Back to: Angular Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Angular Interpolation Data Binding with Examples
In this article, I will discuss Angular Interpolation with Examples. In every real-world web application, displaying dynamic data on the screen is a fundamental requirement. Whether it is showing a logged-in user’s name, displaying product prices, calculating order totals, or updating payment status, the user interface must always remain in sync with the application data. Angular solves this problem using Data Binding.
Among all data binding techniques provided by Angular, Interpolation Data Binding is the simplest, most commonly used, and the first one every Angular developer should master. It allows us to display component data directly inside HTML templates in a clean, readable, and reactive manner. Reactive means the UI automatically responds to changes in data or events, without requiring explicit instructions to update.
In this chapter, you will learn
- What is Angular Interpolation Data Binding?
- Why is it needed?
- How does it work internally?
- How to use it correctly?
- A complete real-world example.
What is Angular Interpolation Data Binding?
Angular Interpolation is a One-Way Data-Binding technique that allows data to flow from the Component Class to the HTML Template. Its primary purpose is to display dynamic values inside the user interface, allowing the UI to reflect application data without manual DOM manipulation.
With interpolation, Angular takes values defined in the component and renders them directly within the template, making the UI responsive to data changes. For a visual understanding of this data flow, refer to the diagram shown above. For a better understanding, please have a look at the following image.
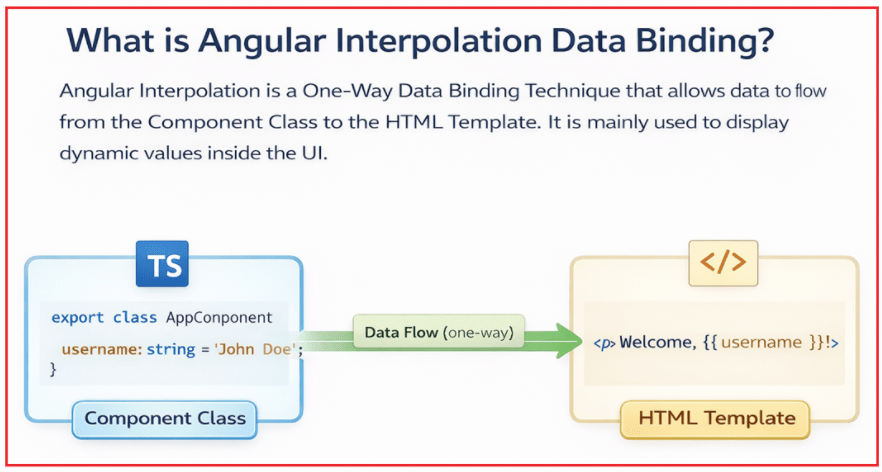
How Angular Interpolation Works?
Angular interpolation uses double curly braces ({{ }}) to embed expressions directly inside HTML content. The expression placed inside the braces is evaluated by Angular in the context of the component class, and the resulting value is converted to a string and rendered in the browser. Angular interpolation uses the following syntax to display dynamic data in the template:
- {{ expression }}
This syntax allows Angular to embed evaluated values directly into the HTML.
Explanation of the Syntax
- {{ }} (Double Curly Braces): These are known as the interpolation operator. They tell Angular that the content inside should be treated as an expression and dynamically evaluated.
- Expression: The expression inside the braces is evaluated in the context of the component class. It can reference:
-
- Component properties
- Simple calculations
- Conditional expressions
- Lightweight method calls
-
- Rendering the Result: After evaluation, Angular converts the result into a string representation and inserts it into the DOM at that location in the template.
How It Behaves at Runtime
Whenever the component data changes, Angular automatically re-evaluates the interpolation expression and updates the UI value. This ensures that the view always reflects the latest application state. In simple words, Angular interpolation connects application data with UI text. It allows the UI to react automatically to data changes, making the interface dynamic, reactive, and always in sync with the application state.
Key Characteristics of Angular Interpolation
Angular interpolation has the following important characteristics:
- One-way Data Flow: Data moves only from the Component Class to the View.
- Read-only Binding: The template can display data but cannot modify it.
- Ideal for text and calculations: Best suited for rendering strings, numbers, and calculated values.
- Automatic UI updates: The UI updates automatically whenever the component data changes.
These characteristics make interpolation safe, predictable, and easy to reason about.
