Back to: Angular Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Local Storage vs Session Storage in Angular
When building Angular applications, we often need a simple way to store data on the client side, such as user preferences, login flags, or temporary form data. Two very common options provided by the browser itself are Local Storage and Session Storage. Angular does not reinvent these; it simply uses the browser APIs in a clean and structured way. In this post, we will understand what Local Storage and Session Storage are, how they differ, and how to use them in Angular.
What Is Browser Storage?
Browser Storage refers to a set of features provided by web browsers that allow web applications to store data on the client side. This data is saved in the user’s browser and can be accessed using JavaScript without involving a backend server.
Browser storage is primarily used to improve performance, reduce unnecessary API calls, and enhance the user experience by storing application state or preferences locally.
Key Points to Remember:
- Data is stored as key–value pairs
- Data is stored on the client (browser)
- No database or server interaction is required
- Data is accessible using JavaScript
- Browser storage is limited in size and meant for small amounts of data
The data is stored as strings, so objects must be converted to JSON before saving. There are two commonly used storage options:
- Local Storage
- Session Storage
Both are part of the Web Storage API and work in all modern browsers.
What Is Local Storage?
Local Storage is a type of browser storage that allows data to be stored persistently in the browser. The data remains available even after the browser is closed and reopened, until it is explicitly removed by the application or the user. This makes Local Storage suitable for information that should survive page refreshes and browser restarts.
Key Points to Remember:
- Data persists even after a browser restart
- Data is shared across all tabs of the same website
- Data is stored as strings
- Data remains until manually removed
- Best for long-term, non-sensitive data
Syntax to Use Local Storage in Angular
Angular does not provide a special API for Local Storage. Instead, it uses the browser’s built-in Local Storage API directly inside components or services.
Basic Syntax
- localStorage.setItem(key, value) → Stores data
- localStorage.getItem(key) → Reads data
- localStorage.removeItem(key) → Removes specific data
- localStorage.clear() → Removes all stored data
Syntax Explanation:
- key: A string used to identify the stored value
- value: Must be a string. Objects must be converted using JSON.stringify()
- Data is automatically saved in the browser’s storage area
When to Use Local Storage in Angular?
Use Local Storage when the data should remain available even after the browser is closed and reopened. This type of storage is suitable for data that improves user experience over time and does not change frequently.
- Theme preference (dark/light mode)
- Selected language
- Remember me flag
- User interface settings
- Cached static dropdown data
What Is Session Storage?
Session Storage is another type of browser storage designed to store data only for the current browser session. Once the browser tab or window is closed, the stored data is automatically removed. Session Storage is useful when data is required temporarily and should not persist beyond the current session.
Key Points to Remember:
- Data exists only during the current session
- Data is cleared when the tab or browser closes
- Data is not shared across tabs
- Data is stored as strings
- Best for short-lived application data
Syntax to Use Session Storage in Angular
Session Storage also uses the browser’s built-in API, similar to Local Storage.
Basic Syntax
- sessionStorage.setItem(key, value) → Stores data
- sessionStorage.getItem(key) → Reads data
- sessionStorage.removeItem(key) → Removes specific data
- sessionStorage.clear() → Clears session data
Syntax Explanation:
- key: Identifies the stored data
- value: Must be a string
- Data is tied strictly to the current browser session
When to Use Session Storage in Angular?
Session Storage is best used when the data is required only during a single user session and should be discarded automatically afterward. This helps prevent stale data and improves security for temporary information.
- Multi-step form values
- Checkout, or registration progress
- Temporary filters or sorting
- One-time session flags
- OTP or verification steps in progress
Real-Time Angular Application: Local Storage vs Session Storage
The best way to understand Local Storage and Session Storage is to see them in action in a small, real-time Angular application. The following app will clearly show what data goes into Local Storage, what goes into Session Storage, and why. Let’s use an eCommerce example: Cart, Coupon, and Checkout Progress.
- Local Storage (Remember even after browser restart) → Cart items and wishlist.
- Session Storage (Only for current tab/session) → Checkout step and temporary coupon message.
