Back to: Angular Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Data Binding in Angular (Template ↔ Class Communication)
In this article, I will discuss Data Binding in Angular Applications. Please read our previous article, which discusses HTML Attributes VS DOM Properties. Whenever you want to develop any data-driven web application, then as a developer, you need to keep the focus on two important things, i.e., Data and the UI (User Interface), and it is more important for us to find an efficient way to bind them (Data and UI) together. Again, the data can arrive in several chunks, and we need to update the user interface with the latest or updated data.
This chapter focuses entirely on Data Binding in Angular—the mechanism that enables a component class and its template to communicate. Data binding is what makes Angular applications Dynamic and Interactive. By the end of this chapter, you will clearly understand:
- What is data binding?
- Why does data binding exist?
- What are all the data binding techniques supported by Angular?
- Why does Angular provide different types of bindings?
What Is Data Binding in Angular?
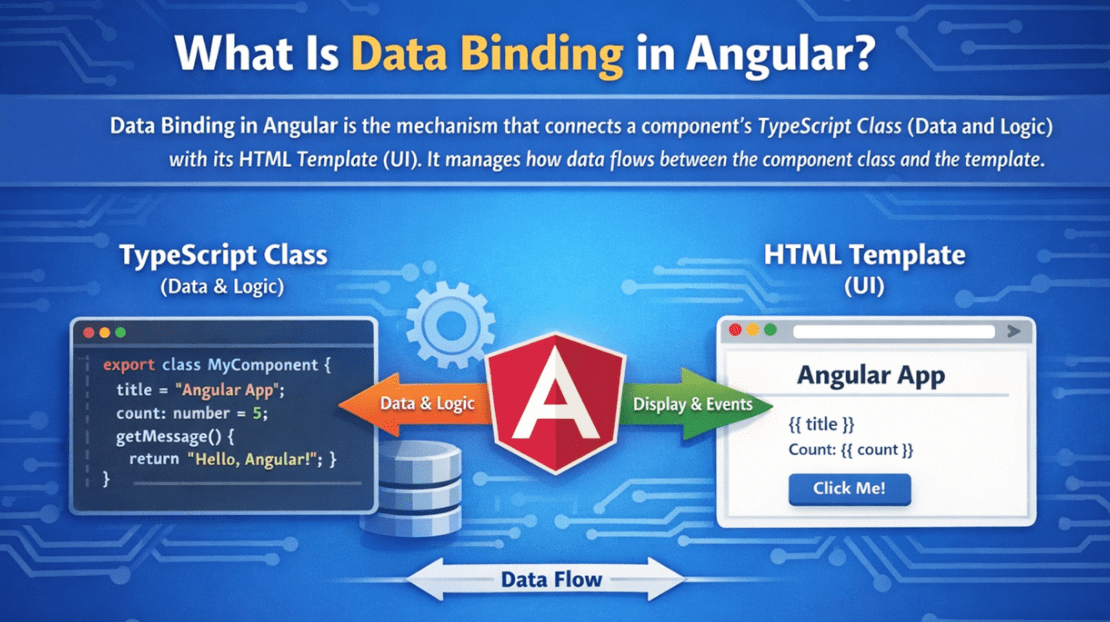
Data Binding in Angular is the mechanism that establishes a connection between a component’s TypeScript Class (Data and Logic) and its HTML Template (User Interface). It defines how data flows between the component and the view.
Using Data Binding, Angular ensures that:
- The template can read values from the component class.
- User actions in the template can be sent back to the component.
- The UI automatically updates when component data changes.
- Components react to user interactions without direct DOM manipulation.
Angular internally manages this synchronization through its Change Detection Mechanism, eliminating the need to manually update HTML elements with JavaScript.
Why Data Binding in Angular?
Data binding in Angular simplifies the development of interactive, dynamic user interfaces.
Without data binding, developers must manually:
- Access DOM Elements
- Update UI Values
- Handle User Events
- Maintain UI and Data Consistency
For a better understanding, please look at the following image:
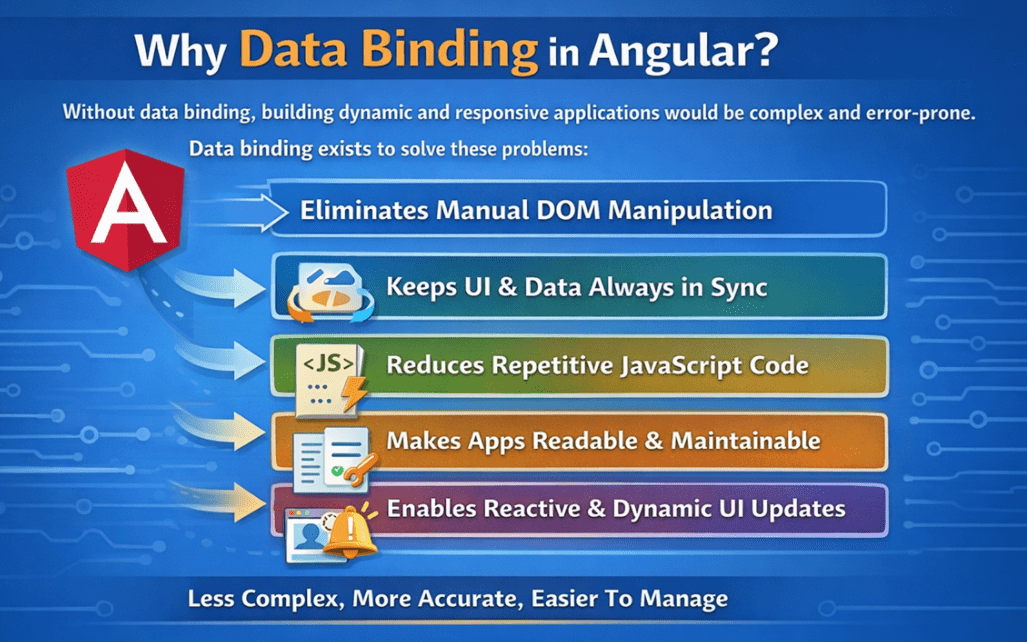
Data binding solves these problems by automatically synchronizing the Component Data and the UI. It:
- Eliminates Manual DOM Manipulation: Data binding eliminates the need for JavaScript code such as getElementById() or innerHTML to update the UI. Angular automatically updates the DOM whenever the component data changes.
- Keeps the UI and Data always in sync: If the component value changes, the screen updates; if the user changes the input (in two-way binding), the component value updates, and both stay consistent without extra code.
- Reduces Repetitive JavaScript Code: Without data binding, developers must write repeated code to read values, update elements, and handle events. Data binding handles these tasks automatically, reducing repetitive and redundant logic.
- Improves Code Readability and Maintainability: Your UI logic stays clean and predictable because templates show what is bound to what, and changes are made in one place (component), making future updates easier.
- Enables Reactive and Dynamic UI Updates: With data binding, the UI reacts instantly to data changes such as API responses, user actions, or timers. This allows applications to feel dynamic and responsive without manual refresh logic.
Thus, data binding allows developers to declare relationships between data and UI rather than manually managing updates.
Types of Data Binding in Angular:
Angular provides two types of data binding: One-Way and Two-Way, which define how data flows between a component (TypeScript class) and its template (HTML view). These binding mechanisms help Angular maintain synchronization between application data and the user interface in a structured and predictable manner. To better understand and remember, please have a look at the following image, which describes the classification of Data Binding.