Why Do We Need Angular Interpolation Binding?
Without Angular interpolation, HTML pages would be static, meaning they could not reflect changes in application data. However, modern applications are highly dynamic—user information, prices, order details, notifications, and statuses constantly change based on user actions and backend responses. Angular interpolation solves this problem by allowing dynamic data to be displayed declaratively inside templates.
Real-World Problems Solved by Interpolation
Angular interpolation is commonly used for:
- Displaying user-specific information after login
- Showing dynamic prices, totals, and item counts
- Performing lightweight inline calculations in templates
- Displaying conditional status or informational messages
- Keeping the UI automatically synchronized with application data
All of this is achieved with minimal code and maximum clarity, making interpolation one of the most important data binding techniques for Angular beginners.
What can be used inside Angular Interpolation expressions?
Inside Interpolation, Angular allows:
- Component Class Properties
- Mathematical Expressions
- Ternary Operators
- Lightweight Method Calls of Component Class
Examples Include:
- Displaying a Property Value
- Performing Inline Calculations
- Showing Conditional Text
- Formatting Display Messages
What should NOT be used inside Angular Interpolation?
Interpolation expressions should Not Contain Complex or Heavy Computation Logic. The following are not allowed or not recommended:
- Assignments
- Loops
- Complex Business Logic
- Heavy Computations
Why should interpolation expressions be simple?
Angular evaluates interpolation expressions every time change detection runs. If expressions are complex or slow:
- Performance can degrade
- UI responsiveness may suffer
- Debugging becomes harder
Therefore, the best practice is to keep interpolation expressions:
- Simple
- Fast
- Free from heavy logic
Complex business rules should be handled in the component class rather than in the template.
Creating a New Angular Application to Understand Angular Interpolation
Let us now understand Angular Interpolation Data Binding by creating a new Angular application using Visual Studio Code. We will understand this using a real e-commerce order summary screen, which makes the concepts easy to relate to real applications.
- Showing Customer + Order Details
- Showing Confirmation Messages (Fixed + Dynamic)
- Showing Calculations (Total Amount)
- Showing Conditional Labels (Premium/Regular, Paid/Pending)
- Showing Business-Rule Results (Final Payable Amount, Order Status)
Step 1: Create a New Angular App
Open Visual Studio Code, then open the Terminal, and execute the following command:
- ng new interpolation-demo
During project creation, Angular CLI asks a few questions. You should select the following options:
- Which stylesheet system would you like to use? → CSS
- Do you want to enable Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and Static Site Generation (SSG/Prerendering)? → No
- Which AI tools do you want to configure with Angular best practices? → None
Why these choices?
- CSS keeps the example simple and beginner-friendly.
- SSR/SSG is disabled because interpolation concepts do not depend on server rendering.
- No AI tools keep focus purely on Angular fundamentals.
At this point, Angular creates a fully working application structure for you.
Step 2: Navigate and Run the App
Now move into the project folder and start the development server. So, please execute the following command in the Terminal.
- cd interpolation-demo
- ng serve
Open your browser and navigate to:
- http://localhost:4200
You should see the default Angular welcome screen. This confirms that your Angular application is running correctly.
Step 3: Update the App Component (app.ts)
Now, let us modify the root component to include real-time data that we want to display using Angular interpolation. Please modify the app.ts file as follows. The following code is self-explanatory; please read the comment lines for better understanding.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
/*
Root component of the Angular application.
This component represents a real-time order summary scenario
where UI reacts automatically to data changes using data binding.
*/
@Component({
selector: 'app-root', // Custom HTML tag used to render this component
templateUrl: './app.html', // External HTML template for UI rendering
})
export class App {
// CUSTOMER & ORDER INFORMATION
// Customer name fetched from logged-in user session or backend API
customerName: string = 'Pranaya Rout';
// Unique order identifier generated by the backend system
orderId: string = 'ORD-10021';
// Product selected by the customer
productName: string = 'Angular Course - Full Stack Bundle';
// PRICING DETAILS
// Base price of a single product unit
price: number = 4999;
// Quantity selected by the user (can be changed from UI)
quantity: number = 1;
// CUSTOMER & PAYMENT STATUS FLAGS
// Indicates whether the logged-in customer is a premium user
// Used to apply special business rules such as discounts
isPremiumCustomer: boolean = true;
// Tracks whether payment is completed or still pending
isPaymentDone: boolean = false;
// BUSINESS LOGIC METHODS
/*
Calculates the final payable amount.
