Back to: Angular Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Angular Property Binding with Examples
In this article, I will discuss Angular Property Binding with examples. In modern web applications, displaying text alone is not enough. Real applications must dynamically control HTML properties such as images, input values, button states, CSS classes, styles, and attributes based on application data. This is where Angular Property Binding comes into play.
While Interpolation is mainly used to display text in HTML, Property Binding binds component data directly to DOM element properties. Angular Property Binding is essential for building dynamic, interactive, and state-driven UIs. It allows developers to declaratively control element behaviour using component data, making Angular applications more responsive, readable, and robust.
In this chapter, you will learn:
- What is Angular Property Binding?
- Why is it needed?
- How does it work internally?
- How to use it correctly?
- A real-world order checkout scenario example?
What is Angular Property Binding?
Angular Property Binding is a One-Way Data Binding technique that allows data to flow from the component class to the DOM properties of HTML elements. For a better understanding, please have a look at the below image.
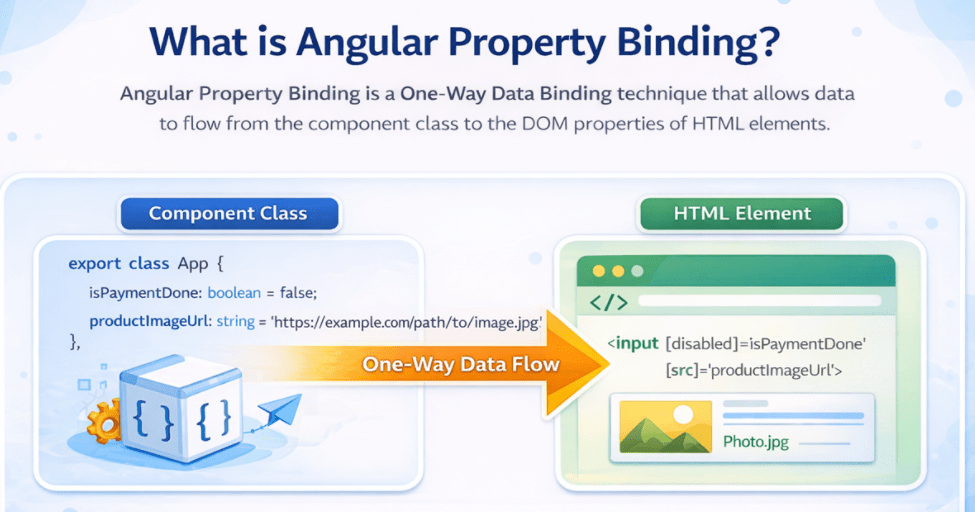
While interpolation is mainly used to display text, property binding goes a step further by allowing Angular to interact directly with live DOM properties, such as disabled, value, src, checked, and hidden. These properties control how an element behaves and appears at runtime, not just what text it shows.
As a result, property binding enables Angular applications to respond intelligently to changing data by dynamically updating the state, behaviour, and visual presentation of UI elements. In simple terms, property binding connects component data to how an element behaves, not what it displays.
Syntax of Angular Property Binding
The syntax of property binding is:
[property]=”expression”
Here:
- The expression inside quotes is evaluated in the context of the component class.
- Angular assigns the evaluated result directly to the corresponding DOM property of the element.
- When the underlying component data changes, Angular’s Change Detection Mechanism automatically updates the DOM property.
This automatic synchronization removes the need for manual DOM manipulation and ensures that the UI always reflects the current application state.
How Angular Property Binding Works Internally?
Angular Property Binding follows a well-defined internal lifecycle that ensures component data and DOM properties stay synchronized without manual intervention. This process is tightly integrated with Angular’s rendering and change detection system. For a better understanding, please have a look at the below image.
