Back to: MongoDB Tutorials
How MongoDB Works?
In this article, I am going to discuss How MongoDB Works. Please read our previous article where we discussed JSON and BSON File Formats in MongoDB.
What is MongoDB?
MongoDB is an open-source NoSQL database. Here NoSQL database means it does not store data in tables like RDBMS. It is also known as a document-oriented database because all the data stored in MongoDB is in documents not in tables. MongoDB is generally designed to store and manage a large amount of data efficiently. It was developed by MongoDB.Inc under Server-Side Public License (SSPL). It was initially released in 2009 and written in C++. It provides official drivers for most programming languages like C++, C#, Go, Java, Python, Ruby, Scala, Swift, etc. so that you can easily create applications with the help of these programming languages. The main agenda for developing MongoDB is high availability, high performance, can handle a large amount of data efficiently, scalability, etc.
How Does MongoDB Exactly Work?
In this article, we will learn how MongoDB works. What will happen at the backend? So before moving to the working of MongoDB first we understand some terms:
Drivers: Drivers are used to communicating with MongoDB. Mongo DB supports various drivers present in different languages like C++, C#, C, Go, Ruby, Perl, PHP, Node.js, Swift, etc.
MongoShell: MongoDB provide an interactive JavaScript interface known as Mongo Shell. It is used to perform queries, administrative operations, etc.
Storage Engine: Storage engines are used to manage how data is going to store in the memory. MongoDB supports various storage engines. You can use your own storage engine and if you do not want to use your own storage engine then you can use the default storage engine which is the Wired Tiger storage engine. It is the most efficient storage engine provided by MongoDB which does its work like reading, writing, etc. very efficiently.
How MongoDB works?
Let us understand the working of MongoDB with the help of an example. So, suppose we are creating a Node application so we have our application and the data layer.
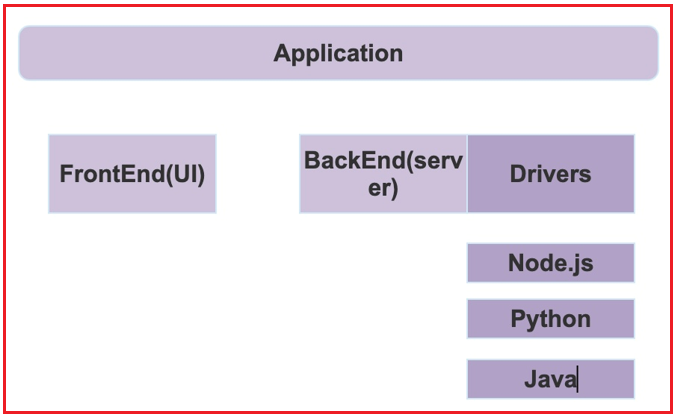
So, the application contains:
- FrontEnd: It is the front end of the application. Here the application can be a single-page application, multiple page application, or a mobile application.
- BackEnd: It is the backend of the application where we have a server and the server-side logic.
- Drivers: Drivers are used to interacting with the MongoDB server. They are used to perform queries with MongoDB.
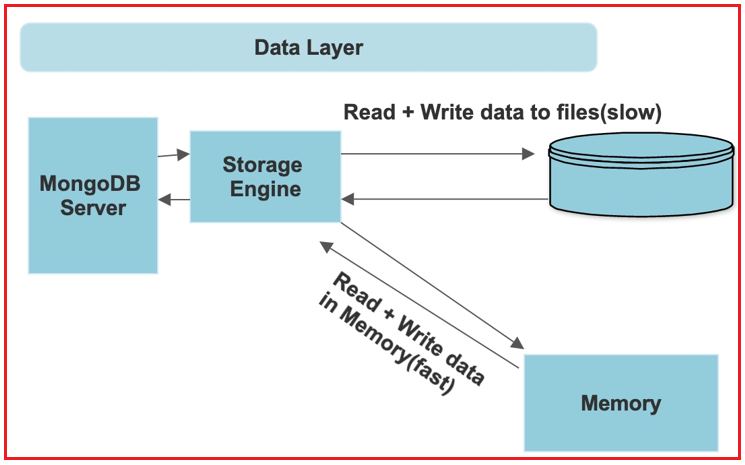
The data layer contains:
- Database: It is used to store files or file systems or we can say data for the application.
- MongoDB Server: It is used to interact with the application and the database.
- Storage engine: MongoDB server does not write directly on the database so it uses a Storage engine that performs read and write operations. By default, MongoDB uses the WiredTiger storage engine but you are allowed to use your own storage engine. It can read or write data both in a database and in memory. The storage engine stores the frequently used data in the memory so that it can easily access the memory.
So, the combined working is:

The divers of the Node.js application interact with the MongoDB server. Now the MongoDB server communicates with the storage engine and the storage engine then reads or writes data in the database. Instead of the drivers, you can also use MongoShell to interact with the MongoDB server. You can use MongoShell as a playground or as an administration. With the help of MongoShell, you can configure something in the MongoDB server as an administrator from your company network, it is like direct access to the MongoDB server through MongoDB shell. So, this is how the whole MongoDB work takes place.
In the next article, I am going to discuss Inserting Documents in MongoDB with Examples. Here, in this article, I try to explain How MongoDB Works. I hope you enjoy this How MongoDB Works article.
Registration Open – Microservices with ASP.NET Core Web API
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 8:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, registration, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