- Multiplies price with quantity
- Applies 20% discount if the customer is premium
- Automatically recalculated whenever related data changes
*/
getFinalAmount(): number {
const total = this.price * this.quantity; // Base total amount
const discount = this.isPremiumCustomer ? total * 0.2 : 0; // Premium discount logic
return total - discount; // Final amount after discount
}
/*
Returns a user-friendly order status message.
- Message changes automatically based on payment status
- Demonstrates dynamic text rendering using Angular binding
*/
getOrderStatusMessage(): string {
return this.isPaymentDone
? `Payment received for order ${this.orderId}. Your order is confirmed`
: `Payment pending for order ${this.orderId}. Please complete payment`;
}
}
What does this component represent?
The above component represents the Order Summary Page.
- customerName, orderId, productName → Normally come from logged-in user and order API.
- price, quantity → Normally come from cart/order details API.
- isPremiumCustomer → Normally from the user profile API.
- isPaymentDone → Normally from the payment gateway result/order status API.
So, our component acts as a Data Provider for the UI.
Step 4: Update the Template (app.html)
Now, let us use Angular Interpolation in the template to display this data. Please modify app.html as follows. The following code is self-explanatory; please read the comment lines for better understanding.
<!--
Root container for the Order Summary UI.
Inline styling is used here only for demo clarity.
In real applications, styles should be placed in CSS files.
-->
<div style="padding: 20px; font-family: Arial">
<!--
Dynamic heading using interpolation.
Combines a static label with customer-specific data.
-->
<h2>{{ 'Order Summary for ' + customerName }}</h2>
<!-- 1) BASIC INTERPOLATION (DATA DISPLAY) -->
<!-- Displays the customer name fetched from component data -->
<p><b>Customer Name:</b> {{ customerName }}</p>
<!-- Displays the unique order identifier -->
<p><b>Order Id:</b> {{ orderId }}</p>
<!-- 2) STATIC TEXT + DYNAMIC DATA COMBINATION -->
<!--
Real-time scenario:
After checkout, show a personalized message to the customer.
Demonstrates combining hardcoded text with dynamic values.
-->
<p>
<b>Message:</b>
{{ 'Thanks for shopping with us, ' + customerName + '!' }}
</p>
<!-- PRODUCT INFORMATION DISPLAY -->
<!-- Shows the name of the purchased product -->
<p><b>Product:</b> {{ productName }}</p>
<!-- 3) INTERPOLATION WITH EXPRESSIONS -->
<!--
Displays price with currency symbol.
Currency formatting is kept simple for learning purposes.
-->
<p><b>Price:</b> {{ '₹' + price }}</p>
<!-- Displays the quantity selected by the user -->
<p><b>Quantity:</b> {{ quantity }}</p>
<!--
Real-time calculation inside interpolation.
Total amount updates automatically when price or quantity changes.
-->
<p><b>Total Amount:</b> {{ '₹' + price * quantity }}</p>
<!-- 4) CONDITIONAL RENDERING USING TERNARY -->
<!--
Real-time scenario:
Shows membership type and discount information.
Ternary operator is used for conditional text rendering.
-->
<p>
<b>Membership:</b>
{{
isPremiumCustomer
? 'Premium Customer (20% Discount Applied)'
: 'Regular Customer (No Discount)'
}}
</p>
<!--
Displays payment status dynamically.
UI updates automatically when payment state changes.
-->
<p>
<b>Payment Status:</b>
{{ isPaymentDone ? 'Payment Successful' : 'Payment Pending' }}
</p>
<!-- 5) INTERPOLATION WITH COMPONENT METHODS -->
<!--
Real-time business logic execution.
Final payable amount includes discount rules for premium customers.
-->
<p>
<b>Final Payable Amount:</b>
{{ '₹' + getFinalAmount() }}
</p>
<!--
Advanced real-time example:
Method returns a complete status message
combining static text, dynamic data, and conditions.