We will build a simple single-page demo with Bootstrap cards:
- Add Products to cart (saved to Local Storage)
- Cart Summary (reload the page, and it stays)
- Checkout Steps (Session Storage, resets when tab closes)
Step 1: Createan Angular Project
- ng new Ecommerce-Storage
- cd Ecommerce-Storage
- ng serve
Step 2: Add Bootstrap CDN
Open, src/index.html and copy-paste the following code.
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Ecommerce Storage</title>
<base href="/">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<link rel="icon" type="image/x-icon" href="favicon.ico">
<link
href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css"
rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<app-root></app-root>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.3/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Step 3: Modify Root Component
Open src/app/app.ts and copy-paste the following code.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
// Product model used in the product catalog
type Product = {
id: number;
name: string;
price: number;
};
// CartItem = Product + quantity
// This means a cart item contains product details + qty
type CartItem = Product & {
qty: number;
};
// Checkout steps are limited to only 3 values: 1, 2, or 3
type CheckoutStep = 1 | 2 | 3;
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
standalone: true,
imports: [FormsModule], // Needed because we use [(ngModel)] in HTML
templateUrl: './app.html',
})
export class App {
// Storage Keys
// These are the "names" under which we save data inside browser storage
private readonly CART_KEY = 'ec_cart_items'; // Local Storage key for cart data
private readonly STEP_KEY = 'ec_checkout_step'; // Session Storage key for checkout step
private readonly COUPON_KEY = 'ec_coupon_code'; // Session Storage key for coupon code
// Product Catalog (Sample Data)
// This is just hardcoded data; in real apps it comes from API/DB
products: Product[] = [
{ id: 1, name: 'Bluetooth Headphones', price: 1999 },
{ id: 2, name: 'Wireless Mouse', price: 699 },
{ id: 3, name: 'USB-C Charger', price: 899 }
];
// Cart (Local Storage)
// Cart should remain even after browser is closed and reopened
cart: CartItem[] = [];
// Checkout (Session Storage)
// Checkout step and coupon should be temporary for the current tab only
checkoutStep: CheckoutStep = 1;
couponCode = '';
// Message shown to user (for feedback)
message = '';
constructor() {
// When the page loads, read any previously saved data from storage
this.loadCartFromLocalStorage(); // Load persistent cart
this.loadCheckoutFromSessionStorage(); // Load session-based step & coupon
}
// CART (LOCAL STORAGE) - persists after restart
addToCart(product: Product): void {
// Check if the product already exists in the cart
const existing = this.cart.find(x => x.id === product.id);
if (existing) {
// If already present, just increase its quantity by 1
existing.qty += 1;
} else {
// If not present, add it with initial quantity = 1
this.cart.push({ ...product, qty: 1 });
}
// Save updated cart to Local Storage
this.saveCartToLocalStorage();
// Show feedback message
this.message = `Added "${product.name}" to cart (saved in Local Storage).`;
}
increaseQty(item: CartItem): void {
// Increase quantity
item.qty += 1;
// Save the updated cart
this.saveCartToLocalStorage();
}
decreaseQty(item: CartItem): void {
if (item.qty > 1) {
// If quantity is more than 1, decrease it
item.qty -= 1;
} else {
// If quantity is 1 and user clicks "-", remove the item completely
this.cart = this.cart.filter(x => x.id !== item.id);
}
// Save updated cart
this.saveCartToLocalStorage();
}
removeItem(item: CartItem): void {
// Remove the item completely from cart
this.cart = this.cart.filter(x => x.id !== item.id);
// Save updated cart
this.saveCartToLocalStorage();
// Feedback message
