Back to: Angular Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Routing in Angular Application
In this article, I will discuss Routing in Angular Applications with Examples. Routing is what turns an Angular application into a real “Multi-Page Feel” SPA: the URL changes, and Angular swaps views without full page reloads. In this chapter, we will explore Angular Routing from absolute basics to advanced concepts.
What is Angular Routing?
Routing in Angular allows us to Navigate Between Different Views (Components) without reloading the page. In simple terms:
- The URL Changes
- Angular decides Which Component to show
- The browser Does Not Refresh
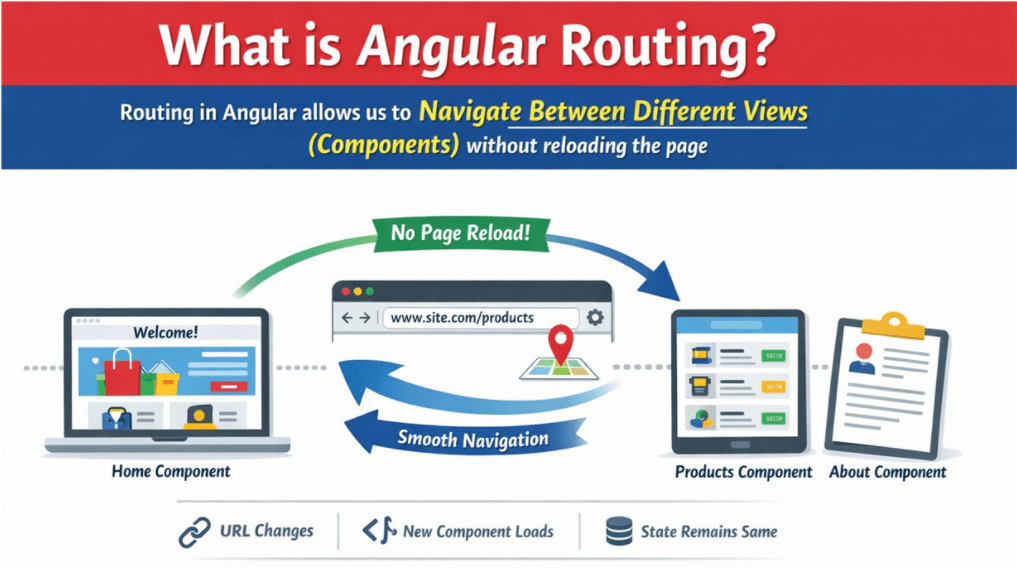
This behaviour is what makes Angular a Single Page Application (SPA) framework. Angular Routing is the mechanism that:
- Maps URL Paths to Components.
- Renders the matched component inside a placeholder (<router-outlet>).
- Supports Nested Routes, Route Parameters, Query Strings, Guards, Lazy Loading, and more
- Keeps the UI in sync with browser History Navigation (Back/Forward)
Why Angular Routing is Important?
Angular Routing solves several real-world problems. They are as follows:
- Enables Multi-Page Navigation in SPAs: Angular Routing allows a single Angular application to behave like a multi-page website by showing different components for different URLs. Even though the browser loads only one HTML page, routing makes it feel like the user is moving between multiple pages, such as Home, Products, and About, without reloading the application.
- Improves User Experience (Fast Navigation): With Angular Routing, only the required component updates rather than reloading the entire page, making navigation fast and smooth. This results in quicker page transitions, no flickering, and a better overall user experience, especially in large applications.
- Helps Build Secure Applications Using Route Guards: Angular Routing provides route guards that control access to pages based on conditions like user authentication or roles. This ensures that unauthorized users cannot access protected routes such as admin dashboards or user-specific pages, making the application more secure.
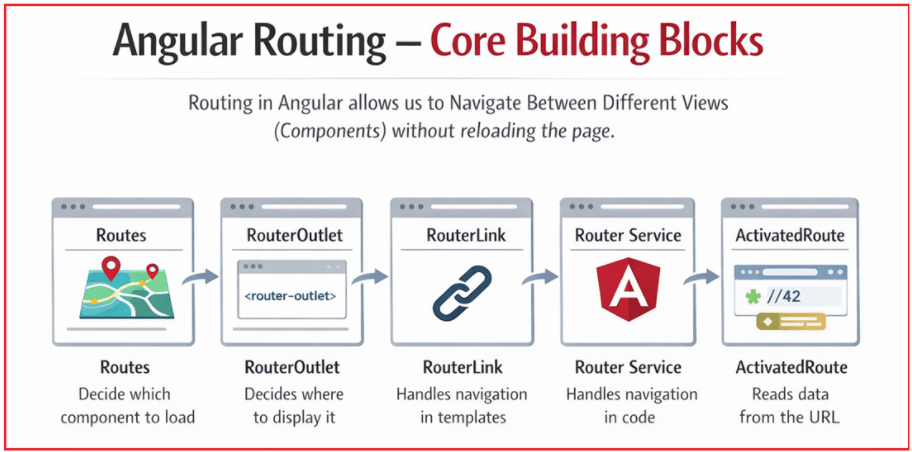
Angular Routing – Core Building Blocks
Angular Routing may look complex at first, but it is built on a few core concepts that work together logically. Each building block has a specific responsibility, and understanding their purpose makes routing simple and predictable in real-world applications. Angular routing revolves around five main concepts:
- Routes: Decide which component to load.
- RouterOutlet: Decides where to display it.
- RouterLink: Handles navigation in templates.
- Router Service: Handles navigation in code.
- ActivatedRoute: Reads data from the URL.
Understanding these clearly makes routing feel simple and predictable.
Routes
Routes define how URLs are mapped to Components in an Angular application. They serve as instructions that tell Angular which component to display when a user navigates to a particular URL. Without routes, Angular would not know which page to show when the URL changes.