One-Way Data Binding
In one-way data binding, data flows in only one direction. This flow can occur either from the component to the template or from the template to the component, but not both simultaneously.
- Component to Template: The component supplies data, and the template displays it.
- Template to Component: User actions in the template (such as clicks or input events) send data back to the component.
Because data moves in a single direction, one-way binding provides:
- Better control over data flow
- Makes application behaviour more predictable
- Easier debugging and performance optimization
This approach is ideal when the UI should reflect data changes without automatically modifying the component state.
Two-Way Data Binding
In two-way data binding, data flows in both directions simultaneously between the component and the template. This means:
- When component data changes, the UI updates automatically.
- When the user modifies the UI (e.g., typing in an input field), the component’s data is updated instantly.
Two-way data binding automatically synchronizes the model and the view, eliminating the need for explicit event handling and manual updates. This type of binding is most commonly used in form controls, where user input and component data must always stay in sync.
What Are the Different Data Binding Techniques in Angular?
Angular supports:
- Interpolation for rendering text
- Property binding for DOM properties
- Attribute binding for non-DOM attributes
- Class binding for conditional CSS classes
- Style binding for dynamic inline styles
- Event binding for user interactions
- Two-way binding for synchronized input handling
Each technique exists to ensure:
- Correct DOM updates
- Better performance
- Clear developer intent
- Predictable application behaviour
Why Do We Have Different Data Bindings in Angular?

Angular provides multiple data-binding syntaxes because the HTML and the browser DOM are not uniform systems. Different parts of the UI behave differently at a technical level, and treating them all the same would lead to incorrect updates, performance issues, and unpredictable behaviour.
For example:
- HTML attributes and DOM properties are fundamentally different and are processed by the browser at different stages.
- CSS classes and inline styles must be applied conditionally and independently to reflect visual state changes.
- Events flow from the UI to the application logic, which is the opposite direction of data rendering.
- Form inputs require continuous, bidirectional synchronization between user input and application state.
Because of these differences, Angular does not rely on a single, generic binding approach.
Purpose of Each Binding Technique
Each data binding technique exists to solve a specific problem:
- Interpolation is ideal for rendering dynamic text content.
- Property Binding targets real DOM properties that control element behaviour.
- Attribute Binding handles cases where required values are not exposed as DOM properties.
- Class and Style Bindings manage visual state without hardcoding presentation logic.
- Event Binding captures user actions and forwards them to the component.
- Two-way Binding simplifies form handling by automatically synchronizing user input and component state.
These bindings are not interchangeable alternatives; they are precision tools, each optimized for correctness, clarity, and performance.
Data binding is a core concept in Angular that connects application data with the user interface. It simplifies UI development by automating synchronization between components and templates. By providing multiple binding techniques, Angular ensures efficient DOM updates, clearer code structure, and better application scalability.
We will discuss each of the above bindings in Angular applications with examples from our next articles. In the next article, I will discuss Interpolation in Angular Applications. In this article, I aim to provide an overview of Data Binding in Angular Applications. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, questions, or comments about this article.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group

can i download the material in pdf format
your way of explaining the concept is very effective and great. Thank you.
very nice explanation sir
If you want to understand Data Binding in Angular in the simplest and most practical way, then don’t miss this video! In this session, I explain how Angular connects your component and template using real examples, clean visuals, and step-by-step guidance.
🎥 Watch the complete video here: https://youtu.be/mJlKNE71Rdg
This video will help you clearly understand:
✔️ How one-way and two-way data binding work
✔️ When to use interpolation, property, attribute, class, and style binding
✔️ How Angular updates the UI automatically
✔️ How template ↔ component communication actually happens
If you’re learning Angular or preparing for interviews, this video will make the concepts crystal clear.
👉 Click the link above and start learning now!