this.message = `Removed "${item.name}" from cart.`;
}
clearCart(): void {
// Remove cart data from Local Storage completely
localStorage.removeItem(this.CART_KEY);
// Clear in-memory cart array
this.cart = [];
// Feedback message
this.message = 'Cart cleared from Local Storage.';
}
private saveCartToLocalStorage(): void {
// Local Storage can store ONLY string values
// So we convert the cart array into a JSON string
localStorage.setItem(this.CART_KEY, JSON.stringify(this.cart));
}
private loadCartFromLocalStorage(): void {
// Read the cart JSON string from Local Storage
const raw = localStorage.getItem(this.CART_KEY);
// If nothing is saved yet, raw will be null, so exit
if (!raw) return;
// Convert JSON string back into CartItem[]
// We use safeJsonParse so the app doesn't crash if JSON is invalid
const parsed = this.safeJsonParse<CartItem[]>(raw);
// If parsing is successful, assign it to cart
if (parsed && Array.isArray(parsed)) {
this.cart = parsed;
}
}
// CHECKOUT (SESSION STORAGE) - tab-only
goToStep(step: CheckoutStep): void {
// Update the current step (in memory)
this.checkoutStep = step;
// Store step in Session Storage (tab-only)
sessionStorage.setItem(this.STEP_KEY, String(step));
}
applyCoupon(): void {
// Trim spaces and convert to uppercase (so "flat10" becomes "FLAT10")
this.couponCode = this.couponCode.trim().toUpperCase();
// If coupon is empty, show message and stop
if (!this.couponCode) {
this.message = 'Please enter a coupon code.';
return;
}
// Save coupon code in Session Storage
// This will survive page refresh but not tab close
sessionStorage.setItem(this.COUPON_KEY, this.couponCode);
// Feedback message
this.message = `Coupon "${this.couponCode}" applied for this session (Session Storage).`;
}
clearCoupon(): void {
// Remove coupon from Session Storage
sessionStorage.removeItem(this.COUPON_KEY);
// Clear in-memory value
this.couponCode = '';
// Feedback message
this.message = 'Coupon cleared from Session Storage.';
}
resetCheckoutSession(): void {
// Clear session-based values (step and coupon)
sessionStorage.removeItem(this.STEP_KEY);
sessionStorage.removeItem(this.COUPON_KEY);
// Reset in-memory values
this.checkoutStep = 1;
this.couponCode = '';
// Feedback message
this.message = 'Checkout session reset (Session Storage cleared).';
}
private loadCheckoutFromSessionStorage(): void {
// Read saved step and coupon from Session Storage
const stepRaw = sessionStorage.getItem(this.STEP_KEY);
const couponRaw = sessionStorage.getItem(this.COUPON_KEY);
// Convert stepRaw (string) to number, default to 1 if not found
const stepNum = stepRaw ? Number(stepRaw) : 1;
// Validate that stepNum is only 1, 2 or 3
if (stepNum === 1 || stepNum === 2 || stepNum === 3) {
this.checkoutStep = stepNum as CheckoutStep;
}
// If coupon exists, restore it
if (couponRaw) {
this.couponCode = couponRaw;
}
}
// CALCULATIONS (simple)
get cartCount(): number {
// Total cart items = sum of qty of each item
return this.cart.reduce((sum, x) => sum + x.qty, 0);
}
get subtotal(): number {
// Subtotal = sum of (price * qty) for all cart items
return this.cart.reduce((sum, x) => sum + x.price * x.qty, 0);
}
get discount(): number {
// Demo rule:
// If coupon is FLAT10 -> 10% discount
if (this.couponCode === 'FLAT10') {
return Math.round(this.subtotal * 0.10);
}
return 0;
}
get total(): number {
// Total = Subtotal - Discount
return this.subtotal - this.discount;
}
// Helper: Safe JSON parsing
private safeJsonParse<T>(value: string): T | null {
// JSON.parse can throw an error if the string is not valid JSON.
// Example: if user manually edited Local Storage and broke the JSON.
// This method prevents the app from crashing.
try {
return JSON.parse(value) as T;
} catch {
return null;
}
}
}
Step 4: Modify Root Template
Open src/app/app.html and copy-paste the following code.