Routes are needed because:
- They connect URLs to components
- They enable page-like navigation in SPAs
- They define the structure of the application
- They control redirects and invalid URLs
Syntax
{
path: 'home',
component: HomeComponent
}
Syntax Explanation
- path specifies the URL segment typed in the browser
- component specifies the Angular component to load
- When the path matches, Angular renders the component
Layman Analogy: Routes are like Direction Boards on a Highway. Each board tells you which road to take to reach a specific destination.
RouterOutlet
RouterOutlet is a Placeholder in the HTML Template where Angular dynamically loads the component selected by the route. Routes determine which component to load, but RouterOutlet determines where that component appears on the screen.
RouterOutlet is needed because:
- It provides a display area for routed components.
- It enables dynamic page rendering.
- Routing cannot work without it.
Syntax
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
Syntax Explanation
- router-outlet is a special Angular directive.
- Angular inserts the routed component template here.
- Only one routed component appears at a time.
Layman Analogy: RouterOutlet is like a Photo Frame. The picture changes, but the frame stays in the same place.
RouterLink
RouterLink is used to navigate between routes Without Reloading the Page. It replaces traditional anchor tags and ensures smooth navigation inside a single-page application. It handles navigation inside the HTML Template.
RouterLink is needed because:
- It prevents full-page reloads.
- It keeps the application fast.
- It updates the URL correctly.
Syntax
- <a routerLink=”/home”>Home</a>
- <a [routerLink]=”[‘/student’, 101]”>View Student</a>
Syntax Explanation
- routerLink tells Angular Router to handle navigation
- The URL changes without refreshing the browser
- Angular loads the corresponding component internally
Layman Analogy: RouterLink is like pressing a Lift Button inside a building. You move to another floor (page) without leaving the building (app).
Router Service
The Router service allows navigation from TypeScript code instead of HTML templates. This is required for real-time scenarios where navigation depends on logic or conditions. It handles navigation inside the TypeScript Code.
Router service is needed because:
- Navigation can be triggered programmatically.
- It supports conditional routing.
- It is used after form submission or login.
- It enables controlled redirection.
Syntax
constructor(private router: Router) {}
goToDashboard() {
this.router.navigate(['/dashboard']);
}
Syntax Explanation
- The router is injected using dependency injection.
- navigate() changes the route programmatically.
- The application navigates without reloading.
Layman’s Analogy: Router service is like telling a driver, “Take me to the airport now.“ You’re not clicking a signboard; you’re giving instructions programmatically.
ActivatedRoute
ActivatedRoute provides information about the Currently Active Route, including route parameters, Query Parameters, and Resolved Data. It allows components to understand the data passed through the URL.
ActivatedRoute is needed because:
- Reads Route Parameters like /order/:id
- Reads Query Parameters like /order?status=pending
- It retrieves resolver data.
- It adapts the component based on URL input.
Syntax
constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.route.paramMap.subscribe(params => {
const id = params.get('id');
});
}
Syntax Explanation
- constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute): Injects the ActivatedRoute service, which provides access to information about the currently active route, including route parameters, query parameters, etc.
- ngOnInit(): Executes after the component is initialized and is the correct lifecycle hook method to read routing information. Route values are guaranteed to be available at this stage.
- this.route.paramMap: Represents an observable that contains the route parameters defined in the route configuration.
- subscribe(…): Subscribes to changes in route parameters, allowing the component to react whenever the URL parameter changes without recreating the component instance.
- params: Holds the current set of route parameters as a ParamMap object.
- params.get(‘id’): Retrieves the value of the route parameter named id from the URL. For a URL like /tasks/101, this returns “101”.
Layman Analogy: ActivatedRoute is like reading the address label on a parcel. The parcel arrives at your component, and you read details such as the house number (id) and special instructions (status=pending).
Step 1: Create the Angular Project
In this step, we create a fresh Angular application using the CLI. This sets up the standard project structure (src, app, assets, etc.) and gives us a runnable base application. Once the dev server starts, we confirm everything is working by checking the default page in the browser.
Angular CLI Commands:
- ng new RoutingBasics
- cd RoutingBasics
- ng serve
At this point, you should see the default Angular landing page in the browser.
Step 2: Create the Pages (Components)
Here, we create the main screens that will behave like website pages in our eCommerce UI. Each component represents one page (Home, About, Products, Product Details, Not Found). At this stage, these pages exist as files in the project, but they are not yet connected to any URL.
Angular CLI Commands:
- ng g component pages/home
- ng g component pages/about
- ng g component pages/products
- ng g component pages/product-details
- ng g component pages/not-found
Angular creates folders, TS/HTML/CSS files, and registers each component in the project structure. Now we have pages, but they’re not connected to URLs yet.
Step 3: Add Bootstrap CDN for Professional UI
In this step, we include Bootstrap via CDN links so the entire app can use professional UI components such as the navbar, grid, cards, buttons, badges, and accordion—without writing custom CSS. Adding the JS bundle also enables interactive Bootstrap components such as collapsing navigation.
src/index.html – Bootstrap Setup
This file is the single HTML page that Angular loads. We add Bootstrap CSS in the <head> so styling is available everywhere, and the Bootstrap JS bundle at the end of the <body> so interactive components work. So, open: src/index.html and copy-paste the following code.
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>RoutingBasics</title> <base href="/"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <link rel="icon" type="image/x-icon" href="favicon.ico"> <!-- Bootstrap 5.3.3 CSS (CDN) --> <link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" > </head> <body> <app-root></app-root> <!-- Bootstrap 5.3.3 JS Bundle (CDN) --> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"> </script> </body> </html>
Step 4: Build the Application Shell (Header + Main + Footer)
In this step, we create a consistent layout that looks like a real eCommerce website. The header (navbar) and footer stay visible across all pages, while the middle content changes based on navigation. This makes the app feel like a real site and keeps the UI consistent.
src/app/app.ts – Root Component
This file defines the root standalone component. It imports RouterOutlet to display routed pages, and imports router directives so the navbar links work. Think of it as the “frame” of the application. Open, src/app/app.ts and copy-paste the following code.
