standardized Error Handling
We will create several stored procedures demonstrating different parameter scenarios to perform the database CRUD Operations. During the database operations, we may encounter some errors, and to return those errors to the client application, we add three standardized output parameters in each stored procedure. They are as follows:
- @ResultCode INT OUTPUT: A status code where 0 indicates success and a nonzero indicates an error.
- @ErrorNumber INT OUTPUT: The SQL error number if an error occurs. The ERROR_NUMBER() is a built-in SQL Server function that returns the error number of the error that occurred in the TRY…CATCH block. This number can be used to identify specific errors programmatically.
- @ErrorMessage NVARCHAR(4000) OUTPUT: The textual description of the error. The ERROR_MESSAGE() is another built-in SQL Server function that returns the complete text of the error message. It helps with debugging and troubleshooting by providing a human-readable error message.
In each stored procedure, we initialize these parameters to a “success” state; then, in the CATCH block, we update them if an error occurs.
Stored Procedure: Retrieve All Customers
This procedure returns all customer records and sets the standardized output parameters for error status. The CATCH block populates the error parameters if an error occurs in the TRY block.
-- Retrieve All Customers
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_GetAllCustomers
@ResultCode INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorNumber INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorMessage NVARCHAR(4000) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
-- Initialize outputs to indicate a successful operation.
SET @ResultCode = 0;
SET @ErrorNumber = 0;
SET @ErrorMessage = NULL;
BEGIN TRY
SELECT CustomerID, FirstName, LastName, Email
FROM Customers;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
-- Capture error details using built-in error functions.
SET @ResultCode = 1;
SET @ErrorNumber = ERROR_NUMBER();
SET @ErrorMessage = ERROR_MESSAGE();
END CATCH
END;
GO
Key Points:
- In the TRY block, the procedure executes a simple SELECT query.
- If an error occurs, the CATCH block sets the error outputs using ERROR_NUMBER() and ERROR_MESSAGE()
Stored Procedure: Retrieve a Customer by Id
This procedure accepts a customer ID as input and returns the matching record. It also sets standard output parameters if an error occurs.
-- Retrieve the record for a specific customer by passing in the CustomerID
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_GetCustomerById
@CustomerID INT,
@ResultCode INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorNumber INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorMessage NVARCHAR(4000) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
-- Initialize outputs for success.
SET @ResultCode = 0;
SET @ErrorNumber = 0;
SET @ErrorMessage = NULL;
BEGIN TRY
SELECT CustomerID, FirstName, LastName, Email
FROM Customers
WHERE CustomerID = @CustomerID;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
SET @ResultCode = 1;
SET @ErrorNumber = ERROR_NUMBER();
SET @ErrorMessage = ERROR_MESSAGE();
END CATCH
END;
GO
Stored Procedure: Update Customer Data
This procedure updates customer details, verifies if any record was updated using @@ROWCOUNT, and returns the updated record as a result set. If no record is updated (i.e., if @@ROWCOUNT equals 0), a custom error is set.
-- Update Customer Data and Return Updated Information
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_UpdateCustomer
@CustomerID INT,
@FirstName NVARCHAR(50),
@LastName NVARCHAR(50),
@Email NVARCHAR(100),
@ResultCode INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorNumber INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorMessage NVARCHAR(4000) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
-- Initialize outputs.
SET @ResultCode = 0;
SET @ErrorNumber = 0;
SET @ErrorMessage = NULL;
BEGIN TRY
UPDATE Customers
SET FirstName = @FirstName,
LastName = @LastName,
Email = @Email
WHERE CustomerID = @CustomerID;
-- @@ROWCOUNT returns the number of rows affected by the last DML statement.
IF @@ROWCOUNT = 0
BEGIN
SET @ResultCode = 1;
SET @ErrorNumber = 50000; -- Custom error number.
SET @ErrorMessage = 'No rows updated. Check if the CustomerID exists.';
RETURN;
END
-- Return the updated record.
SELECT CustomerID, FirstName, LastName, Email
FROM Customers
WHERE CustomerID = @CustomerID;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
SET @ResultCode = 1;
SET @ErrorNumber = ERROR_NUMBER();
SET @ErrorMessage = ERROR_MESSAGE();
END CATCH
END;
GO
What is the use of @@ROWCOUNT?
The @@ROWCOUNT is a system function that returns the number of rows affected by the last executed statement. That means using @@ROWCOUNT here to check whether the UPDATE statement affected any rows. If it returns 0, this indicates that either the CustomerID does not exist or the supplied data did not lead to any changes. The procedure then assigns a custom error code and message. This prevents the application from mistakenly treating the operation as successful.