<div class="container py-4">
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center mb-3">
<div>
<h2 class="mb-1">eCommerce Storage Demo</h2>
</div>
<!-- Shows total number of items in the cart -->
<div class="badge text-bg-dark fs-6">
Cart Items: {{ cartCount }}
</div>
</div>
<!-- Show message box only when 'message' has some value -->
@if (message) {
<div class="alert alert-info d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center">
<div>{{ message }}</div>
<!-- Clears the message when user clicks Close -->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-secondary" (click)="message = ''">Close</button>
</div>
}
<div class="row g-3">
<!--Product Catalog -->
<div class="col-12 col-lg-4">
<div class="card shadow-sm">
<!-- Card header -->
<div class="card-header bg-primary text-white">
<strong>Product Catalog</strong>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<!-- Loop through all products and show them one by one -->
@for (p of products; track p.id) {
<div class="border rounded p-3 mb-2">
<div class="fw-semibold">{{ p.name }}</div>
<div class="text-muted">₹ {{ p.price }}</div>
<!-- Adds this product to cart (saved in Local Storage) -->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-success mt-2" (click)="addToCart(p)">
Add to Cart
</button>
</div>
}
</div>
<div class="card-footer text-muted">
Add products and refresh page → cart remains (Local Storage).
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Cart -->
<div class="col-12 col-lg-4">
<div class="card shadow-sm">
<div class="card-header bg-success text-white">
<strong>Cart (Local Storage)</strong>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<!-- If cart is empty, show a simple message -->
@if (cart.length === 0) {
<div class="text-muted">Cart is empty. Add products from catalog.</div>
} @else {
<!-- If cart has items, show each item one by one -->
@for (item of cart; track item.id) {
<div class="border rounded p-3 mb-2">
<div class="fw-semibold">{{ item.name }}</div>
<!-- Shows price and quantity -->
<div class="text-muted">₹ {{ item.price }} × {{ item.qty }}</div>
<div class="d-flex gap-2 mt-2 flex-wrap">
<!-- Decrease quantity -->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-primary" (click)="decreaseQty(item)">-</button>
<!-- Increase quantity -->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-primary" (click)="increaseQty(item)">+</button>
<!-- Remove item from cart completely -->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-danger" (click)="removeItem(item)">Remove</button>
</div>
</div>
}
}
</div>
<div class="card-footer">
<!-- Clear cart button is disabled when cart is empty -->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-danger" (click)="clearCart()" [disabled]="cart.length === 0">
Clear Cart
</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Checkout -->
<div class="col-12 col-lg-4">
<div class="card shadow-sm">
<div class="card-header bg-warning">
<strong>Checkout (Session Storage)</strong>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<!-- Displays the currently selected checkout step -->
<div class="mb-2">
<span class="fw-semibold">Current Step:</span>
<span class="badge text-bg-secondary ms-2">Step {{ checkoutStep }}</span>
</div>
<!-- Step buttons (highlight the active step) -->
<div class="btn-group w-100 mb-3">
<!-- If step is 1, make it dark (highlight), otherwise outline -->
<button
class="btn"
[class.btn-dark]="checkoutStep === 1"
[class.btn-outline-dark]="checkoutStep !== 1"
(click)="goToStep(1)"
>
Address
</button>
<!-- If step is 2, highlight it -->
<button
class="btn"
[class.btn-dark]="checkoutStep === 2"
[class.btn-outline-dark]="checkoutStep !== 2"
(click)="goToStep(2)"
>
Payment
</button>
<!-- If step is 3, highlight it -->
<button
class="btn"
[class.btn-dark]="checkoutStep === 3"
[class.btn-outline-dark]="checkoutStep !== 3"
(click)="goToStep(3)"
>
Review
</button>
</div>
<!-- Show different message based on which step is selected -->
@if (checkoutStep === 1) {
<div class="alert alert-light border">
<strong>Address Step</strong><br />
This step number is stored in <b>Session Storage</b>.
</div>
} @else if (checkoutStep === 2) {
<div class="alert alert-light border">
<strong>Payment Step</strong><br />
Close the tab → step resets (session ends).
</div>
} @else {
<div class="alert alert-light border">
<strong>Review Step</strong><br />
Review totals and coupon for this tab session.