// Imports the Component decorator, which is used to define an Angular component
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
// Imports routing-related directives used inside the template
// RouterOutlet: enables <router-outlet> in app.html (this is where routed pages load)
// RouterLink: enables routerLink and [routerLink] on <a> / buttons for navigation without page refresh
// RouterLinkActive: enables routerLinkActive and [routerLinkActiveOptions] to highlight the active menu link
import { RouterLink, RouterLinkActive, RouterOutlet } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
// Defines the custom HTML tag for this component
// <app-root> is the root element of the Angular application used inside index.html
selector: 'app-root',
// Tells Angular that this is a Standalone Component (no AppModule required)
// With standalone, every component explicitly declares what directives/components it uses via `imports`.
standalone: true,
// Registers routing directives that are used in the template (app.html)
// RouterOutlet → Acts as a placeholder where routed components are displayed
// RouterLink → Enables navigation between routes without page reload
// RouterLinkActive → Automatically adds/removes CSS classes for active links
imports: [RouterOutlet, RouterLink, RouterLinkActive],
// External template file for the layout (navbar + footer + router-outlet)
templateUrl: './app.html'
})
export class App {
// This root component acts as the layout shell of the application.
// It usually contains shared UI (header/navbar/footer) and a <router-outlet> for page content.
}
src/app/app.html – Navbar + Routed Content + Footer
This file contains the permanent site layout: Bootstrap navbar at the top, footer at the bottom, and a central placeholder (router-outlet) where the current page renders. Using min-vh-100 and flex layout keeps the header and footer pinned nicely. Open, src/app/app.html and copy-paste the following code.
<div class="min-vh-100 d-flex flex-column bg-light">
<!-- HEADER (Navbar) -->
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-dark bg-dark">
<div class="container">
<!-- routerLink="/home"
When the user clicks the brand/logo, Angular navigates to /home
without reloading the page (client-side navigation). -->
<a class="navbar-brand fw-bold" routerLink="/home">ShopSphere</a>
<!-- This button is purely Bootstrap behavior (mobile menu toggle) -->
<button class="navbar-toggler" type="button"
data-bs-toggle="collapse" data-bs-target="#mainNav"
aria-controls="mainNav" aria-expanded="false" aria-label="Toggle navigation">
<span class="navbar-toggler-icon"></span>
</button>
<div class="collapse navbar-collapse" id="mainNav">
<ul class="navbar-nav ms-auto align-items-lg-center gap-lg-2">
<li class="nav-item">
<!-- routerLink="/home"
Navigates to the Home route when clicked.
routerLinkActive="active"
Adds the Bootstrap "active" class automatically when the current URL
matches this link (used to highlight the active menu item).
[routerLinkActiveOptions]="{ exact: true }"
Ensures the link is active ONLY for the exact /home route.
(Example: it will NOT be active for /home/anything or other partial matches.) -->
<a class="nav-link"
routerLink="/home"
routerLinkActive="active"
[routerLinkActiveOptions]="{ exact: true }">
Home
</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<!-- routerLink="/products"
Navigates to the product listing page.
routerLinkActive="active"
Highlights this link when the current URL starts with /products
(e.g., /products and /products/101 will both mark it active). -->
<a class="nav-link" routerLink="/products" routerLinkActive="active">Shop</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item">
<!-- routerLink="/about"
Navigates to the About page.
routerLinkActive="active"
Highlights the menu item when /about is the active route. -->
<a class="nav-link" routerLink="/about" routerLinkActive="active">About</a>
</li>
<li class="nav-item ms-lg-3">
<!-- routerLink="/products"
Another navigation link that routes to /products.
Still client-side navigation; no page refresh. -->
<a class="btn btn-outline-light btn-sm" routerLink="/products">View Catalog</a>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</nav>
<!-- MAIN CONTENT AREA -->
<main class="container flex-grow-1 d-flex align-items-center my-3">
<div class="w-100">
<!-- router-outlet
This is the placeholder where Angular renders the component
of the currently matched route.
Example:
- URL /home -> Home component renders here
- URL /products -> Products component renders here
- URL /products/101 -> ProductDetails component renders here
- invalid URL -> NotFound component renders here -->
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
</main>
<!-- FOOTER -->
<footer class="border-top bg-white">
<div class="container py-3">
<div class="d-flex flex-column flex-md-row justify-content-between align-items-center gap-2">
<div class="fw-bold">ShopSphere</div>
<div class="text-muted small text-center">
Premium essentials • Fast delivery • Easy returns
</div>
<div class="d-flex gap-3 small">
<!-- Footer links also use routerLink for SPA navigation -->
<a class="text-decoration-none" routerLink="/about">Company</a>
<a class="text-decoration-none" routerLink="/products">Shop</a>
<a class="text-decoration-none" routerLink="/home">Support</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</footer>
</div>
Step 5: Create the Route Table (URL → Page Mapping)
In this step, we define the website’s URL structure. Each path is mapped to one of our page components. This is what makes navigation possible: when the URL changes, Angular determines which component to render in the router-outlet.
src/app/app.routes.ts – Route Definitions
This file contains the route list for the entire app. It defines routes for home, about, product list, product details (with :id), and a wildcard route for invalid URLs. So, Open src/app/app.routes.ts and replace the content with the following code:
// Imports the Routes type, which represents an array of route configuration objects
import { Routes } from '@angular/router';
// Importing page-level (routed) components
// Each of these components represents one navigable "page"
import { Home } from './pages/home/home';
import { About } from './pages/about/about';
import { Products } from './pages/products/products';
import { ProductDetails } from './pages/product-details/product-details';
import { NotFound } from './pages/not-found/not-found';
// This is the "Route Table" (URL → Component mapping).
// Angular checks this list from top to bottom and renders the FIRST matching route
// inside <router-outlet> (in app.html).
export const routes: Routes = [
// Default route (root URL)
// When the user visits "/" (empty path), redirect them to "/home".
{ path: '', component: Home },
// Static routes (fixed URLs)
// Visiting "/home" loads the Home component in <router-outlet>.
{ path: 'home', component: Home },
// Visiting "/about" loads the About component in <router-outlet>.