Stored Procedure: Insert New Customer
This procedure inserts a new customer record and returns the new CustomerID via an output parameter using SCOPE_IDENTITY(). If an error occurs, it sets the output CustomerID to –1.
-- Insert New Customer and Return New ID via Output Parameter
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_InsertCustomer
@FirstName NVARCHAR(50),
@LastName NVARCHAR(50),
@Email NVARCHAR(100),
@NewCustomerID INT OUTPUT,
@ResultCode INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorNumber INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorMessage NVARCHAR(4000) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
-- Initialize outputs.
SET @ResultCode = 0;
SET @ErrorNumber = 0;
SET @ErrorMessage = NULL;
BEGIN TRY
INSERT INTO Customers (FirstName, LastName, Email)
VALUES (@FirstName, @LastName, @Email);
-- SCOPE_IDENTITY returns the last identity value inserted in the current scope.
SET @NewCustomerID = SCOPE_IDENTITY();
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
SET @ResultCode = 1;
SET @ErrorNumber = ERROR_NUMBER();
SET @ErrorMessage = ERROR_MESSAGE();
SET @NewCustomerID = -1;
END CATCH
END;
GO
What is SCOPE_IDENTITY()?
The SCOPE_IDENTITY() is a built-in function that returns the last identity value inserted into an identity column within the current scope (e.g., within the same stored procedure). Unlike @@IDENTITY, it does not include identity values inserted by triggers or other operations outside the current scope, making it more reliable for capturing newly generated keys.
Stored Procedure: Delete an Existing Customer
This procedure deletes a customer based on the provided CustomerID. It uses @@ROWCOUNT to determine if a deletion occurred and returns a Boolean value (1 for success, 0 for failure). In the event of an error, it sets @IsDeleted to 0.
-- Delete an Existing Customer and Return Success via a Boolean Output Parameter
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_DeleteCustomer
@CustomerID INT,
@IsDeleted BIT OUTPUT,
@ResultCode INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorNumber INT OUTPUT,
@ErrorMessage NVARCHAR(4000) OUTPUT
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
-- Initialize outputs.
SET @ResultCode = 0;
SET @ErrorNumber = 0;
SET @ErrorMessage = NULL;
BEGIN TRY
DELETE FROM Customers
WHERE CustomerID = @CustomerID;
IF @@ROWCOUNT > 0
SET @IsDeleted = 1;
ELSE
SET @IsDeleted = 0;
END TRY
BEGIN CATCH
SET @ResultCode = 1;
SET @ErrorNumber = ERROR_NUMBER();
SET @ErrorMessage = ERROR_MESSAGE();
SET @IsDeleted = 0;
END CATCH
END;
GO
Why Output Parameters Are Preferred to Return Error Information:
Output Parameters offer several advantages over embedding error details in result sets:
- Separation of Concerns: They clearly separate business data (e.g., customer records) from error or status metadata.
- Predictable Contract: The calling application always expects specific parameters for status and error information (e.g., a @ResultCode of 0 indicates success).
- Easier Error Handling: It’s simpler for client code to check a return code or output parameters rather than parsing a result set for error columns.
- Consistency: Many enterprise systems adopt a standard pattern (using output parameters or return codes) to ease troubleshooting, logging, and reporting.
In some cases, you may also want to log error details internally (for example, writing to a log table or an external logging service), but for the stored procedure–to–application contract, the error details via output parameters are often sufficient.
Consuming Stored Procedures Using ADO.NET Core
When consuming these stored procedures from a .NET Core application (for example, in a console or web application), we typically:
- Establish a connection using a connection string.
- Create a SqlCommand object that targets the stored procedure.
- Add input and output parameters as needed, including the standardized error output parameters.
- Open the connection asynchronously (using OpenAsync()), then execute the command using asynchronous methods (such as ExecuteReaderAsync() or ExecuteNonQueryAsync()).
- After execution, inspect the output parameters for any error (if @ResultCode is not 0) before processing data.
Now, let us create a .NET Core Console Application to see how to consume the stored procedures. The following example code is self-explained, so please read the comment lines for a better understanding.
using System.Data;
using Microsoft.Data.SqlClient;
namespace ADOCRUDDemoUsingStoredProcedure
{
class Program
{
// Connection String to the CustomersDB database
public static string connectionString = "Server=LAPTOP-6P5NK25R\\SQLSERVER2022DEV;Database=CustomersDB;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True;";
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Starting ADO.NET CRUD Operations using Stored Procedures (Async)...\n");
// Example 1: Retrieve all customers
await GetAllCustomers();
// Example 2: Retrieve a single customer by ID
await GetCustomerById(1);
// Example 3: Update a customer's details and return the updated record
await UpdateCustomer(1, "UpdatedFirst", "UpdatedLast", "updated@example.com");
// Example 4: Insert a new customer and return the new CustomerID via output parameter
int newCustomerId = await InsertCustomerReturnId("Alice", "Johnson", "alice.johnson@example.com");
if (newCustomerId == -1)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error occurred during insertion. See error details above.");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("\nNew Customer inserted with ID: " + newCustomerId);
}
// Example 5: Delete a customer and check if deletion succeeded
bool isDeleted = await DeleteCustomer(2); // Use an appropriate CustomerID.
