Back to: Java Struts Tutorials
Struts 2 Environment Setup
In this article, I am going to discuss the Struts 2 Environment Setup. Please read our previous article where we discussed Struts 2 Architectures and Flow. Before we start programming using Struts 2, we have to install and set up several things. They are:
- Java SDK
- Apache Tomcat
- Eclipse IDE
- Struts 2 Libraries
Java SDK
The Java SDK (Software Development Kit) is a collection of tools, libraries, and documentation provided by Oracle (previously Sun Microsystems) to develop, compile, debug, and run Java applications. The Java SDK includes the following key components:
- Java Development Kit (JDK): The JDK is the primary component of the Java SDK. It provides the necessary tools and utilities for Java application development, including the Java compiler (javac), runtime environment (java), debugger (jdb), and other development utilities.
- Java Runtime Environment (JRE): The JRE is a subset of the JDK and includes only the necessary components to run compiled Java applications. It contains the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), core libraries, and runtime environment required to execute Java programs.
- Java Standard Libraries: The Java SDK includes a vast set of standard libraries, known as the Java Class Library or Java API (Application Programming Interface). These libraries provide a wide range of pre-built classes and methods for common tasks, such as string manipulation, file handling, networking, database connectivity, graphical user interface (GUI) development, and more.
- Documentation and API Reference: The Java SDK provides comprehensive documentation, including guides, tutorials, and API reference documentation. The documentation helps developers understand the usage and functionality of various Java classes and libraries and serves as a valuable resource during application development.
- Development Tools: The Java SDK includes various development tools that aid in building, testing, and debugging Java applications. These tools include an integrated development environment (IDE) like Eclipse or NetBeans, or command-line tools like javac (Java compiler), jar (Java Archive tool), and javadoc (Java documentation generator).
- Additional Utilities: The Java SDK includes additional utilities and tools to assist in the development process, such as the Java debugger (jdb), Java Mission Control (JMC) for performance monitoring and analysis, Java Flight Recorder (JFR) for profiling and recording application events, and more.
The Java SDK is essential for Java application development, as it provides all the necessary components and tools to write, compile, and run Java programs. It enables developers to create robust, platform-independent applications that can run on any system with a compatible Java runtime environment. To install this, follow these steps:
Step 1: Download the latest version of the SDK from https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/. The latest version available is JDK 20.
Step 2: Select the appropriate operating system and download its package.
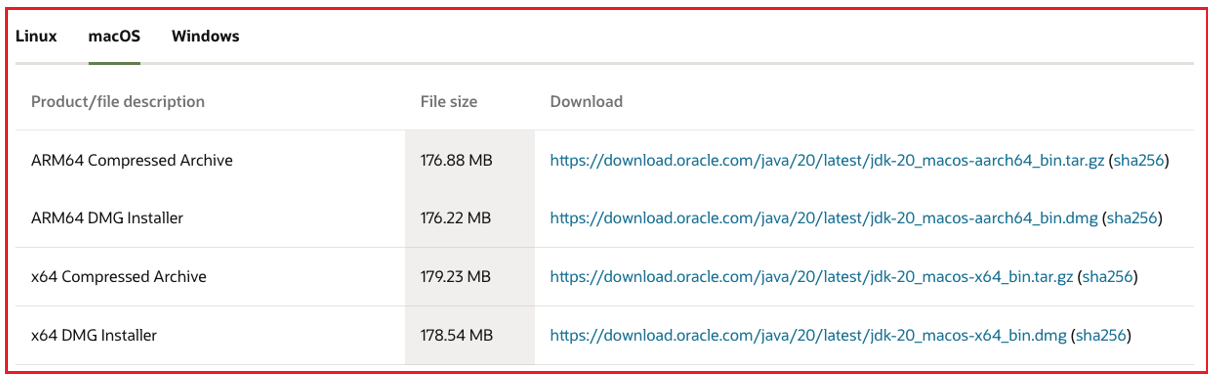
Step 3: Install the application.
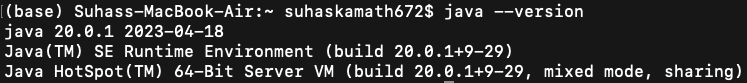
Step 4: Verify that the installation is successful. To do this, open the terminal/command prompt on your computer. Enter the java –version into the prompt. The reply will indicate if Java is installed properly.
Apache Tomcat
Apache Tomcat, often referred to simply as Tomcat, is an open-source web server and Servlet container. It is developed by the Apache Software Foundation and is widely used for hosting Java-based web applications. Here are the main purposes and features of Apache Tomcat:
- Servlet Container: Tomcat serves as a Servlet container, implementing the Java Servlet, JavaServer Pages (JSP), and JavaServer Faces (JSF) specifications. It provides an environment for running Java web applications, processing HTTP requests, and generating dynamic web content.
- Web Server: Tomcat also functions as a standalone web server capable of serving static web content, such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and image files. It can handle HTTP requests and deliver static files directly to clients without involving a separate web server.
- Java EE Compatibility: Tomcat implements a subset of the Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE) specifications, allowing developers to deploy and run Java EE applications on Tomcat. It supports features like servlets, JSPs, web services, JDBC connections, and more, providing a lightweight alternative to full-fledged Java EE application servers.
- Portability: Tomcat is platform-independent and can run on various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, macOS, and more. It allows developers to build web applications that can be easily deployed and run on different platforms without modification.
- Configuration and Management: Tomcat provides a simple and flexible configuration mechanism through XML-based configuration files. It allows customization of various server settings, such as ports, connection pools, security settings, and more. Tomcat also offers a web-based administration console for managing and monitoring server resources, applications, and logging.
- Scalability and Clustering: Tomcat supports scalability and high availability through clustering and load balancing. Multiple Tomcat instances can be configured to work together, distributing the application load and ensuring fault tolerance and reliability.
- Embeddability: Tomcat can be embedded within other Java applications, allowing developers to integrate it into their software as a lightweight web server or Servlet container. This feature is useful when building standalone applications that require web functionality.
- Community and Ecosystem: Tomcat has a large and active open-source community, providing support, documentation, and a wide range of third-party extensions and plugins. Many Java frameworks and tools are designed to work seamlessly with Tomcat, making it a popular choice for Java web development.
Overall, Apache Tomcat is widely used as a lightweight and versatile web server and Servlet container for hosting Java web applications, providing a reliable and scalable environment for running Java-based web projects. To install this, follow these steps:
Step 1: Download the latest version of the SDK from https://tomcat.apache.org/. The latest version available is Tomcat 10.
Step 2: Select the appropriate operating system and download its package.