{ path: 'about', component: About },
// Products list route
// Visiting "/products" shows the product catalog (list page).
// Query strings like "?category=electronics" are NOT part of the route path.
// They are read separately using ActivatedRoute.queryParamMap.
{ path: 'products', component: Products },
// Parameterized route (Dynamic URL)
// Visiting "/products/101" loads ProductDetails and provides "101" as the route parameter "id".
// The ":id" portion is a placeholder that can match any value.
// Inside ProductDetails, we can read it using ActivatedRoute.paramMap (pm.get('id')).
{ path: 'products/:id', component: ProductDetails },
// Wildcard route (404 handler)
// "**" matches ANY URL that didn't match the routes above.
// Must be placed LAST—otherwise it would catch everything and your valid routes would never load.
{ path: '**', component: NotFound }
];
Step 6: Enable Routing in Global Configuration
In this step, we “turn on” the router at application startup. Because your app uses the standalone approach (no AppModule), routing is enabled through providers and configured at bootstrap time.
src/app/app.config.ts – Router Provider Registration
This file registers the router using provideRouter(routes) so Angular can handle URL changes, navigation, redirects, and route matching. Open, src/app/app.config.ts, and copy-paste the following code.
// Imports ApplicationConfig, which is used to configure global providers for a standalone Angular application
import { ApplicationConfig, provideBrowserGlobalErrorListeners } from '@angular/core';
// Imports provideRouter, which sets up Angular's routing system
import { provideRouter } from '@angular/router';
// Imports the application's route definitions
// This contains the URL → Component mapping
import { routes } from './app.routes';
// Global application configuration object
// This replaces the traditional AppModule in standalone Angular apps
// This file defines the application's global configuration for a Standalone Angular app.
// The config is passed to bootstrapApplication(...) in main.ts.
export const appConfig: ApplicationConfig = {
providers: [
// Registers Angular’s global error handling in the browser runtime.
// If an error occurs during change detection, template rendering, or event handling,
// Angular can report it consistently (useful for debugging and logging).
provideBrowserGlobalErrorListeners(),
// Enables Angular Routing for the whole application.
// - It registers the Router service and all routing directives (routerLink, router-outlet, etc.)
// - It tells Angular to use the route table defined in `routes`
// - After this, Angular can:
// • match URLs to components
// • handle redirects
// • support browser back/forward buttons
// • update the URL without page reload (SPA navigation)
provideRouter(routes)
]
};
src/main.ts – Application Startup
This file bootstraps the root component (App) and applies appConfig. This is the entry point that starts the whole Angular application. Open, src/main.ts and copy-paste the following code.
// Imports the bootstrapApplication function,
// which is responsible for starting (bootstrapping)
// a standalone Angular application in the browser
import { bootstrapApplication } from '@angular/platform-browser';
// Imports the global application configuration (providers, routing, error handling, etc.)
import { appConfig } from './app/app.config';
// Imports the root component of the application
// This is the first component Angular creates and renders
import { App } from './app/app';
// Bootstraps (starts) the Angular application
// This is the entry point of the Angular application.
// Angular starts running from this file.
// - App → Root component of the application
// - appConfig → Global configuration (routing, providers)
bootstrapApplication(App, appConfig)
// Global error handling during application startup
// Catches errors that occur while bootstrapping the app,
// such as:
// - Dependency injection failures
// - Configuration issues
// - Runtime errors during initialization
//
// Logging the error helps with debugging and diagnostics.
.catch((err) => console.error(err));
Step 7: Build the Home Page
In this step, we create a compact, professional home page, similar to an eCommerce landing screen. It contains marketing content, a featured offer, and call-to-action buttons that navigate to the Products page.
src/app/pages/home/home.ts – Home Component Setup
This file defines the Home component and imports RouterLink because the Home page contains navigation links and query parameters (category filtering). Without importing RouterLink, bindings like [queryParams] won’t work. So, open, src/app/pages/home/home.ts, and copy-paste the following code.
// Imports the Component decorator to define an Angular component
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
// Imports RouterLink directive, which allows
// this component’s template to perform route-based navigation
import { RouterLink } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
// Registers routing directives used in the template (home.html).
// RouterLink enables navigation to other routes
// without triggering a full page reload.
imports: [RouterLink],
// External template where routerLink / queryParams are used.
templateUrl: './home.html',
styleUrl: './home.css',
})
export class Home {
// This component represents the "Home" page of the application.
// It is activated when the URL matches /home.
// The router creates and destroys this component automatically
// based on navigation, without reloading the browser.
}
src/app/pages/home/home.html – Home Page UI
This file contains the professional landing layout using Bootstrap grid, badges, cards, and CTA (Call to Action) buttons. All styling is done using only Bootstrap classes. So, open src/app/pages/home/home.html, and copy-paste the following code.
<div class="bg-white border rounded-3 shadow-sm p-4 p-md-5">
<div class="row align-items-center g-4">
<div class="col-lg-7">
<span class="badge text-bg-dark mb-3">Limited Time Offer</span>
<h1 class="fw-bold display-6 mb-2">Smart essentials for modern work</h1>
<p class="text-muted fs-5 mb-4">
Shop premium accessories and productivity gear with fast delivery and easy returns.
</p>
<div class="d-flex flex-column flex-sm-row gap-2">
<!-- Routing: routerLink="/products"
Navigates to the Products route (path: 'products') without refreshing the page.
Angular updates the URL to /products and renders the Products component in <router-outlet>. -->
<a class="btn btn-primary btn-lg" routerLink="/products">Shop Now</a>
<!-- Routing: routerLink + query params
routerLink="/products" navigates to the Products page.
[queryParams] appends query string values to the URL, producing:
/products?category=electronics
Note: Query params are NOT part of the route path itself.
They are "extra data" usually used for filtering/sorting.