Console.WriteLine("\nDeletion Status for CustomerID 2: " + (isDeleted ? "Deleted" : "Not Deleted"));
// Example 6: Retrieve all customers after deletion
Console.WriteLine("Retrieve all customers after deletion");
await GetAllCustomers();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Global exception handling for unexpected errors.
Console.WriteLine("Global Exception occurred: " + ex.Message);
}
}
// Checks the standardized error output parameters for a stored procedure.
private static bool HasError(SqlCommand cmd, out int errorNumber, out string? errorMessage)
{
// Set the Error number if any error occurred
errorNumber = Convert.ToInt32(cmd.Parameters["@ResultCode"].Value) != 0 ?
Convert.ToInt32(cmd.Parameters["@ErrorNumber"].Value) : 0;
// Set the Error Message if any error occurred
errorMessage = cmd.Parameters["@ErrorMessage"].Value?.ToString();
// Return True if any error occurred else false
return Convert.ToInt32(cmd.Parameters["@ResultCode"].Value) != 0;
}
// Retrieve all customers using sp_GetAllCustomers.
static async Task GetAllCustomers()
{
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("sp_GetAllCustomers", conn))
{
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
// Add standardized error output parameters.
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ResultCode", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorNumber", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorMessage", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 4000) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
await conn.OpenAsync();
using (SqlDataReader reader = await cmd.ExecuteReaderAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine("All Customers:");
while (await reader.ReadAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine($"ID: {reader["CustomerID"]}, Name: {reader["FirstName"]} {reader["LastName"]}, Email: {reader["Email"]}");
}
}
// Check the output parameters for errors.
if (HasError(cmd, out int errorNumber, out string? errorMsg))
{
Console.WriteLine("Error occurred in sp_GetAllCustomers: {0} - {1}", errorNumber, errorMsg);
}
}
}
}
// Retrieve a customer by ID using sp_GetCustomerById.
static async Task GetCustomerById(int customerId)
{
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("sp_GetCustomerById", conn))
{
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", customerId);
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ResultCode", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorNumber", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorMessage", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 4000) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
await conn.OpenAsync();
using (SqlDataReader reader = await cmd.ExecuteReaderAsync())
{
if (await reader.ReadAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine($"\nCustomer Details for CustomerID {customerId}:");
Console.WriteLine($"ID: {reader["CustomerID"]}, Name: {reader["FirstName"]} {reader["LastName"]}, Email: {reader["Email"]}");
}
}
if (HasError(cmd, out int errorNumber, out string? errorMsg))
{
Console.WriteLine("Error occurred in sp_GetCustomerById: {0} - {1}", errorNumber, errorMsg);
}
}
}
}
// Update a customer's details using sp_UpdateCustomer and return the updated record.
static async Task UpdateCustomer(int customerId, string firstName, string lastName, string email)
{
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("sp_UpdateCustomer", conn))
{
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", customerId);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@FirstName", firstName);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@LastName", lastName);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Email", email);
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ResultCode", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorNumber", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorMessage", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 4000) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
await conn.OpenAsync();
using (SqlDataReader reader = await cmd.ExecuteReaderAsync())
{
if (await reader.ReadAsync())
{
Console.WriteLine("\nUpdated Customer Record:");
Console.WriteLine($"ID: {reader["CustomerID"]}, Name: {reader["FirstName"]} {reader["LastName"]}, Email: {reader["Email"]}");
}
}
if (HasError(cmd, out int errorNumber, out string? errorMsg))
{
Console.WriteLine("Error occurred in sp_UpdateCustomer: {0} - {1}", errorNumber, errorMsg);
}
}
}
}
// Insert a new customer using sp_InsertCustomer.
