Back to: Microservices using ASP.NET Core Web API Tutorials
User Microservice with ASP.NET Core Web API
The User Microservice is a standalone service that owns the entire user lifecycle, registration, authentication, authorization, profile, and address management, within a microservices architecture. It keeps user data, business rules, and API contracts in one place so you can deploy, scale, and secure it independently from the rest of your system. This separation improves maintainability and makes it easy to evolve user features without impacting other domains.
This microservice follows a layered, modular design that promotes separation of concerns and aligns with best practices in enterprise application development. Key features include:
- Secure registration and login using NET Core Identity.
- JWT-based authentication for stateless and scalable session management.
- Role-based access control to support Admin, Customer, and Vendor roles.
- Management of user profiles, multiple addresses, and email/phone verification.
- Integration with external services via secure REST APIs.
Built with ASP.NET Core Web API, Entity Framework Core, and JWT, the User Microservice serves as the identity and access gateway for your entire application ecosystem.
What is the User Domain?
The User Domain is the area of your system that handles all aspects of a user’s lifecycle, including creation, authentication, authorization, profile management, addresses, security, and more. In microservices architecture, we break down a large system into focused, independent services. The User Microservice:
- Owns all user-related data and operations.
- Has its own database, API, and business rules.
- Can be deployed, scaled, and updated independently from other parts of the system.
For a better understanding, please refer to the following image.
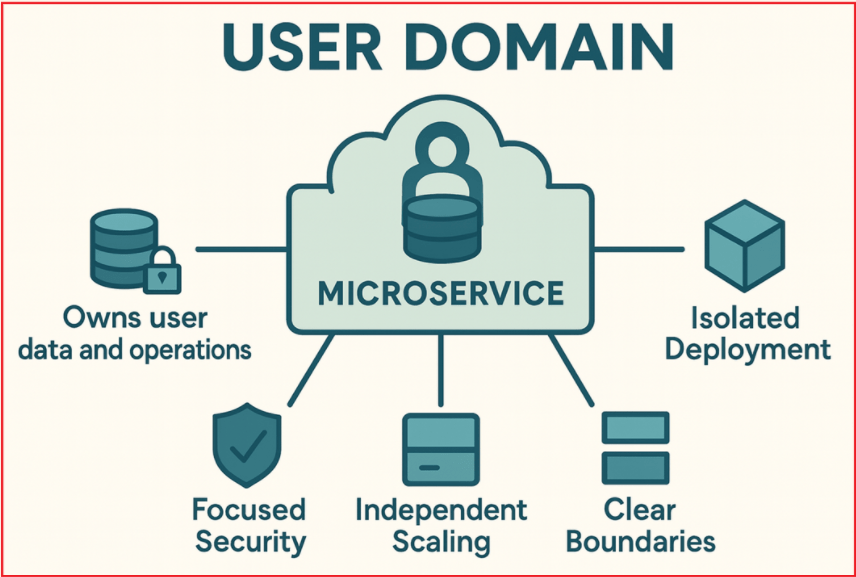
Benefits:
- Independent Scaling: User-related operations (logins, registrations) may have different traffic patterns and performance needs. Isolating the domain lets you scale the service independently.
- Focused Security: User data is sensitive and requires strict security controls. Separation helps in applying dedicated security and compliance mechanisms.
- Isolated Deployment: New features or fixes in user management can be deployed without impacting other business services.
- Clear Boundaries: Encourages clean separation of concerns, improving maintainability and clarity of responsibilities.