In Products component, we will read this using ActivatedRoute.queryParamMap. -->
<a class="btn btn-outline-secondary btn-lg"
routerLink="/products"
[queryParams]="{ category: 'electronics' }">
Electronics
</a>
</div>
<div class="d-flex flex-wrap gap-2 mt-4">
<span class="badge text-bg-light border">Free delivery over ₹999</span>
<span class="badge text-bg-light border">7-day returns</span>
<span class="badge text-bg-light border">Secure payments</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-5">
<div class="border rounded-3 bg-light p-4">
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between align-items-start">
<div>
<div class="text-muted small">Featured Product</div>
<div class="fw-semibold">Workstation Bundle</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Keyboard • Mouse • USB-C Hub</div>
</div>
<span class="badge text-bg-success">25% OFF</span>
</div>
<div class="display-2 text-center my-3">🛒</div>
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center">
<div>
<div class="fs-4 fw-bold mb-0">₹4,499</div>
<div class="text-muted small text-decoration-line-through">₹5,999</div>
</div>
<!-- Routing: another routerLink to /products
This is the same client-side navigation as above, just styled differently.
Clicking it routes the user to the Products component inside <router-outlet>. -->
<a class="btn btn-dark" routerLink="/products">View Deals</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="row g-2 mt-3">
<div class="col-4">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-2 text-center bg-white">
<div class="fw-semibold">4.6★</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Ratings</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-4">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-2 text-center bg-white">
<div class="fw-semibold">24h</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Dispatch</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-4">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-2 text-center bg-white">
<div class="fw-semibold">7d</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Returns</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Step 8: Build the About Page
In this step, we create a professional About page that looks like a brand/company profile. It provides a clean presentation using Bootstrap cards and a “snapshot” section, making it feel like a real eCommerce company page.
src/app/pages/about/about.ts – About Component Setup
This file defines the About component. If you include router links (such as “Browse Products” or “Back to Home”), you should import RouterLink here as well. So, open src/app/pages/about/about.ts, and copy-paste the following code.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterLink } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-about',
// RouterLink enables SPA navigation:
// - Updates the URL without a full page refresh
// - Loads the matched route component inside <router-outlet>
imports: [RouterLink],
templateUrl: './about.html',
styleUrl: './about.css',
})
export class About {
// This component is displayed when the route table matches:
// { path: 'about', component: About }
}
src/app/pages/about/about.html – About Page UI
This file contains a well-structured About page UI using Bootstrap grid, borders, and layout utilities to look like a real website page. So, open src/app/pages/about/about.html, and copy-paste the following code.
<div class="bg-white border rounded-3 shadow-sm p-4 p-md-5">
<div class="row g-4 align-items-center">
<div class="col-lg-7">
<h2 class="fw-bold mb-2">About ShopSphere</h2>
<p class="text-muted fs-5 mb-4">
We’re a modern eCommerce experience focused on quality essentials, transparent pricing,
and reliable delivery.
</p>
<div class="row g-3">
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-3 h-100">
<div class="fw-semibold">Curated Products</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Only items we’d recommend for daily use.</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-3 h-100">
<div class="fw-semibold">Fast Delivery</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Quick dispatch with consistent packaging.</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-3 h-100">
<div class="fw-semibold">Easy Returns</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Simple return process and fast refunds.</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-3 h-100">
<div class="fw-semibold">Secure Payments</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Industry-standard security practices.</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="d-flex flex-column flex-sm-row gap-2 mt-4">
<!-- Routing: routerLink="/products"
Navigates the user to the Products page (path: 'products') without reloading the page.
Angular updates the URL to /products and renders the Products component inside <router-outlet>. -->
<a class="btn btn-primary" routerLink="/products">Browse Products</a>
<!-- Routing: routerLink="/home"
Navigates back to the Home page (path: 'home') via client-side routing.
This is SPA navigation (no full-page refresh). -->
<a class="btn btn-outline-secondary" routerLink="/home">Back to Home</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-lg-5">
<div class="border rounded-3 bg-light p-4">
<h5 class="fw-semibold mb-3">Company Snapshot</h5>
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between py-2 border-bottom">
<span class="text-muted">Founded</span>
<span class="fw-semibold">2026</span>
</div>
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between py-2 border-bottom">
<span class="text-muted">Delivery</span>
<span class="fw-semibold">Pan-India</span>
</div>
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between py-2 border-bottom">
<span class="text-muted">Returns</span>
<span class="fw-semibold">7 Days</span>
</div>
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between py-2">
<span class="text-muted">Support</span>
<span class="fw-semibold">Email & Chat</span>
</div>
<div class="alert alert-light border mt-3 mb-0" role="alert">
We focus on essentials that are practical, durable, and well-rated.
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Step 9: Build the Products Page (Catalog + Search + Filter)
In this step, we build a realistic product catalog page. It shows multiple products in cards and supports searching and filtering. It reads the category filter from the query string and updates the UI accordingly.
src/app/pages/products/products.ts – Product Catalog Logic
This file stores a hardcoded product list, reads the query-string category from the URL, filters products by search/category, and provides navigation actions. It also contains helper functions like currency formatting and discount calculation. So, open src/app/pages/products/products.ts, and copy-paste the following code.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { ActivatedRoute, Router, RouterLink } from '@angular/router';
type Product = {
id: number;
name: string;
brand: string;
price: number;
mrp: number;
rating: number;
stock: 'In Stock' | 'Limited' | 'Out of Stock';
category: 'electronics' | 'accessories' | 'wfh' | 'new';
badge?: 'Bestseller' | 'New' | 'Top Rated';
};
@Component({
selector: 'app-products',
standalone: true,
// Template needs routerLink
// The products.html template uses router directives such as:
// <a [routerLink]="['/products', p.id]">View</a>
// So we must import RouterLink in this Standalone component,
// otherwise Angular will not recognize routerLink in the template.