// Uses an output parameter to return the new CustomerID and standardized error information.
static async Task<int> InsertCustomerReturnId(string firstName, string lastName, string email)
{
int newCustomerId = 0;
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("sp_InsertCustomer", conn))
{
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@FirstName", firstName);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@LastName", lastName);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Email", email);
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@NewCustomerID", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ResultCode", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorNumber", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorMessage", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 4000) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
await conn.OpenAsync();
await cmd.ExecuteNonQueryAsync();
if (HasError(cmd, out int errorNumber, out string? errorMsg))
{
Console.WriteLine("Error occurred in sp_InsertCustomer: {0} - {1}", errorNumber, errorMsg);
newCustomerId = -1;
}
else
{
newCustomerId = Convert.ToInt32(cmd.Parameters["@NewCustomerID"].Value);
}
}
}
return newCustomerId;
}
// Delete an existing customer using sp_DeleteCustomer.
// Uses an output parameter to return a boolean indicating success along with standardized error information.
static async Task<bool> DeleteCustomer(int customerId)
{
bool isDeleted = false;
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
using (SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("sp_DeleteCustomer", conn))
{
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@CustomerID", customerId);
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@IsDeleted", SqlDbType.Bit) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ResultCode", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorNumber", SqlDbType.Int) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
cmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("@ErrorMessage", SqlDbType.NVarChar, 4000) { Direction = ParameterDirection.Output });
await conn.OpenAsync();
await cmd.ExecuteNonQueryAsync();
if (HasError(cmd, out int errorNumber, out string? errorMsg))
{
Console.WriteLine("Error occurred in sp_DeleteCustomer: {0} - {1}", errorNumber, errorMsg);
isDeleted = false;
}
else
{
isDeleted = Convert.ToBoolean(cmd.Parameters["@IsDeleted"].Value);
}
}
}
return isDeleted;
}
}
}
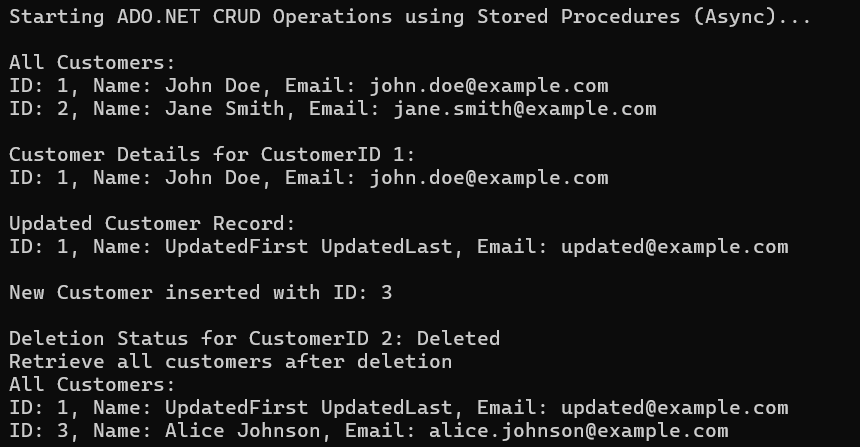
Output:
FAQa
What are CRUD operations?
CRUD stands for Create, Read, Update, and Delete, the four operations that form the foundation of data manipulation in any database-driven application.
Why are CRUD operations important in real-time applications?
They enable applications to manage data dynamically by adding new records, retrieving current data, modifying existing records, and deleting obsolete data. This flexibility is critical for maintaining up-to-date user information, inventory, transactions, and more.
Why use stored procedures instead of inline SQL queries?
Stored procedures help encapsulate the SQL logic on the database side, improve security by minimizing SQL injection risks, enhance performance through execution plan reuse, and simplify code management by separating data access logic from application code.
How do ERROR_NUMBER() and ERROR_MESSAGE() help?
These functions capture and return details about errors in the TRY-CATCH block, allowing the calling application to log and handle specific errors.
What does @@ROWCOUNT do?
It returns the number of rows affected by the most recent SQL statement, enabling you to verify if an UPDATE or DELETE succeeded.
Why is SCOPE_IDENTITY() used?
It returns the last identity value generated in the current scope and session, ensuring that only the intended identity is returned when inserting new rows.
Can these techniques be used in web applications?
Yes. While this example uses a console application for simplicity, the same ADO.NET techniques and stored procedures can be incorporated into ASP.NET Core web applications to manage database interactions effectively.
CRUD operations are the bread and butter of any database-driven application. Using ADO.NET Core with Stored Procedures allows you to:
- Keep SQL logic on the server for better security and performance.
- Maintain a clear separation of concerns in your code.
- Handle typical Create, Read, Update, and Delete scenarios efficiently.
Following the above, you can set up a robust and maintainable data-access layer using ADO.NET Core, SQL Server, and stored procedures in a .NET Core application.
In the next article, I will discuss CRUD Operations using ADO.NET Core with SqlDataAdapter and Stored Procedures with Examples. In this article, I explain how to perform CRUD Operations using ADO.NET Core with Stored Procedures. I would like to have your feedback. Please post feedback, questions, or comments about this article.