Key Features of User Microservice
The User Microservice domain encompasses various subdomains and responsibilities essential for secure, reliable, and flexible user management:
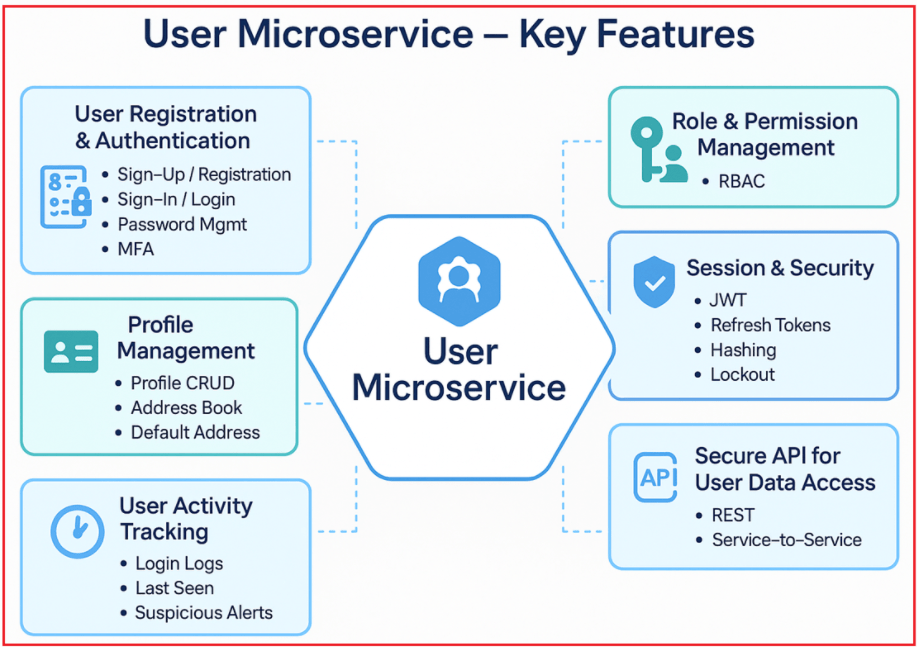
User Registration & Authentication
- Sign Up / Registration: New users can register using details such as username, email, and password. The microservice validates the data to ensure data integrity and prevent duplicate accounts, and may trigger verification steps.
- Login / Sign In: Users authenticate by providing valid credentials (email, username, mobile number, and password). On success, the service issues JWT tokens for stateless session management.
- Password Management: Support for password reset, forgotten passwords, and password change, typically via email OTPs or secure links. Always store passwords using secure hashing algorithms (e.g., bcrypt).
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Optionally enhances login security by requiring additional verification steps, like OTPs sent via SMS/email or authenticator apps (Google Authenticator, Authy).
User Profile Management
- CRUD Operations: Users (or admins) can create, view, update, and delete user profile information.
- Profile Data: Stores user details, including name, email, phone number, profile photo, preferences, and other metadata.
- Address Book: Store multiple addresses per user (shipping, billing, etc.), with the ability to add, edit, or remove them.
- Default Address Selection: Users can mark certain addresses as their default for faster checkout or communication.
Role and Permission Management
- Role Definition: Roles categorize users based on permissions, e.g., Admins have full access, Customers have shopping-related permissions, and Vendors can manage products. Typical roles: Admin, Customer, Vendor, each with its own set of permissions.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): The service restricts access to endpoints based on the user’s assigned role. For example, only Admins can manage other users.
- Authorization Policies: Define business policies, such as who can edit profiles, view sensitive data, or perform admin tasks, enhancing security and flexibility.
Session Management and Security
- JWT Authentication: After logging in, a JWT token is generated and sent to the client, which uses it in subsequent requests. This enables stateless authentication (no need to store session info on the server side).
- Refresh Tokens: Supports token refresh mechanisms to securely extend user sessions without requiring frequent logins.
- Password Hashing: Uses strong, one-way hashing algorithms to store passwords securely.
- Account Lockout: If multiple failed login attempts are detected, the account will be temporarily locked to prevent brute-force attacks.
User Activity Tracking
- Login Tracking: Maintains a history of user logins with metadata, including login times, IP addresses, device information, and browser details, to detect unusual patterns or potential breaches. This is helpful for auditing and alerting users to suspicious logins.
- Last Seen: Tracks last active times, useful for features like “last online” indicators or session timeout enforcement.
- Suspicious Activity Alerts: Detect and notify users and administrators about suspicious activity (e.g., multiple failed logins, logins from new locations).
Account Verification
- Email Verification: Upon registration or email update, send a verification email to confirm the address via OTP or a confirmation link, thereby enhancing account authenticity.
- Phone Number Verification: Send an OTP (one-time password) via SMS to verify mobile numbers.
- Activation Status: Users can only access the platform once their account is verified and active. Maintains user account status (active/inactive/blocked) to control access.
API for User Data Access
- Secure APIs: Other microservices (such as Order, Payment, and Notification) can request user information for processing transactions, personalizing experiences, or verifying identity. Therefore, it provides REST endpoints with appropriate authentication and authorization for other microservices to retrieve necessary user data (e.g., the Order Microservice fetching shipping information).