imports: [RouterLink],
templateUrl: './products.html'
})
export class Products {
// This value is driven by the query string:
// Example URL: /products?category=electronics
// category = "electronics"
category = '';
search = '';
products: Product[] = [
{ id: 101, name: 'Mechanical Keyboard', brand: 'KeyPro', price: 2499, mrp: 2999, rating: 4.6, stock: 'In Stock', category: 'electronics', badge: 'Bestseller' },
{ id: 102, name: 'Wireless Mouse', brand: 'SwiftTech', price: 999, mrp: 1299, rating: 4.4, stock: 'Limited', category: 'electronics', badge: 'Top Rated' },
{ id: 103, name: '27-inch Monitor', brand: 'ViewMax', price: 12999, mrp: 14999, rating: 4.5, stock: 'In Stock', category: 'electronics' },
{ id: 104, name: 'USB-C Hub (6-in-1)', brand: 'Portify', price: 1499, mrp: 1999, rating: 4.2, stock: 'In Stock', category: 'accessories', badge: 'New' },
{ id: 105, name: 'Ergonomic Chair Cushion', brand: 'ComfortCo', price: 1199, mrp: 1599, rating: 4.3, stock: 'In Stock', category: 'wfh' },
{ id: 106, name: 'Fast Charger 65W', brand: 'VoltOne', price: 1799, mrp: 2199, rating: 4.4, stock: 'Out of Stock', category: 'accessories' },
{ id: 107, name: 'Laptop Stand (Aluminium)', brand: 'LiftDesk', price: 1299, mrp: 1699, rating: 4.1, stock: 'In Stock', category: 'wfh', badge: 'Bestseller' },
{ id: 108, name: 'Braided USB-C Cable', brand: 'CableX', price: 399, mrp: 599, rating: 4.0, stock: 'In Stock', category: 'new', badge: 'New' }
];
filtered: Product[] = [];
// Routing-related injections:
// ActivatedRoute -> read information FROM the current URL (here: query string)
// Router -> navigate / update the URL programmatically from code
constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute, private router: Router) {
// Reading query params
// queryParamMap emits whenever the query string changes while staying on the same route.
// Example:
// /products?category=electronics -> category = electronics
// /products?category=wfh -> category = wfh
// This is why we subscribe (URL can change without reloading the component).
this.route.queryParamMap.subscribe((qpm) => {
this.category = qpm.get('category') ?? '';
this.applyFilters();
});
// Initial load: filter once so page shows products immediately.
this.applyFilters();
}
setCategory(category: string) {
// Programmatic navigation + query params
// Updates the URL to /products?category=<value>
// This does NOT reload the page; it only changes the URL and triggers queryParamMap subscription.
this.router.navigate(['/products'], { queryParams: { category } });
}
clearCategory() {
// Programmatic navigation (remove query string)
// Updates URL back to /products (no query params).
this.router.navigate(['/products']);
}
onSearchChange(value: string) {
this.search = value;
this.applyFilters();
}
private applyFilters() {
const cat = this.category.trim().toLowerCase();
const q = this.search.trim().toLowerCase();
this.filtered = this.products.filter(p => {
const matchesCategory = !cat || p.category === cat;
const matchesSearch = !q || (p.name.toLowerCase().includes(q) || p.brand.toLowerCase().includes(q));
return matchesCategory && matchesSearch;
});
}
discountPercent(mrp: number, price: number) {
return Math.round(((mrp - price) / mrp) * 100);
}
}
src/app/pages/products/products.html – Product Grid UI
This file renders the product catalog in a professional Bootstrap layout. So, open src/app/pages/products/products.html, and copy-paste the following code.
<div class="bg-white border rounded-3 p-3 p-md-4 shadow-sm">
<div class="d-flex flex-column flex-lg-row justify-content-between align-items-lg-center gap-3 mb-3">
<div>
<h2 class="fw-bold mb-1">Shop</h2>
<div class="text-muted">Find the best deals on essentials and accessories.</div>
</div>
<div class="d-flex flex-column flex-sm-row gap-2">
<div class="input-group">
<span class="input-group-text">🔎</span>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
placeholder="Search products or brands..."
(input)="onSearchChange(($any($event.target)).value)">
</div>
<div class="btn-group">
<!-- These buttons call setCategory(...), which uses Router.navigate(...)
to update the URL query string (e.g., /products?category=electronics). -->
<button class="btn btn-outline-dark" (click)="setCategory('electronics')">Electronics</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-dark" (click)="setCategory('accessories')">Accessories</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-dark" (click)="setCategory('wfh')">WFH</button>
<button class="btn btn-outline-dark" (click)="setCategory('new')">New</button>
</div>
<!-- clearCategory() navigates to /products (removes query params),
so the URL is cleaned and the filter state resets. -->
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary" (click)="clearCategory()">Clear</button>
</div>
</div>
@if (category) {
<div class="alert alert-info d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center" role="alert">
<div>
Category:
<span class="badge text-bg-dark">{{ category }}</span>
</div>
<!-- Removes query string from the URL by navigating to /products.
This is still client-side navigation (no page refresh). -->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-dark" (click)="clearCategory()">Remove</button>
</div>
}
<div class="row g-3">
@for (p of filtered; track p.id) {
<div class="col-sm-6 col-lg-3">
<div class="card h-100 shadow-sm">
<div class="card-body">
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between align-items-start gap-2">
<div>
<div class="text-muted small">{{ p.brand }}</div>
<div class="fw-semibold">{{ p.name }}</div>
</div>
@if (p.badge) {
<span class="badge text-bg-dark">{{ p.badge }}</span>
}
</div>
<div class="mt-2 text-muted small">
Rating: <span class="fw-semibold">{{ p.rating }}</span>/5
</div>
<div class="mt-3">
<div class="d-flex align-items-baseline gap-2">
<div class="fs-5 fw-bold">₹{{ p.price }}</div>
<div class="text-muted text-decoration-line-through small">₹{{ p.mrp }}</div>
</div>
<span class="badge text-bg-success">
{{ discountPercent(p.mrp, p.price) }}% OFF
</span>
</div>
<div class="mt-3 d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center">
<span class="badge"
[class.text-bg-success]="p.stock === 'In Stock'"
[class.text-bg-warning]="p.stock === 'Limited'"
[class.text-bg-danger]="p.stock === 'Out of Stock'">
{{ p.stock }}
</span>
<!--
[routerLink]="['/products', p.id]" navigates to a parameterized route:
/products/101, /products/102, etc.