If you are using Windows, download the Windows Service Installer and execute it. Follow the instructions in the installed to successfully install Tomcat. Skip directly to step 9.
If you are using a Unix-based based system, such as MacOS or Linux, download the zip or tar.gz version and extract it. Then, follow the below steps to install Tomcat.
Step 3: Open the terminal and navigate to the directory in which the archive has been extracted.
![]()
Step 4: These files must exist in this folder:

Step 5: Navigate to the bin/ folder. It should contain the following files:

Step 6: List all the shell scripts (files which have the .sh extension):

As can be seen from the above screenshot, the execute permission is not given to these shell scripts.
Step 7: Provide the shell scripts with the execute permission using the chmod command.

Step 8: Execute the startup.sh script. The following output must be shown:

This indicates that Tomcat has been successfully initialized and started.
Step 9: Verify that the installation is successful. To do this, open any browser on your device and navigate to the http://localhost:8080 webpage. The following default webpage must be seen:

Note that when Tomcat is running, it uses a significant number of resources on your system. Hence, you must always remember to shut down Tomcat after use. To do this, execute the shutdown.sh shell script in the bin/ folder.

Check that Tomcat has been shut down by navigating to the aforementioned webpage:

Eclipse IDE
Eclipse IDE (Integrated Development Environment) is a popular open-source development tool widely used by software developers for building applications in various programming languages. Eclipse provides a comprehensive set of features and tools that support the entire software development life cycle. Here are some common uses and purposes of Eclipse IDE:
- Java Development: Eclipse is particularly well-known for Java development. It offers robust support for Java programming, including code editing, debugging, testing, and project management. Developers can write and refactor Java code, leverage automated code completion, and use built-in tools for debugging and profiling Java applications.
- Other Programming Languages: While Eclipse is primarily associated with Java, it also supports other programming languages, such as C/C++, Python, PHP, JavaScript, and more. It provides language-specific editors, compilers, and debuggers for these languages, enabling developers to work on diverse projects using their preferred language.
- Plugin Ecosystem: Eclipse has a vast plugin ecosystem that allows developers to extend its functionality. Through the Eclipse Marketplace, developers can install and manage various plugins, including those for specific frameworks, libraries, and tools. These plugins enhance Eclipse’s capabilities for specific programming languages or development environments.
- Project Management: Eclipse provides project management features to organize and manage software development projects. Developers can create, import, and organize projects, manage dependencies, and collaborate with team members using version control systems like Git or Subversion.
- Integrated Debugging: Eclipse offers powerful debugging capabilities, allowing developers to step through their code, inspect variables, set breakpoints, and analyze program execution. The integrated debugger supports various programming languages and provides a unified debugging experience within the IDE.
- Refactoring and Code Analysis: Eclipse includes automated refactoring tools that simplify code maintenance and improve code quality. Developers can use refactoring options to rename variables, extract methods, move code blocks, and more. Eclipse also offers code analysis features to identify potential issues, provide code suggestions, and enforce coding standards.
- User Interface Design: Eclipse provides tools for designing graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for desktop and web applications. It includes visual editors, such as the WindowBuilder tool, which allows developers to create and modify user interfaces using drag-and-drop functionality.
- Testing and Continuous Integration: Eclipse supports various testing frameworks, such as JUnit, for writing and executing unit tests. It integrates with build tools like Apache Maven and Ant for automated building and testing. Eclipse can also be integrated with continuous integration servers like Jenkins to automate the build and test processes.
Overall, Eclipse IDE is a versatile development tool used for various software development tasks, including code editing, debugging, testing, project management, and collaboration. Its extensibility, wide language support, and rich feature set make it a popular choice among developers working on different types of projects. To install this, follow these steps:
Step 1: Navigate to the website https://www.eclipse.org/downloads/ and click on the download button.

Eclipse automatically downloads the appropriate installer for your system.
Step 2: Use the installer to install Eclipse.
Struts 2 Libraries
For this course, we will be using Maven to handle repositories. Maven is a piece of software that automatically downloads JARs and implements them into the application. This means that we do not have to manually install struts2 JARs, or any other JAR for that matter.
In the next article, I am going to discuss the Steps to Creating a Struts 2 Basic Application. Here, in this article, I try to explain Struts 2 Environment Setup and I hope you enjoy this Struts 2 Environment Setup article.