Recommended Technology Stack for Building a Modern User Microservice
Let us understand the best technology stack for implementing a secure and scalable User Microservice. This approach combines ASP.NET Core Web API, Entity Framework Core, ASP.NET Core Identity, and JWT authentication to deliver robust user management, seamless data access, and stateless security, making your microservices architecture modern, efficient, and ready for production.

Framework: ASP.NET Core Web API
- ASP.NET Core Web API is Microsoft’s modern, cross-platform framework designed for building RESTful APIs.
- It supports the latest .NET versions (currently, .NET 8 LTS is the latest Long-Term Support version), ensuring performance, security, and ongoing support.
- ASP.NET Core Web API offers built-in dependency injection, middleware pipelines, configuration systems, logging, and great integration with authentication and authorization mechanisms.
- It is ideal for microservices due to its lightweight, modular, and scalable design.
Real-World Benefit: You can run your service on Windows, Linux, or containers (Docker, Kubernetes) with full Microsoft support and a vibrant ecosystem.
ORM: Entity Framework Core (EF Core)
- Entity Framework Core is Microsoft’s official Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) for .NET applications.
- EF Core enables developers to interact with relational databases (such as SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQLite) using strongly typed .NET objects.
- It supports Code-First and Database-First approaches, making it flexible for various project needs.
- EF Core automatically manages database schema creation, migrations, and relationships between entities.
- In the User Microservice, EF Core persists user data, roles, claims, and related profile information securely and efficiently.
Real-World Benefit: EF Core accelerates development, reduces boilerplate, and keeps your code maintainable as your data model evolves.
Membership Management: ASP.NET Core Identity
ASP.NET Core Identity is the standard framework for handling all user-related functionalities:
- User Registration: It provides built-in mechanisms for signing up users, including validation for unique usernames and emails.
- Login and Password Management: Handles secure user login and password operations, including password resets.
- Password Hashing: Uses industry-standard hashing algorithms (e.g., PBKDF2) to securely store passwords, protecting against password leaks.
- Role and Claims Management: Enables assigning users to roles (e.g., Admin, Customer) and attaching claims (permissions or attributes) to users.
- Security Best Practices: Implement features such as account lockout after multiple failed attempts, two-factor authentication (2FA), and email confirmation workflows.
- Extensibility: You can extend the IdentityUser class to include custom user profile fields, such as address, phone number, and profile pictures.
Real-World Benefit: You get a mature, tested security system that’s customizable to your business needs, with rapid development and proven best practices.
Authentication: JWT (JSON Web Tokens) for Stateless Authentication
JWT is a compact, URL-safe token format that encodes claims about the user (such as identity, roles, and permissions) and is digitally signed to prevent tampering.
Instead of traditional cookie-based authentication (good for web apps), APIs prefer stateless token authentication. Upon successful login, ASP.NET Core Identity can be configured to generate a JWT access token, which clients (web/mobile apps) use for subsequent API calls.
Key Properties:
- Statelessness: JWT tokens contain all necessary user claims and do not require server-side session storage, enabling easy horizontal scaling.
- Scalability: Multiple microservices can validate JWT tokens independently without a central session store.
- Interoperability: JWTs are widely supported across platforms and can be easily passed via HTTP headers.
- Security: Tokens are signed (and optionally encrypted), ensuring data integrity and authenticity.
- Compatibility: Works well with API Gateways and inter-service communication by passing tokens securely for authorization.
- Standard: Supported everywhere, web, mobile, desktop, IoT.
Real-World Benefit: With JWT, your User Microservice can authenticate users once, issue a token, and let any microservice (Order, Payment, etc.) verify the user by simply checking the token; no central session store or database call is required.
By adopting ASP.NET Core Web API with EF Core, Identity, and JWT, the service achieves a modern, stateless, and interoperable architecture that other microservices (Order, Payment, Notification) can integrate with via secure REST endpoints. This yields clear boundaries, easier maintenance, and a production-ready foundation for identity at scale.
Registration Open – Mastering Design Patterns, Principles, and Architectures using .NET
Session Time: 6:30 AM – 08:00 AM IST
Advance your career with our expert-led, hands-on live training program. Get complete course details, the syllabus, and Zoom credentials for demo sessions via the links below.
- View Course Details & Get Demo Credentials
- Registration Form
- Join Telegram Group
- Join WhatsApp Group