This matches our route table:
{ path: 'products/:id', component: ProductDetails }
Angular updates the URL and loads ProductDetails inside <router-outlet>
without reloading the browser page. -->
<a class="btn btn-outline-primary btn-sm"
[routerLink]="['/products', p.id]">
View
</a>
</div>
</div>
<div class="card-footer bg-white">
<small class="text-muted">Free delivery over ₹999</small>
</div>
</div>
</div>
}
</div>
@if (filtered.length === 0) {
<div class="alert alert-warning mt-3 mb-0" role="alert">
No products found. Try clearing filters or searching a different keyword.
</div>
}
</div>
Step 10: Build Product Details Page
In this step, we show a professional product details layout. It displays a single product based on the URL parameter (id). To avoid scrolling, additional information (highlights/specs) is placed in a Bootstrap accordion, collapsed by default.
src/app/pages/product-details/product-details.ts – Product Details
This file reads the id parameter from the URL, finds the matching product from a hardcoded catalog, and exposes it to the UI. It also provides formatting helpers and a back navigation function. So, Open, src/app/pages/product-details/product-details.ts, and copy-paste the following code.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
// Routing-related imports:
// ActivatedRoute → used to READ route parameters from the URL
// Router → used to NAVIGATE programmatically
// RouterLink → used in the template for navigation links
import { ActivatedRoute, Router, RouterLink } from '@angular/router';
type ProductInfo = {
id: number;
name: string;
brand: string;
price: number;
mrp: number;
rating: number;
inStock: boolean;
shortDescription: string;
highlights: string[];
specs: { label: string; value: string }[];
};
@Component({
selector: 'app-product-details',
standalone: true,
// Template needs routerLink:
// product-details.html contains router links such as:
// <a routerLink="/products">Shop</a>
// or any routerLink-based navigation.
// Since this is a Standalone Component, we must import RouterLink explicitly,
// otherwise Angular won't recognize routerLink in the template.
imports: [RouterLink],
templateUrl: './product-details.html'
})
export class ProductDetails {
// This "id" comes from the route parameter in the URL:
// Route pattern: /products/:id
// Example URL: /products/101 --> id = 101
id: number | null = null;
product: ProductInfo | null = null;
private catalog: ProductInfo[] = [
{
id: 101,
brand: 'KeyPro',
name: 'Mechanical Keyboard',
price: 2499,
mrp: 2999,
rating: 4.6,
inStock: true,
shortDescription: 'Tactile, durable, and comfortable for daily work and gaming.',
highlights: ['Hot-swappable switches', 'Compact layout', 'Durable keycaps'],
specs: [
{ label: 'Connectivity', value: 'Wired USB' },
{ label: 'Switch Type', value: 'Tactile' },
{ label: 'Warranty', value: '12 Months' }
]
},
{
id: 102,
brand: 'SwiftTech',
name: 'Wireless Mouse',
price: 999,
mrp: 1299,
rating: 4.4,
inStock: true,
shortDescription: 'Lightweight ergonomic mouse with smooth tracking.',
highlights: ['Ergonomic grip', 'Precision sensor', 'Battery efficient'],
specs: [
{ label: 'Connectivity', value: '2.4GHz Wireless' },
{ label: 'Battery', value: 'Up to 12 months' },
{ label: 'Warranty', value: '12 Months' }
]
},
{
id: 103,
brand: 'ViewMax',
name: '27-inch Monitor',
price: 12999,
mrp: 14999,
rating: 4.5,
inStock: false,
shortDescription: 'Large screen for productivity and entertainment.',
highlights: ['Large display', 'Sharp visuals', 'Multi-task friendly'],
specs: [
{ label: 'Size', value: '27-inch' },
{ label: 'Resolution', value: 'Full HD (Demo)' },
{ label: 'Warranty', value: '24 Months' }
]
}
];
// ActivatedRoute -> used to READ data from the current route (route param :id, query params, etc.)
// Router -> used to NAVIGATE programmatically from code
constructor(private route: ActivatedRoute, private router: Router) {}
ngOnInit() {
// Reading the route parameter (:id)
// This subscribes to paramMap so it will also work if the user navigates from
// /products/101 to /products/102 while staying on the same component instance.
//
// Route table link:
// { path: 'products/:id', component: ProductDetails }
this.route.paramMap.subscribe((pm) => {
const value = pm.get('id'); // reads ":id" from /products/:id
this.id = value ? Number(value) : null;
// Use the route param to decide which product to show
this.product = this.catalog.find(x => x.id === this.id) ?? null;
});
}
backToProducts() {
// Programmatic navigation
// Navigates back to the products list route (path: 'products') without reloading the page.
this.router.navigate(['/products']);
}
discountPercent(mrp: number, price: number) {
// Not routing-related: calculation helper.
return Math.round(((mrp - price) / mrp) * 100);
}
}
src/app/pages/product-details/product-details.html – Product Details UI
This file builds a product page UI with image placeholder, pricing, actions, delivery badges, and a collapsible accordion for additional details. It uses Bootstrap only and modern Angular syntax (@if, @for). So, open, src/app/pages/product-details/product-details.html, and copy-paste the following code.