-->
<p>
<b>Order Status Message:</b>
{{ getOrderStatusMessage() }}
</p>
</div>
Output:
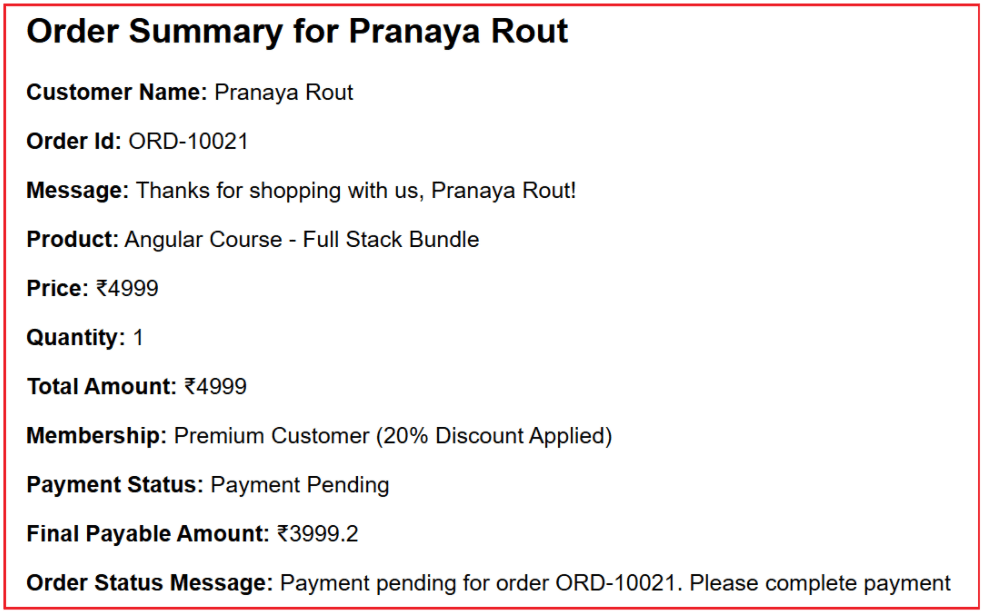
How does interpolation handle calculations?
Angular interpolation can evaluate mathematical expressions directly in the template. For example:
{{ price * quantity }}
Angular first evaluates the expression and then displays the result. This is commonly used for:
- Cart totals
- Invoice amounts
- Tax calculations
- Discounted prices
How does interpolation support conditional display?
Interpolation supports conditional logic using the ternary operator. This allows the UI to display different text based on conditions such as:
- User role
- Payment status
- Subscription status
- Stock availability
This is useful for displaying human-readable status messages without writing additional JavaScript code.
Is calling methods inside interpolation a good practice?
Calling small, lightweight methods within interpolation is acceptable for learning and small applications. However, in large applications:
- Template methods may run multiple times during change detection
- Heavy methods can impact performance
Best practice is to:
- Keep template methods simple
- Precompute complex values in the component
- Avoid expensive logic inside interpolation
Why is Angular Interpolation important for beginners?
Angular interpolation is usually the first data binding technique developers learn because:
- It is simple and readable
- It introduces the concept of reactive UI
- It helps understand how Angular connects data and templates
Once interpolation is mastered, learning Property Binding, Event Binding, and Two-Way Binding becomes much easier.
Conclusion: Why Angular Interpolation Matters
Angular Interpolation Data Binding forms the foundation of dynamic UI rendering in Angular applications. It provides a clean, declarative, and reactive way to display component data in HTML templates.
From showing user details and order summaries to performing calculations and conditional rendering, interpolation plays a vital role in real-world Angular applications. Mastering interpolation lays a strong foundation for understanding advanced Angular binding techniques and for developing scalable, data-driven applications.
In the next article, I am going to discuss Angular Property Binding with Examples. In this article, I explain Angular Interpolation with Examples. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, questions, or comments about this Angular Interpolation with Examples article.

Nice!!!!
Nice
Very Nice tutorial.
Nice example but for me LastName:string=null; did not work
instead is used LastName:any=null;
Super Explanation ….great work.
superb
If you want to understand Angular Interpolation Data Binding clearly with real-world examples, this video will help you a lot.
It explains how {{ }} works, how data flows one way from the component to the template, and how Angular automatically keeps the UI in sync with changing data.
👉 Watch the complete video explanation here: https://youtu.be/YxxNoM6JIwY
This video complements the written tutorial and is especially useful for Angular beginners and interview preparation.