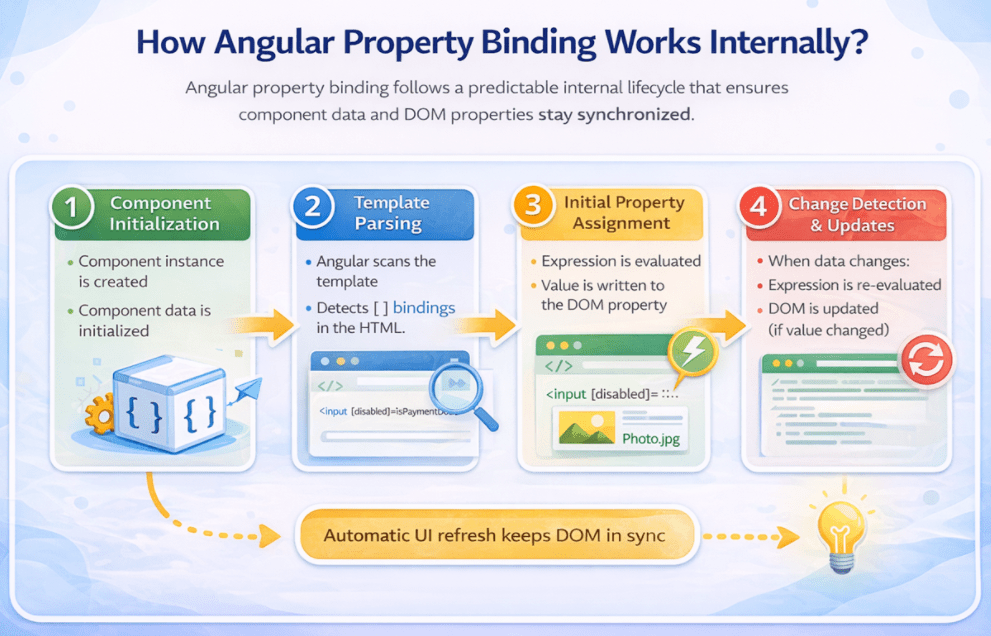
Step-by-Step Internal Flow
- Component Initialization: Angular first loads the component class and initializes all its properties. At this stage, the component serves as the template’s data source.
- Template Parsing: Angular then parses the HTML template and identifies all binding expressions, including property bindings written using the [property]=”expression” syntax.
- Initial Property Assignment: Whenever Angular encounters a property binding:
-
- The binding expression is evaluated in the context of the component class.
- The evaluated value is assigned directly to the corresponding DOM property, not to the HTML attribute.
-
- Change Detection and Updates: When any component data changes:
-
- Angular’s Change Detection Mechanism is triggered.
- The property binding expression is re-evaluated.
- The DOM property is updated only if the new value differs from the previous value.
-
Angular effectively takes ownership of DOM updates, allowing developers to focus on application logic instead of low-level UI updates. In Simple Terms, Angular continuously watches component data and automatically updates DOM properties whenever their bound values change, ensuring the UI always reflects the latest state.
Why do we need Angular Property Binding?
Modern web applications need more than just displaying text; they must control element behaviour and appearance dynamically based on application state. Angular Property Binding enables this by allowing component data to directly control the behavior of HTML elements.
It is used to:
- Enable or disable buttons conditionally
- Set image URLs dynamically
- Pre-fill and update input fields
- Control link activation and navigation
- Apply styles and CSS classes dynamically
- Provide clear visual feedback to users
These dynamic behaviours cannot be handled effectively using interpolation alone, as interpolation is limited to text rendering.
Real-World Example
In an e-commerce checkout page:
- The “Pay Now” button should be disabled after payment
- Product images should load dynamically from backend data
- Invoice download links should activate only after successful payment
- Status labels should change color based on the payment state
All these behaviours are implemented using Angular Property Binding, which makes the UI reactive, state-driven, and user-friendly.
What Can Be Used Inside Angular Property Binding?
Angular property binding expressions are evaluated in the context of the component class, so they can safely use anything that produces a value suitable for the target DOM property.
You can use:
- Component Class Properties: Used to bind dynamic values such as booleans, numbers, strings, objects, or arrays.
- Boolean Expressions: Useful for enabling or disabling elements based on conditions.
- Ternary (conditional) Operators: Commonly used to switch values based on application state.
- Simple Calculations: Lightweight arithmetic expressions that compute, display, or state values.
- Lightweight Component Methods: Methods that return simple values and have no side effects.
The expression should be fast, predictable, and side-effect-free.
Creating a New Angular Application to Understand Property Binding
We will continue with the same real-time e-commerce order summary scenario, but now focus on controlling UI behaviour, not just displaying text.
Step 1: Create a New Angular App
ng new property-binding-demo
Choose:
- Stylesheet → CSS
- SSR / SSG → No
- AI tools → None
Step 2: Navigate and Run the App
- cd property-binding-demo
- ng serve
Open:
- http://localhost:4200
Step 3: Update the Root Component (app.ts)
Please modify app.ts as follows. The following code is self-explanatory; please read the comment lines for better understanding.
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
/*
Root component of the application.
This component represents a real-world order summary screen
where UI behavior and appearance are driven by component data.
*/
@Component({
selector: 'app-root', // Custom HTML element used to render this component
templateUrl: './app.html', // External HTML template for better separation of concerns
})
export class App {
// CUSTOMER & ORDER DATA
// Customer name retrieved from logged-in user session or API
customerName: string = 'Pranaya Rout';
// Unique order identifier generated by the backend system
orderId: string = 'ORD-10021';
// Product name returned from product/catalog service
productName: string = 'Angular Course - Full Stack Bundle';
// PRICING DETAILS
// Price of a single product unit
price: number = 4999;
// Quantity selected by the user
quantity: number = 1;
// USER & PAYMENT STATE FLAGS
// Indicates whether the customer has premium membership
// Used to apply special business rules like discounts
isPremiumCustomer: boolean = true;
// Tracks payment completion status
isPaymentDone: boolean = false;
// RESOURCE LINKS (DYNAMIC)
// Product image URL typically served from CDN or backend
productImageUrl: string = 'https://placehold.co/180x120/png?text=Angular+Course';
// Invoice download URL generated by backend after order/payment
invoiceUrl: string = 'https://example.com/invoice/ORD-10021.pdf';
// UI HELPER METHODS
/*
Generates dynamic tooltip text for UI elements.