</div>
}
<hr />
<!-- Coupon section (stored in Session Storage) -->
<div class="mb-2 fw-semibold">Coupon (Session Storage)</div>
<div class="input-group mb-2">
<!-- ngModel binds input value to couponCode -->
<input class="form-control" [(ngModel)]="couponCode" placeholder="Try: FLAT10" />
<!-- Apply coupon -->
<button class="btn btn-outline-primary" (click)="applyCoupon()">Apply</button>
</div>
<!-- Show applied coupon UI only if couponCode has value -->
@if (couponCode) {
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between align-items-center mb-2">
<div class="text-muted">Applied: <b>{{ couponCode }}</b></div>
<!-- Clear coupon -->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-danger" (click)="clearCoupon()">Clear</button>
</div>
}
<!-- Bill summary section -->
<div class="border rounded p-3">
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between">
<span>Subtotal</span>
<span>₹ {{ subtotal }}</span>
</div>
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between">
<span>Discount</span>
<span>₹ {{ discount }}</span>
</div>
<hr class="my-2" />
<div class="d-flex justify-content-between fw-semibold">
<span>Total</span>
<span>₹ {{ total }}</span>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Clears checkout step + coupon from Session Storage -->
<button class="btn btn-sm btn-outline-danger w-100 mt-3" (click)="resetCheckoutSession()">
Reset Checkout Session
</button>
</div>
<div class="card-footer text-muted">
Open app in NEW tab → coupon/step won't carry over (Session Storage).
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
How to test quickly:
- Add to cart → Refresh → cart stays (Local Storage).
- Change checkout step or apply coupon → Refresh → stays in the same tab.
- Open new tab → checkout step/coupon resets (Session Storage).
- Close tab and reopen → step/coupon resets (Session Storage).
For a better understanding, please look at the following image:
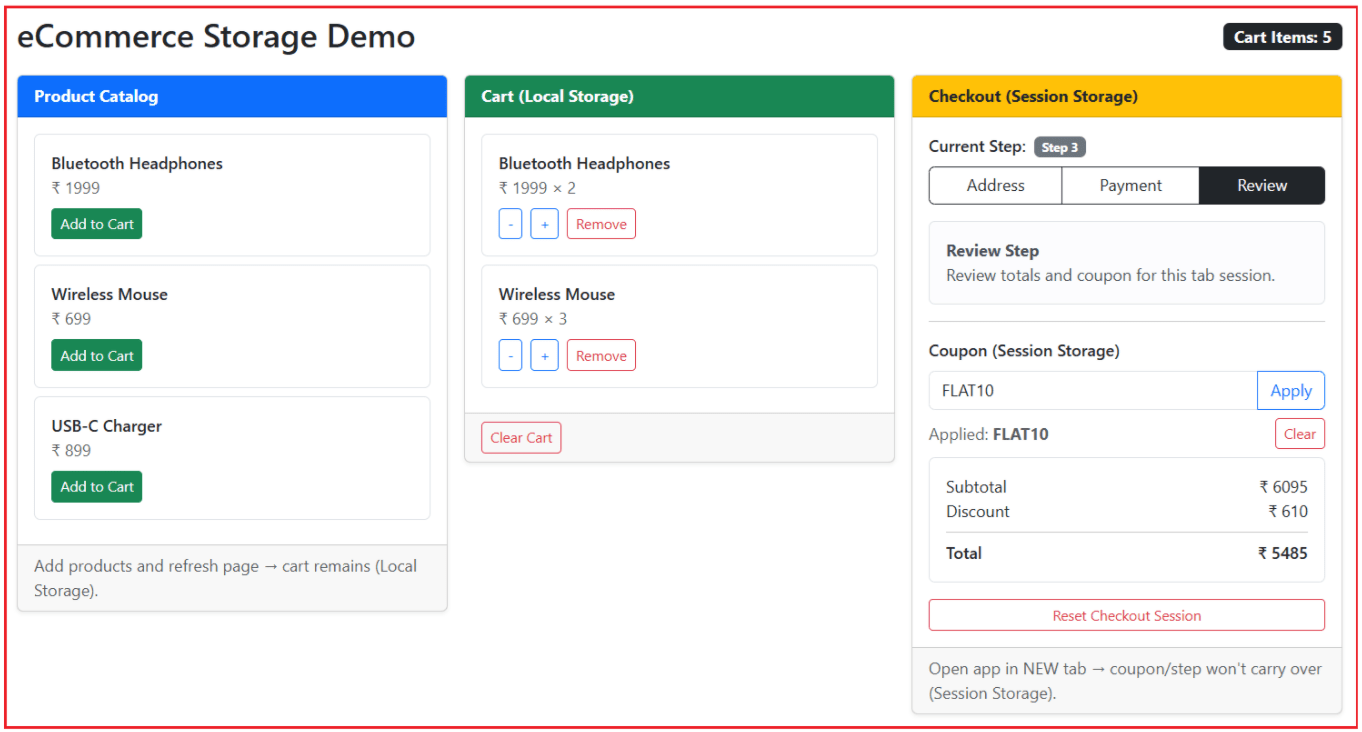
How to check Local Storage and Session Storage in Google Chrome DevTools?