@if (product) {
<div class="bg-white border rounded-3 shadow-sm p-3 p-md-4">
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between align-items-start gap-2 mb-3">
<div class="me-2">
<div class="text-muted small">{{ product.brand }}</div>
<h2 class="fw-bold mb-1">{{ product.name }}</h2>
<div class="d-flex align-items-center flex-wrap gap-2">
<span class="badge text-bg-success">★ {{ product.rating }}</span>
@if (product.inStock) {
<span class="badge text-bg-success">In Stock</span>
} @else {
<span class="badge text-bg-danger">Out of Stock</span>
}
<span class="badge text-bg-light border">Free delivery over ₹999</span>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Programmatic navigation:
This button calls backToProducts() in the component (.ts),
and inside that method we do:
this.router.navigate(['/products']);
So clicking Back changes the route to /products and loads the Products component
in <router-outlet> without refreshing the browser page. -->
<button class="btn btn-outline-secondary btn-sm" type="button" (click)="backToProducts()">
Back
</button>
</div>
<div class="row g-3 align-items-center">
<div class="col-md-4">
<div class="border rounded-3 bg-light text-center p-3">
<div class="text-muted small mb-1">Product Image</div>
<div class="display-3 mb-0">📦</div>
</div>
<div class="d-flex gap-2 mt-2">
<span class="badge text-bg-dark">Bestseller</span>
<span class="badge text-bg-light border">Secure packaging</span>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-md-8">
<p class="text-muted mb-2">{{ product.shortDescription }}</p>
<div class="d-flex align-items-baseline flex-wrap gap-2 mb-2">
<div class="fs-2 fw-bold">₹{{ product.price }}</div>
<div class="text-muted text-decoration-line-through">₹{{ product.mrp }}</div>
<span class="badge text-bg-success">{{ discountPercent(product.mrp, product.price) }}% OFF</span>
</div>
<div class="d-flex flex-column flex-sm-row gap-2 mb-2">
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="button" [disabled]="!product.inStock">
Add to Cart
</button>
<button class="btn btn-success" type="button" [disabled]="!product.inStock">
Buy Now
</button>
<button class="btn btn-secondary" type="button">
Wishlist
</button>
</div>
<div class="row g-2 mt-1">
<div class="col-6 col-lg-3">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-2 text-center">
<div class="fw-semibold">7 Days</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Returns</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-6 col-lg-3">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-2 text-center">
<div class="fw-semibold">24h</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Dispatch</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-6 col-lg-3">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-2 text-center">
<div class="fw-semibold">COD</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Available</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="col-6 col-lg-3">
<div class="border rounded-3 p-2 text-center">
<div class="fw-semibold">Secure</div>
<div class="text-muted small">Payments</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="accordion mt-3" id="detailsAccordion">
<div class="accordion-item">
<h2 class="accordion-header" id="headingOne">
<button class="accordion-button collapsed" type="button"
data-bs-toggle="collapse" data-bs-target="#collapseOne"
aria-expanded="false" aria-controls="collapseOne">
Product Details
</button>
</h2>
<div id="collapseOne" class="accordion-collapse collapse"
aria-labelledby="headingOne" data-bs-parent="#detailsAccordion">
<div class="accordion-body">
<div class="row g-3">
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="fw-semibold mb-2">Highlights</div>
<ul class="text-muted mb-0">
@for (h of product.highlights; track h) {
<li>{{ h }}</li>
}
</ul>
</div>
<div class="col-md-6">
<div class="fw-semibold mb-2">Specifications</div>
<div class="table-responsive">
<table class="table table-sm table-bordered align-middle mb-0">
<tbody>
@for (s of product.specs; track s.label) {
<tr>
<td class="text-muted" style="width: 40%;">{{ s.label }}</td>
<td class="fw-semibold">{{ s.value }}</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
} @else {
<div class="alert alert-danger mb-0" role="alert">
Product not found.
<!-- routerLink="/products"
If the product id in the URL is invalid (e.g., /products/999),
we show this message and provide a routerLink back to /products.
Clicking "Shop" navigates to /products without refreshing the page. -->
Go back to <a class="alert-link" routerLink="/products">Shop</a>.
</div>
}
Step 11: Build the Not Found Page
In this step, we handle invalid URLs. If the user enters a route that doesn’t exist, we display a clean, professional 404 page with links to return to Home or Products.
src/app/pages/not-found/not-found.ts – NotFound Component Setup
This file defines the 404 component. If the template contains routerLink buttons, import RouterLink here as well. Open, src/app/pages/not-found/not-found.ts, and copy-paste the following code
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-not-found',
templateUrl: './not-found.html',
styleUrl: './not-found.css',
})
export class NotFound {
}
src/app/pages/not-found/not-found.html – 404 UI
This file contains a clean Bootstrap 404 page using a centered card layout and navigation buttons. So, open, src/app/pages/not-found/not-found.html, and copy-paste the following code
<div class="bg-white border rounded-3 p-4 p-md-5 shadow-sm text-center">
<div class="display-1 fw-bold">404</div>
<h2 class="fw-bold mb-2">We can’t find that page</h2>
<p class="text-muted mb-4">
The page you’re looking for may have been removed, renamed, or is temporarily unavailable.
</p>
<div class="d-flex flex-column flex-sm-row justify-content-center gap-2">
<!-- routerLink="/home"
Navigates to the Home route (path: 'home') using Angular Router.
This is SPA navigation: URL changes to /home, and the Home component
loads inside <router-outlet> without a full page refresh. -->
<a class="btn btn-primary" routerLink="/home">Go to Home</a>
<!-- routerLink="/products"
Navigates to the Products list route (path: 'products').
URL becomes /products and Angular renders the Products component
inside <router-outlet> (no browser reload). -->
<a class="btn btn-outline-dark" routerLink="/products">Shop Products</a>
</div>
<div class="mt-4 text-muted small">
Need help? Visit
<!-- routerLink="/about"
Navigates to the About route (path: 'about') through Angular routing.
Useful for guiding users from the 404 page to a valid page. -->
<a class="text-decoration-none" routerLink="/about">About</a>.
</div>
</div>
Angular Routing is a core feature that enables single-page applications to behave like multi-page websites without reloading the browser. By mapping URLs to components, rendering them in the router-outlet, and navigating with routerLink or the Router service, Angular provides fast, smooth, and structured navigation. Understanding these fundamentals makes it easy to build scalable, user-friendly, and real-world Angular applications with predictable navigation behaviour.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group

While creating routing i got error “unknown -flat”. after i refered Angularjs site i got the below cmd. now its working…
ng generate module app-routing –flat –module=app
Very Nice