Combines static text with order and customer information.
*/
getOrderTooltip(): string {
return `Order: ${this.orderId} | Customer: ${this.customerName}`;
}
/*
Calculates the final payable amount.
- Multiplies price and quantity
- Applies 20% discount for premium customers
- Used for real-time amount calculation in the UI
*/
getFinalAmount(): number {
const total = this.price * this.quantity; // Base order total
const discount = this.isPremiumCustomer ? total * 0.2 : 0; // Premium discount
return total - discount; // Final payable amount
}
/*
Returns a user-friendly payment status label.
Used for displaying readable payment information in the UI.
*/
getPaymentLabel(): string {
return this.isPaymentDone ? 'Payment Successful' : 'Payment Pending';
}
/*
Returns a color based on payment status.
Provides visual feedback to the user (status indication).
*/
getStatusColor(): string {
return this.isPaymentDone ? 'green' : 'crimson';
}
}
Step 4: Update the Root Template (app.html)
Now we use Property Binding to control real UI behaviour and appearance. Please modify app.html as follows. The following code is self-explanatory; please read the comment lines for better understanding.
<!--
Order Summary UI
This template demonstrates how Angular Property Binding
controls element behavior, state, and appearance dynamically.
-->
<div style="padding: 20px; font-family: Arial">
<!-- Static heading (no binding required here) -->
<h2>Order Summary</h2>
<!-- TEXT DISPLAY USING INTERPOLATION -->
<!-- Interpolation is best suited for plain text rendering -->
<p><b>Customer:</b> {{ customerName }}</p>
<p><b>Order Id:</b> {{ orderId }}</p>
<!-- 1) PROPERTY BINDING: IMAGE SOURCE -->
<!--
Product image URL is provided by backend/CDN.
[src] binds directly to the DOM image source property.
[alt] improves accessibility and SEO.
-->
<div style="margin: 12px 0">
<img
[src]="productImageUrl"
[alt]="productName"
style="border: 1px solid #ccc; border-radius: 6px"
/>
</div>
<!-- 2) PROPERTY BINDING: TOOLTIP -->
<!--
[title] binds a dynamic tooltip.
Useful for admin/support or additional contextual information.
-->
<p [title]="getOrderTooltip()">
<b>Product:</b> {{ productName }}
<span style="font-size: 12px; color: gray">
(Hover to see tooltip)
</span>
</p>
<!-- 3) PROPERTY BINDING: INPUT VALUE -->
<!--
[value] pre-fills the input with component data.
This is a one-way flow from component → input field.
-->
<p>
<b>Quantity:</b>
<input
type="text"
[value]="quantity"
style="width: 60px; padding: 4px"
/>
<span style="font-size: 12px; color: gray">
(Value is coming from the component)
</span>
</p>
<!-- 4) PROPERTY BINDING: DISABLED STATE -->
<!--
[disabled] controls button availability.
Button remains disabled until payment is completed.
-->
<p>
<b>Invoice:</b>
<button
[disabled]="!isPaymentDone"
style="padding: 6px 10px"
>
Download Invoice
</button>
<span style="font-size: 12px; color: gray">
(Disabled until payment is successful)
</span>
</p>
<!-- 5) PROPERTY BINDING: LINK CONTROL -->
<!--
[href] is set only after payment is done.
Pointer events and opacity are controlled to visually
and functionally disable the link when required.
-->
<p>
<a
[href]="isPaymentDone ? invoiceUrl : null"
[style.pointerEvents]="isPaymentDone ? 'auto' : 'none'"
[style.opacity]="isPaymentDone ? '1' : '0.5'"
target="_blank"
>
Open Invoice Link
</a>
<span style="font-size: 12px; color: gray">
(Link becomes usable after payment)
</span>
</p>
<!-- 6) PROPERTY BINDING: VISUAL FEEDBACK -->
<!--
Visual payment status indicator.
- Color and font weight reflect payment state
- Class binding allows custom CSS styling if needed
-->
<p>
<b>Payment Status:</b>
<span
[style.color]="getStatusColor()"
[style.fontWeight]="isPaymentDone ? 'bold' : 'normal'"
[class]="isPaymentDone ? 'paid-status' : 'pending-status'"
>
{{ getPaymentLabel() }}
</span>
</p>
<!-- FINAL AMOUNTS (TEXT DISPLAY) -->
<!--
Calculations are fine in interpolation for simple expressions.