You can view both Local Storage and Session Storage directly inside Chrome DevTools under the Application tab. This is the easiest way to confirm that your Angular app is really saving data. Please follow the steps below:
Step-1: Open Chrome DevTools
- Open your Angular app in Chrome.
- Open DevTools using any one method:
-
- Right-click anywhere on the page → Inspect
- Press F12
- Press Ctrl + Shift + I (Windows / Linux)
- Press Cmd + Option + I (Mac)
-
Step-2: Go to the Application tab
- In DevTools, click Application.
- If you don’t see it:
-
- Click the >> (More tabs) and select Application
-
Step-3: Find the Storage section
- On the left side panel of the Application tab, you will see a section called Storage.
- Under Storage, expand:
-
- Local Storage
- Session Storage
-
For a better understanding, please look at the following image:
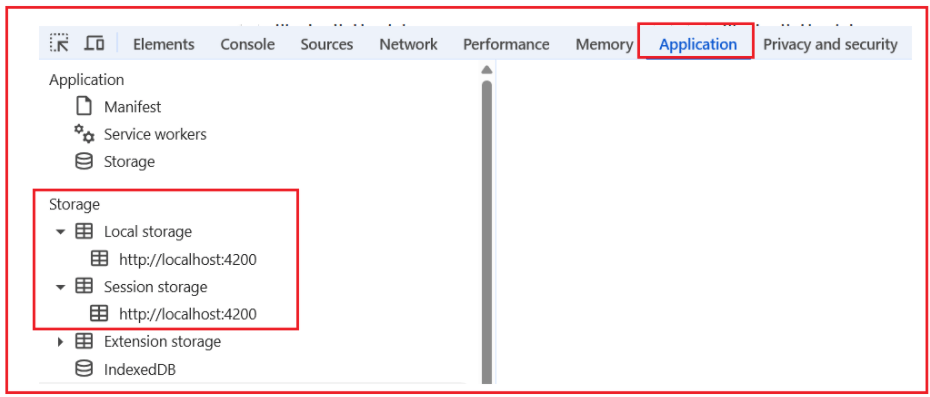
Step-4: Check Local Storage
- Click Local Storage → then click your site (example: http://localhost:4200)
- On the right side, you will see a table with:
-
- Key
- Value
-
- For your app, you should see keys like:
-
- ec_cart_items (cart saved permanently)
-
For a better understanding, please look at the following image:

Step-5: Check Session Storage
- Click Session Storage → then click your site (example: http://localhost:4200)
- You will see Key and Value again.
- For your app, you should see keys like:
-
- ec_checkout_step
- ec_coupon_code
-
For a better understanding, please look at the following image:

Local Storage vs Session Storage in Angular
Local Storage and Session Storage are often confused because they use similar syntax, but their behaviour is very different. The main difference lies in how long the data survives and how it is shared across browser tabs.
- Local Storage is persistent; Session Storage is temporary.
- Local Storage survives browser restart; Session Storage does not.
- Local Storage is shared across tabs; Session Storage is tab-specific.
- Both store data as strings.
- Both are part of the browser, not Angular.
Local Storage is used for persistent browser data, while Session Storage is used for temporary, session-specific data in Angular applications.
Conclusion
Local Storage and Session Storage are simple yet powerful tools for managing client-side data in Angular applications. They allow developers to store and retrieve information quickly without depending on a server. The key is choosing the right storage type based on data lifespan and purpose. Understanding these concepts theoretically helps you make better architectural decisions before implementing them in real-world Angular applications.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