-->
<p><b>Total Amount:</b> ₹{{ price * quantity }}</p>
<p><b>Final Payable:</b> ₹{{ getFinalAmount() }}</p>
</div>
Output:

How does Property Binding work with images using [src] and [alt]?
Example: <img [src]=”productImageUrl” [alt]=”productName” />
What happens internally:
- src and alt are DOM properties of the <img> element
- Angular evaluates the expressions
- Assigns values directly to the DOM properties
- If the image URL changes, Angular updates the image automatically
Real-world usage:
- Product images from APIs
- Profile pictures
- Banners loaded from CDN
Property binding ensures these updates are safe, dynamic, and reliable.
Why is Property Binding preferred over interpolation for images?
Although this may work: <img src=”{{ productImageUrl }}”>
Angular treats it differently internally, and it is not recommended for behavior-related properties. Property binding ensures:
- Correct type handling
- Secure DOM updates
- Predictable change detection
That is why [src] is preferred over src=”{{ }}”.
How does Property Binding work with tooltips using [title]?
Example: <p [title]=”getOrderTooltip()”>Product</p>
What happens:
- title is a native DOM property
- Angular assigns a dynamic value to it
- The browser automatically shows a tooltip on hover
How does Property Binding work with input values using [value]?
Example: <input [value]=”quantity” />
What happens:
- Angular assigns the quantity to the input’s value property
- The input is prefilled
- Data flows only from component to view
Why is [disabled] one of the most important Property Binding examples?
Example: <button [disabled]=”!isPaymentDone”>Download Invoice</button>
What happens:
- disabled expects a boolean
- Angular evaluates the condition
- Button behaviour changes dynamically
This demonstrates how property binding controls the actual behaviour of an element, not just its appearance.
Real-world usage:
- Disable submit buttons until validation passes
- Prevent duplicate actions
- Lock workflows after approval.
How is Property Binding different from Interpolation?
Although both interpolation and property binding are used to display dynamic data in Angular templates, they serve fundamentally different purposes and operate at different levels of the DOM.
Interpolation: Updating What the User Sees
Angular Interpolation is primarily used to render text content inside HTML elements. It takes data from the component class, converts it into a string, and inserts it into the template.
- It updates text nodes, not element behaviour.
- It is ideal for showing names, labels, messages, totals, and calculated values.
- The result is always rendered as readable text.
In simple terms, interpolation controls what the user reads on the screen.
Property Binding: Controlling How Elements Behave
Property binding updates live DOM properties that control the behaviour, state, and appearance of HTML elements. It allows Angular to dynamically manage properties such as:
- src, href – resource loading and navigation
- value, disabled – form input state
- checked, hidden – visibility and selection
- class, style – visual presentation
Property binding does not just change what is displayed; it changes how the element functions at runtime.
Why This Difference Matters
The distinction between interpolation and property binding is crucial because:
- Interpolation always produces text output
- Property binding preserves data types (boolean, number, object)
- Property binding updates live DOM state
- Certain behaviours (like disabling a button or setting an image URL) cannot be achieved using interpolation
In Real-World Angular Applications
- Interpolation is used for displaying information
- Property binding is used for controlling interaction and behaviour
Most real Angular applications use both together—interpolation for content and property binding for behaviour.
Conclusion: Why Property Binding is Important?
Angular Property Binding is essential for building real, interactive, and professional UIs because it lets you control HTML elements dynamically using component data. While interpolation focuses mainly on rendering text, property binding empowers you to handle real application requirements, such as loading images, enabling/disabling controls, setting dynamic links, applying conditional styling, and improving usability with tooltips.
In the next article, I will discuss Angular Attribute Binding with Examples. Here, in this article, I explain Angular Property Binding with examples. I hope this article will help you with your needs. I would like to have your feedback. Please post your feedback, questions, or comments about this article.

Good explanation
Awesome tutorial
When set IsDisabledClick:boolean=true;
in interpolation
the button still disable
why ?
Becuause interpolation will take everything as string ..
if u provide boolean false , it will consider it as ‘false’… in programming only empty string is false but remaining are true. so here true .. so button is disbaled
if u provide boolean true, it will consider it as ‘true’ … in programming only empty string is false but remaining are true. here also true .. so button is disbaled
Watch the Full Video on Angular Property Data Binding
Want to control dynamic behavior like enabling/disabling buttons, updating input values, and setting image sources in real-time using Angular? This video explains Property Binding with real-world examples that go beyond just text display.
📺 Click here to watch now 👉 https://youtu.be/NHQ5SQ5NDxA
Ideal for Angular developers who want to build dynamic and reactive user interfaces with clean, maintainable code!